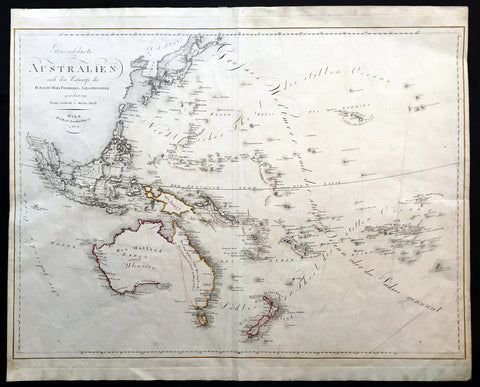
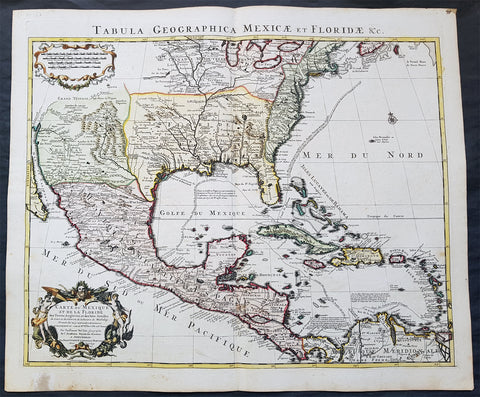
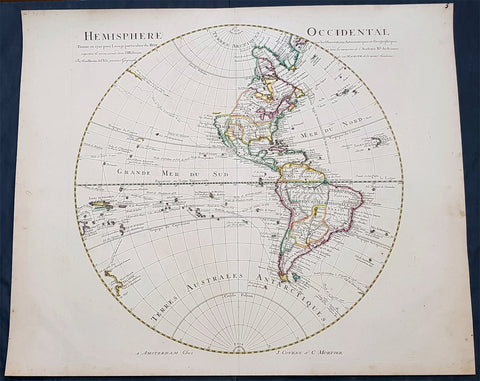
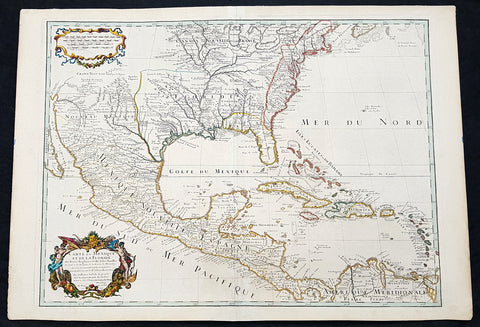
Recent Acquisitions (295)
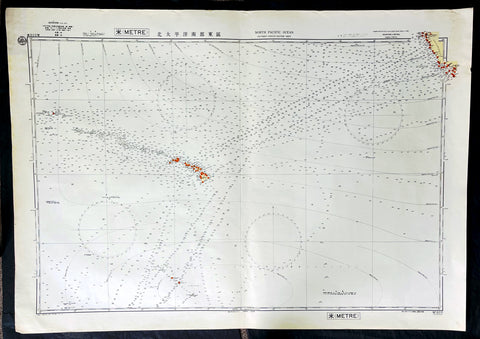
1939 Japanese Safety Agency Large Antique Map of Hawaii, Pacific - Pearl Harbor
- Title : North Pacific Ocean Southern Portion Eastern Sheet, Compiled from the United States and the British Charts to 1939
- Date : 1939
- Size: 43in x 30in (1.090m x 760mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27101
Description:
This original very large lithograph map, a sea chart, with depth soundings, of The Central Pacific, centering on the Hawaiian Islands was complied by the Maritime Safety Agency Japan (MSAJ) from American & British charts. The maps centers on the Hawaiian Islands east to California and south to the Christmas Islands.
The importance of this map cannot be overstated in the context of time and would have no doubt been used by the Japanese carrier group and their attack on Pearl Harbour in 1941.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 43in x 30in (1.090m x 760mm)
Plate size: - 43in x 30in (1.090m x 760mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Hawaii, just before 8:00 a.m. (local time) on Sunday, December 7, 1941. The United States was a neutral country at the time; the attack led to its formal entry into World War II on the side of the Allies the next day. The Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning.
The attack was preceded by months of negotiations between the U.S. and Japan over the future of the Pacific. Japanese demands included that the U.S. end its sanctions against Japan, cease aiding China in the Second Sino-Japanese war, and allow Japan to access the resources of the Dutch East Indies. Anticipating a negative response from the US, Japan sent out its naval attack groups in November 1941 just prior to receiving the Hull note—the U.S. demand that Japan withdraw from China and French Indochina.
Japan intended the attack as a preventive action. Its aim was to prevent the United States Pacific Fleet from interfering with its planned military actions in Southeast Asia against overseas territories of the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and those of the United States. Over the course of seven hours there were coordinated Japanese attacks on the U.S.-held Philippines, Guam, and Wake Island and on the British Empire in Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong.
The attack commenced at 7:48 a.m. Hawaiian Time (6:18 p.m. GMT). The base was attacked by 353 Imperial Japanese aircraft (including fighters, level and dive bombers, and torpedo bombers) in two waves, launched from six aircraft carriers. Of the eight U.S. Navy battleships present, all were damaged, with four sunk. All but USS Arizona were later raised, and six were returned to service and went on to fight in the war. The Japanese also sank or damaged three cruisers, three destroyers, an anti-aircraft training ship, and one minelayer. More than 180 US aircraft were destroyed. A total of 2,403 Americans were killed and 1,178 others were wounded, making it the deadliest event ever recorded in Hawaii. Important base installations such as the power station, dry dock, shipyard, maintenance, and fuel and torpedo storage facilities, as well as the submarine piers and headquarters building (also home of the intelligence section) were not attacked. Japanese losses were light: 29 aircraft and five midget submarines lost, and 64 servicemen killed. Kazuo Sakamaki, the commanding officer of one of the submarines, was captured.
Japan announced declarations of war on the United States and the British Empire later that day (December 8 in Tokyo), but the declarations were not delivered until the following day. The British government declared war on Japan immediately after learning that their territory had also been attacked, while the following day (December 8) the United States Congress declared war on Japan. On December 11, though they had no formal obligation to do so under the Tripartite Pact with Japan, Germany and Italy each declared war on the U.S., which responded with a declaration of war against Germany and Italy. There were numerous historical precedents for the unannounced military action by Japan, but the lack of any formal warning (required by part III of the Hague Convention of 1907), particularly while negotiations were still apparently ongoing, led President Franklin D. Roosevelt to proclaim December 7, 1941, a date which will live in infamy. Because the attack happened without a declaration of war and without explicit warning, the attack on Pearl Harbor was later judged in the Tokyo Trials to be a war crime.
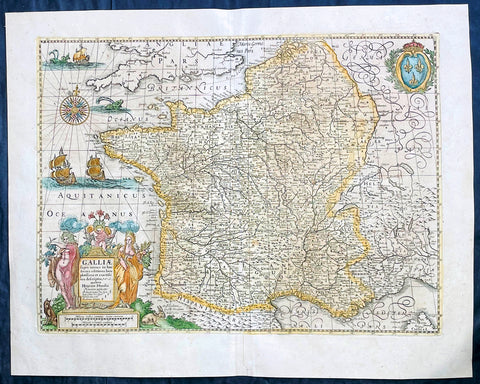
1639 Henricus Hondius Antique Map of France
- Title : Galliae supera omnes in hac...auctore Henrico Hondio
- Date : 1639
- Size: 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 455mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 17039
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of France was published by Henricus Hondius & Jan Jansson in the 1639 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 18in (570mm x 455mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14 1/2in (500mm x 375mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
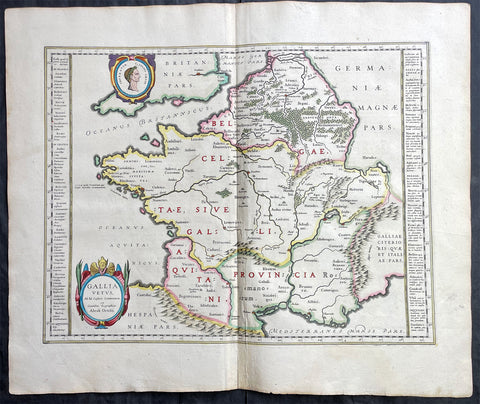
1638 Joan Blaeu & Abraham Ortelius Antiue Map of France
- Title : Gallia Vetus...Abrah Ortelii
- Date : 1638
- Size: 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70606
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of France, after Abraham Ortelius, was published by Joan Blaeu in the 1638 French edition of Atlas Nouvs,.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20in (585mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
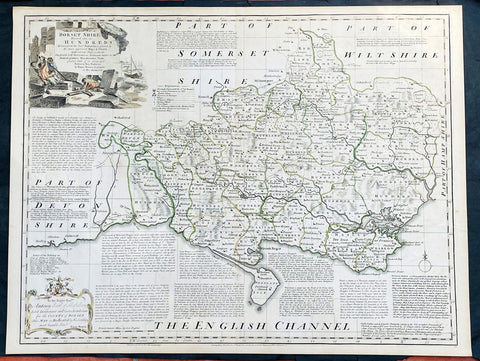
1760 Emanuel Bowen Large English County Map of Dorset Shire
- Title : An Accurate Map of Dorsetshire, Divided into its Hundreds. Drawn from the best Authorities, assisted by the most approved Maps and Charts with various Improvements illustrated with Historical Extracts relative to its Natural Produce, Manufactures, Trade, present state of it’s principal Towns and Sea Ports, by Eman Bowen geographer to His Majesty.
- Date : 1760
- Size: 29in x 22 1/2in (750mm x 570mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35614
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured antique map of the English County of Dorset Shire by Emmanuel Bowen was published by Carrington Bowles in the 1760 edition of The Large English Atlas. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29in x 22 1/2in (750mm x 570mm)
Plate size: - 27 1/2in x 21 1/2in (700mm x 545mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The Large English Atlas was, as its name suggests, a large folio series of county maps conceived in about 1749 but, because of financial problems, not completed until 1760. Hodson describes the atlas as by far the most important eighteenth-century English atlas to be published before the appearance of John Carys New And Correct English Atlas in 1787. Earlier county atlases were predominantly derivative, using old survey work, many in fact, traceable back to Saxtons work of the sixteenth century. The Large English Atlas maps were drawn from the most up-to-date surveys, and so mark an important stage in the development of the county atlas (Hodson). Through its commercial success, this atlas encouraged a new generation of county atlases, of both large and small scales, but of greater precision than before. The maps, drawn either by Emanuel Bowen or Thomas Kitchin, are finely produced. A particular feature is the vast amount of additional detail engraved in the blank areas around the map, lists of the landed gentry, descriptions of the towns, produce and other notable features of each county, and in some cases, fine insets of the county town. All have elaborate title cartouches, illustrating the produce of the county, rural scenes and so on, many signed by Antony Walker Jr. Besides the separately published multi-sheet maps of various counties these are the most detailed and most interesting county maps of the eighteenth century.
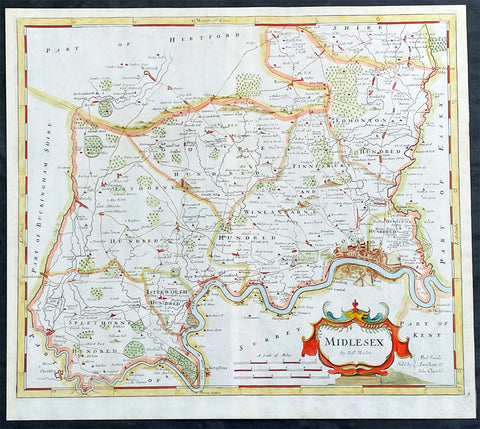
1722 Robert Morden Antique Map of The English County of Middlesex, London
- Title : Midlesex
- Date : 1722
- Size: 17 1/2in x 15 1/2in (445mm x 395mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35603
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of the county of Middlesex and London by Robert Morden was published in the 1722 edition of Camdens Britannia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 15 1/2in (445mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 15 1/2in (445mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
These maps are the first county maps to show roads (based on Ogilby’s road maps) and show three scales representing great, middle and small miles as different scales were used in different parts of the country. Morden was employed to replace the outdated maps by Saxton, engraved by Kip and Hole. He based his maps on manuscript sources plus the surveys of Ogilby and Morgan, Seller, Palmer and the coastal charts of Captain Grenville Collins. One innovation was the showing of longitudes measured from the meridian of St. Paul's Cathedral given in the form of time in minutes at the top of the map in Roman numerals and at the bottom in degrees. This was done to clarify local times that were taken from the sun as there was no national standard time. Gibson said:' Where actual Surveys could be had, they were purchased at any rate; and for the rest, one of the best Copies extanct was sent to some of the most knowing Gentlemen in each County; with a request to supply the defects, rectified the positions, and correct the false spellings. And that nothing might be wanting to render them as complete and accurate as might be, this whole business was commited to Mr Robert Morden, a person of know abilities in these matters'..from the Preface of the Britannia.
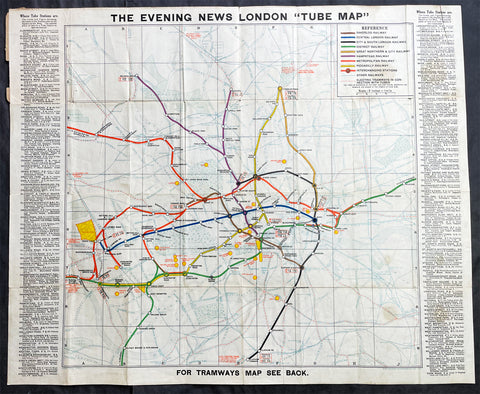
1907-10 George Philip Large Early London Underground Map
- Title : The Evening News London "Tube Map"
- Date : 1907-10
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 27100
Description:
This original folding lithograph London Underground Antique Map was designed by the London Geographical Institute & printed by George Philip & Son for the Evening News, London between 1907 to 1910. On the verso is the London Tram Map.
The Evening News London Tube map & Guide ran from 1907-1910. At its release in 1907 it predated the first official 'unified' London Underground map (published in 1908). The EN Tube map was the first to refer to the wider network of Underground Railways as the 'Tube'; it was among the first to apply colour-coding for the lines and is widely believed to be the origin of the name 'Bakerloo' for the Baker Street & Waterloo Railway.
This map design would later be used as a basis for the official London Underground Railways pocket map in 1912.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, red, yellow, purple, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Creasing in margings
Plate area: - Light wear along folds
Verso: - Light wear along folds
Background:
As Londons early transport system was operated by a variety of independent companies, there were no complete maps of the network, just for the individual companies routes. The maps were not typically schematic and were simply the line overlaid on a regular city map. There was no integration of the companies services or any co-operation in advertising.
In 1907, The Evening News commissioned a pocket map, The Evening News London Tube Map. It was the first map to show all of the lines with equal weight being given to each line, and it was the first map to use a different colour for each line.
Another early combined map was published in 1908 by the Underground Electric Railways Company of London (UERL) in conjunction with four other underground railway companies that used the Underground brand as part of a common advertising factor.
The map showed eight routes – four operated by the UERL and one from each of the other four companies:
UERL lines:
Bakerloo Railway – brown
Hampstead Railway – indigo
Piccadilly Railway – yellow
District Railway – green
Other lines:
Central London Railway – blue
City and South London Railway – black
Great Northern and City Railway – orange
Metropolitan Railway – red
A geographical map presented restrictions since for sufficient clarity of detail in the crowded central area of the map required the extremities of the District and Metropolitan lines to be omitted and so a full network diagram was not provided. The problem of truncation remained for nearly half a century. Although all of the western branches of the District and Piccadilly lines were included for the first time in 1933 with Harry Becks first proper Tube map, the portion of the Metropolitan line beyond Rickmansworth did not appear until 1938, and the eastern end of the District line did not appear until the mid-1950s.
The route map continued to be developed and was issued in various formats and artistic styles until 1920, when, for the first time, the geographic background detail was omitted in a map designed by MacDonald Gill. That freed the design to enable greater flexibility in the positioning of lines and stations. The routes became more stylised but the arrangement remained, largely, geographic in nature. The 1932 edition was the last geographic map to be published before Becks diagrammatic map was introduced.
The first diagrammatic map of Londons rapid transit network was designed by Harry Beck in 1931. He was a London Underground employee who realised that because the railway ran mostly underground, the physical locations of the stations were largely irrelevant to the traveller wanting to know how to get from one station to another; only the topology of the route mattered. That approach is similar to that of electrical circuit diagrams although they were not the inspiration for Becks map. His colleagues pointed out the similarities, however, and he once produced a joke map with the stations replaced by electrical circuit symbols and names, with terminology such as Bakerlite for the Bakerloo line.
To that end, Beck devised a simplified map with stations, straight-line segments connecting them, and the River Thames; and lines running only vertically, horizontally, or on 45° diagonals. To make the map clearer and to emphasise connections, Beck differentiated between ordinary stations, marked with tick marks, and interchange stations, marked with diamonds. London Underground was initially sceptical of his proposal since it was an uncommissioned spare-time project and was tentatively introduced to the public in a small pamphlet in 1933. However, it immediately became popular, and the Underground has used topological maps to illustrate the network ever since.
Despite the complexity of making the map, Beck was paid just ten guineas for the artwork and design of the card edition (five guineas for the poster). After its initial success, he continued to design the Tube map until 1960, a single (and unpopular) 1939 edition by Hans Scheger being the only exception. Meanwhile, as well as accommodating new lines and stations, Beck continually altered the design, such as changing the interchange symbol from a diamond to a circle and altering the line colours of the Central line from orange to red and of the Bakerloo line from red to brown. Becks final design, in 1960, bears a strong resemblance to the current map. Beck lived in Finchley, North London, and one of his maps is still preserved on the southbound platform at Finchley Central station, on the Northern line.
In 1997, Becks importance was posthumously recognised, and as of 2021, this statement is printed on every Tube map: This diagram is an evolution of the original design conceived in 1931 by Harry Beck.
1879 Lorenz Large Antique Map Coal Seams Schuylkill County, Pennsylvania Reading
- Title : Map Showing Coal Laterals of the Philadelphia & Reading Rail Raod company William Lorenz Chief Eng. 1879
- Date : 1879
- Size: 29in x 19 1/2in (735mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 93520
Description:
This original, large folding rare lithograph map of the Coal Fields of Schuylkill County, Pennsylvania, owned at the time by the Pennsylvania & Reading Railroad Company by William Lorenz was engraved and published in 1879 - dated.
The Definition of a Coalseam lateral is any system of development in coal seams or thick orebodies in which headings are driven horizontally across the coal or ore and connected to main haulage drifts, entries, or shafts. There are many variations and modifications depending on the thickness, shape, and inclination of the deposit.(Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29in x 19 1/2in (735mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 29in x 19 1/2in (735mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Chipping to map edges not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light wear along sectioned edges
Verso: - Backed in linen
Background:
Schuylkill is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is located in the heart of Pennsylvanias Coal Region and is part of Northeastern Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, the population was 143,049. The county seat is Pottsville.
The county was created on March 1, 1811, from parts of Berks and Northampton counties and named for the Schuylkill River, which originates in the county. On March 3, 1818, additional territory in its northeast was added from Columbia and Luzerne counties. The county is part of the Pottsville, Pennsylvania Micropolitan Statistical Area.
The lands that today constitute Schuylkill County were acquired by William Penns proprietors by treaty executed August 22, 1749, with representatives of the Six Nations and the Delaware, Shamokin and Shawnee, who received 500 pounds lawful money of Pennsylvania. The territory described included all of Schuylkill County except the northern part of Union Township, which was included in the purchase of 1768.
In the year 1754, the area that would become Schuylkill County along with the areas that today are Berks, Dauphin, Lebanon, and Lehigh counties were settled by German immigrants. The earliest settlers in southeastern Schuylkill County, which was then part of Northampton County, were primarily Moravian missionaries from Saxony. Other early settlers in southern Schuylkill County were German Palatines.
An early mill in the county was built in 1744 by John Finscher, but it later burned down. The first log church in the county was built in 1755. Native American massacres were commonplace in Schuylkill County between 1755 and 1765. Warrant for tracts of land in the vicinity of McKeansburg were in existence as early as 1750. Found by Sammy Hepler in 1789.
Anthracite coal (then called stone coal) was discovered by Necho Allen near the area where Pottsville was ultimately developed in 1790. In 1795, a blacksmith in Schuylkill County named Whetstone learned how to use the coal successfully for smithing purposes. In 1806 coal was found while the tail-race was cut of the Valley (Iron) Forge, on the Schuylkill. Daniel Berlin, another blacksmith, also used it successfully, and smiths in the neighborhood adopted using the coal.
Schuylkill County was created via an Act of Assembly on March 1, 1811, from portions of Berks and Northampton counties. More land was added to the county in 1818, from Columbia and Luzerne counties. At the time of its creation, the county had a population of about 6,000. An early book of Schuylkill County history was written by Daniel Deibert in 1802.
Orwisgsburg was the first community in Schuylkill County to be laid out. During the early years of Schuylkill County, there was an attempt to make McKeansburg the county seat; Orwigsburg was also a contender. Orwigsburg was agreed upon to be the county seat, as it was deemed to be well-suited for industries. Beginning in 1831, sentiment began to rise for moving the county seat to Pottsville. In 1846, the Legislature passed an Act that was approved by Governor Francis R. Shunk on March 13, submitting the question to the voters. The change was desired principally because the railroad and canal connections with Orwigsburg were problematic to transport the public to that town without losing valuable time while Pottsville had such facilities and was within easy access from all parts of the county.
In 1812, George Shoemaker who, with Necho Allen, had discovered stone coal at Centerville in Schuylkill County, personally delivered some coal to Philadelphia. He gave away most of the coal, intending to encourage individuals to find ways to use it. Most of the experiments failed and though Shoemaker was nearly run out of town and called an imposter, Mellon and Bishop of Delaware County successfully used it in their rolling mill. When other rolling mills also adopted the fuel, a large industrial market and demand developed.
The Schuylkill Navigation Company was chartered in 1815 to build a series of navigation improvements in the Schuylkill River. This was during a period when the much larger Erie Canal along the Mohawk River in New York also was being developed. It was well ahead of other key canals fueling the Industrial Revolution, such as the Delaware and Hudson, the Lehigh, the Chesapeake and Ohio, Delaware and Raritan, and Morris canals. The originators of the project did not count upon the coal trade to promote the success of the undertaking. They looked forward mainly to transporting the agricultural products being produced below the mountains, the lumber of Schuylkill County, and the grain and other products of the counties between the Susquehanna and Schuylkill rivers. The first shipments of coal by canal were made in 1822 when 1,480 tons were sent down the line.
With a regular supply of anthracite coal ensured, the southern anthracite coal field in Schuylkill County attracted speculators and fortune hunters. They were inspired by dreams of becoming millionaires. This was the first speculative era of the Schuylkill coal trade. Pottsville became the center of the movement. The more successful explorers revealed numerous veins of coal, extending over a vast stretch of county and with a seemingly inexhaustible quantity of coal. These discoveries brought excitement and speculation; lands were bought (and sold); roads were laid out in the forest, mines were opened and railroads projected, and innumerable town plots planned. The demand for houses was so great that the lumber for many was framed in Philadelphia and sent by canal to the burgeoning coal region.
At this stage, coal-mining firms were small and family owned. The residents and entrepreneurs of the Schuylkill region opposed the entry here of incorporated coal companies. In these years, coal mining operations in the Schuylkill region were conducted with economy, and relatively little capital was required. As the workings were all above the water level, no machinery was required for water drainage or for hoisting coal to the surface. Coal breakers and other expensive fixtures and appliances for the preparation of coal had not then been introduced. Numerous operators produced from five to six thousand tons for market annually (which was then considered a respectable business), who had never committed thousands of dollars to their enterprises, including their first land purchases of coal mines. It was commonly asserted that coal land could be bought and mines opened for less capital than the purchase and stocking of a decent farm. Such mines could be worked for less capital than that required to establish a line of stagecoaches or transportation wagons.
Eventually, railroads replaced the canals as the primary means of transporting coal to markets. Mining was taken over by major corporate business, especially after the Civil War. As a result, the Middle Coal Field was developed in the 1860s and the Philadelphia and Reading Railroad created a subsidiary (Philadelphia and Reading Coal and Iron Company) to buy or lease, and develop the expanding industrial coal trade. Consumption of coal along the Schuylkill above Philadelphia in 1839 was 30,290 tons when the Pioneer at Pottsville, the first anthracite furnace in the United States, became operational. By 1849, consumption had increased to 239,290 tons, to 554,774 tons in 1859, and to 1,787,205 tons in 1873.
The numerous jobs in the mining industry comprised a catalyst for mass immigration to Schuylkill County from the British Isles and Europe in the 19th and 20th centuries. As mines became more numerous (by 1846 there were 110 operators in the region and 142 collieries in Schuylkill County) and more complex (in 1846 there were 35 collieries below water level), mechanical breakers, steam locomotive, it became more labor-intensive both for accomplishing mining tasks and supporting minings peripheral industries. Such industries included manufacturing of explosives, metal screens, pump components, piping, and timber for support. This led to an influx of population into Schuylkill and other anthracite counties to fill these jobs. Beginning with the Irish immigration in the 1840s (fueled by the Great Famine), after the Civil War, beginning in the 1870s, newcomers arrived from Eastern Europe. Poles, Hungarians, Lithuanians, Slovaks, Rusyns and Ukrainians (Ruthenians), often from the Austro-Hungarian monarchy settled in the villages of Schuylkill County and took their place among the laborers in the coal mines. By the 1880s and 1890s, thousands of Italians immigrated for jobs related to mining.
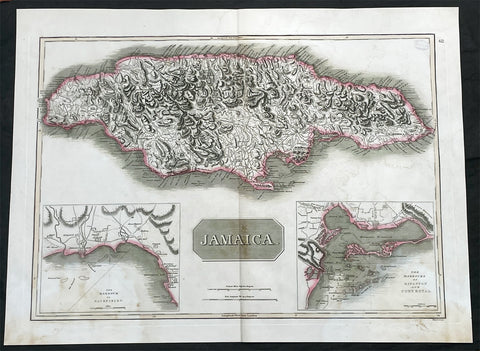
1817 John Thompson Large Antique Map of the Caribbean Island of Jamaica
- Title : Jamaica
- Date : 1817
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35605
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning, small library stamp to right
Verso: - Age toning
1817 John Thompson Large Antique Map Caribbean Islands South Florida West Indies
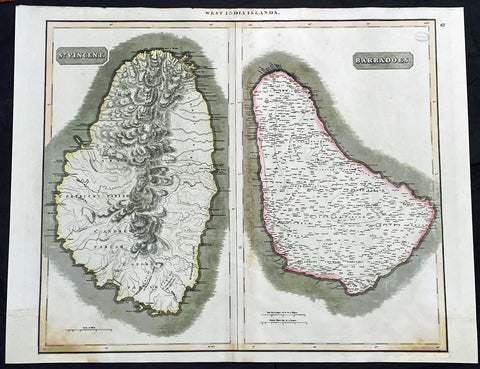
- Title : West India Islands: St Vincent; Barbados
- Date : 1817
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35611
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning, small library stamp to right
Verso: - Age toning
1817 John Thompson Large Antique Map Caribbean Islands of St Vincent & Barbados
- Title : West India Islands: St Vincent; Barbados
- Date : 1817
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35610
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning, small library stamp to right
Verso: - Age toning
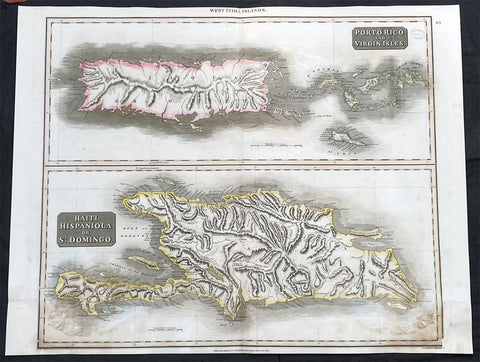
1815 John Thompson Large Antique Map Caribbean Is. of Porto Rico, Virgins, Haiti
- Title : West India Islands: Porto Rico and Virgin Islands; Haiti, Hispaniola or St Dominigo
- Date : 1815 - dated
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35608
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning, small library stamp to right
Verso: - Age toning
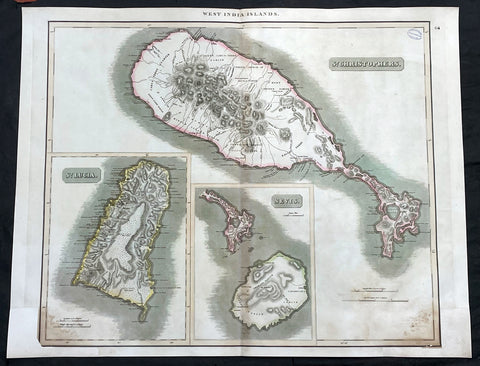
1817 John Thompson Large Antique Map Caribbean Is. St Christopher St Lucia Nevis
- Title : West India Islands: St Christopher; St Lucia; Nevis
- Date : 1817
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35609
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning, small library stamp to right
Verso: - Age toning
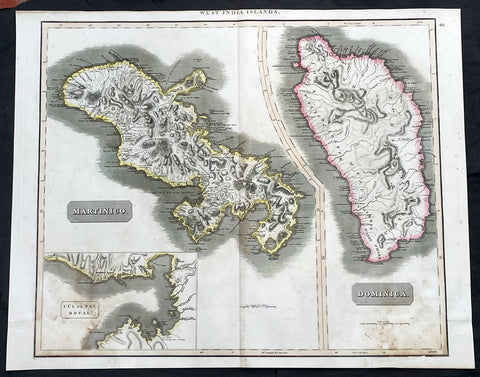
1817 John Thompson Large Antique Map Caribbean Islands of Martinique & Dominica
- Title : West India Islands: Martinico (Cul de Sac Royal); Dominica
- Date : 1817
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35606
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands of Martinique and Dominica was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Age toning
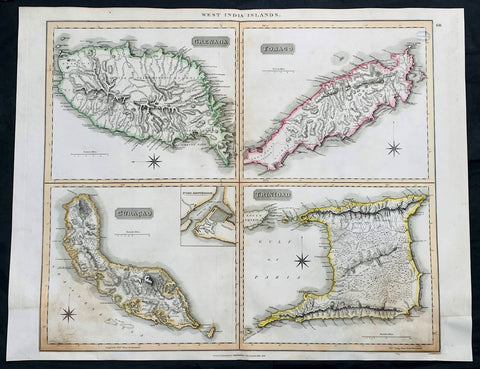
1816 John Thompson Large Antique Map Grenada, Tobago, Curacao Trinidad Caribbean
- Title : West India Islands: Grenada; Tobago; Curacao; Trinadad.
- Date : 1816
- Size: 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35612
Description:
This large original, beautifully hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of the Caribbean Islands Grenada, Tobago, Curacao & Trinidad was published by John Thomson in his large elephant folio 1817 edition of A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref Tooley M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 21in (685mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom L&R margins extended from borders, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning, small library stamp to right
Verso: - Age toning
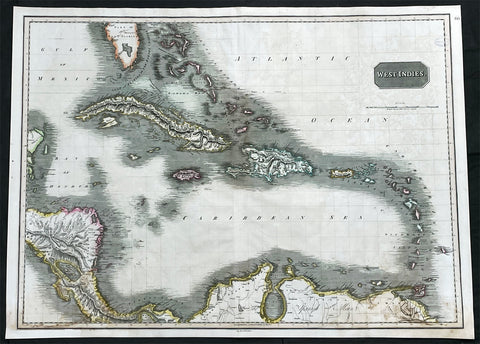
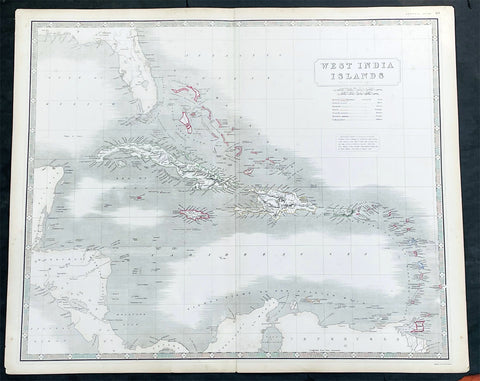
1845 Johnston Large Antique Map Florida, Caribbean, Cuba, Haiti, Central America
- Title : West India Islands
- Date : 1845
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35619
Description:
This large original hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of West Indian, Caribbean Islands, was published by W & AK Johnston in his General Atlas, 1845.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
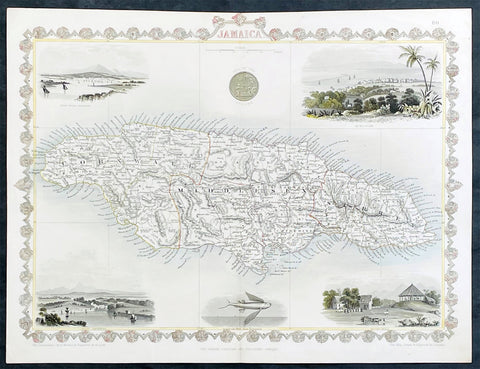
1851 John Tallis Antique map of the Island of Jamaica
- Title : Jamaica
- Date : 1851
- Size: 15in x 11in (380mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35616
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of Jamaica, with decorative vignettes of Kingston, Port Antonio, Port Royal, a sugar mill and a flying fish, was published by John Tallis in 1851.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 11in (380mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light crease left side of image
Verso: - None
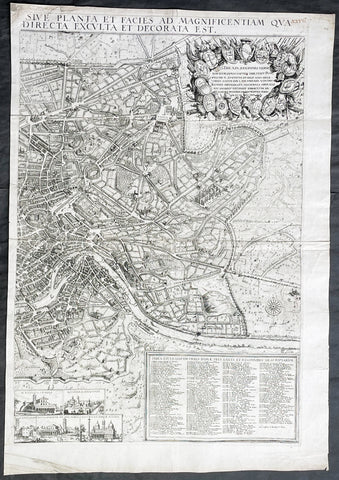
1679 Jacob von Sandrart & Giovanni Battista Falda Large Left Hand Sheet of Rome
- Title : Recentis Romae Ichnographia et Hypsographia Sive Planta et Faies Ad Magnificentiam Qua Prioribus Annis Urbs Ipsa Directa Exculta et Decorata Est.
- Date : 1679
- Size: 26 3/4in x 18 3/4in (680mm x 475mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43188
Description:
This large, original copper plate engraved scarce left hand section of the map of Rome by Jacob Von Sandrart, after Giovanni Battista Falda map, was published in 1679.
This map is based on Giovanni Battista Falda's 12-sheet view of Rome, Nuova Pianta et alzata della citta di Roma, first published in 1676.
Sandrart's view of Rome is rare, we are aware of only 2 examples appearing at auction during the last 25 years.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 26 3/4in x 18 3/4in (680mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 17in (635mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Jacob von Sandrart's rare and exquisitely engraved view of Rome, one of the finest impressions of the 'Eternal City' made during the great Baroque Era of Art and Architecture.
This finely engraved and lavishly decorative view of Rome takes in all of the 'Eternal City', as it was encompassed by its ancient Aurelian Walls, built during the 2nd Century A.D., on the banks of the River Tiber. Numerous monuments and sites, all of which are still present today, can be seem on the view, including the Coliseum, the Pantheon, the Piazza del Popolo, the Church of San Giovanni Laterno, the Baths of Diocletian, and the Vatican, which is dominated by the Dome of St. Peter's Basilica and the Castel Sant'Angelo. Most notable is the great oval Colonnade that lines the square in front of St. Peter's, which had only been completed in 1666 by the Gianlorenzo Bernini, one of the towering figures of the Baroque Era. The quality of the engraving is exceptionally high, as is the composition of the view, which grants the observer a panoptic view over Rome, while the specific details of the cityscape remain sharply distinguishable.
In the upper left, the title cartouche is surmounted by a portrait of Pope Innocent XI (reigned 1676-89), considered to be a leader of great learning and political acumen. In the upper right corner is a montage featuring the shields of the 14 traditional districts (wards) of Rome. Flowing through the view itself, the River Tiber has its orgins in an allegorical personification of its springs.
In the lower left, a table, 'Index Aedium Antiquitatarum' identifies an amazing 253 ancient buildings and ruins throughout the city. The 'Index Ecclesiarium' in the lower right identifies an incredible 178 churches, although it is not surprising that Rome had by far more houses of worship than any other city in Europe.
In the lower center of the plan are seven views of some of the city's most prominent churches, including St. Peter's Basilica (Vatican), St. Paul's Basilica, San Sebastian Church, San Giovanni Laterno, Sacred Cross of Jerusalem Church, Basilica of St. Lawrence Outside the Walls and the Basilica of Santa Maria Maggiore.
At the time that this view was issued, Rome was enjoying a period of prosperity, and the city's population had reached over 120,000, making it one of the 10 largest cities in Europe. The Roman Catholic Church was on a high, having largely succeeded in driving the Counterreformation, and revenues were pouring in to the Vatican from around the world. This funded the great flourishing of art and architecture in Baroque Rome.
The map was engraved by Jacob von Sandrart (1630-1708), one of the leading fine art engravers of the 17th Century. Born in Frankfurt-am-Main, he apprenticed under his famous uncle Joachim von Sandrart in Amsterdam. He worked in Danzing and Regensburg, and by 1656 had established himself in Nuremberg, where he remained for the rest of his life. Sandrart was highly productive, as over 400 different engravings from his burin are known to survive, although the high quality of his work never wavered. Along with his maps, he is especially well-known for his portraits. Sandrart was the founder and first director of the Nuremberg Academy of Fine Arts (chartered 1662).
Sandrart, Jacob von 1630 - 1708
Jacob von Sandrart was a German engraver primarily active in Nuremberg.
At age ten Sandrart obtained his artistic training from his better-known uncle Joachim von Sandrart in Amsterdam. After spending time in Danzig and Regensburg, he married Regina Christina Eimart, daughter of the engraver Georg Christoph Eimart the elder, on 10 June 1654. The couple settled in Nuremberg in 1656 and remained there for the rest of their lives. His daughter Susanne Maria von Sandrart was also an artist and engraver.
Sandrart was a very prolific artist; over 400 engravings from his hand are extant. He was best known as a portraitist of prominent contemporary citizens of Nuremberg, as an engraver of maps, and as an illustrator of the literary works of Nuremberg writers, especially Sigmund von Birken. Today Sandrart is best remembered as the founder and first director of the Nuremberg Academy of Fine Arts (est. 1662).
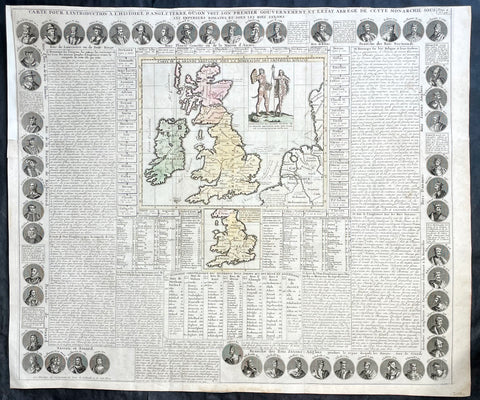
1719 Chatelain Antique Map Great Britain & Ireland Royalty Egbert to Queen Anne
- Title : Carte Pour L Introduction a L Historire S Angleteerre...
- Date : 1719
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93426
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map and illustration of Great Britain and Ireland, with text and pictorial representations of all the Kings and Queens from Egbert in 801 to Queen Anne in 1701, was published by Henri Abraham Chatelain in 1719, in his famous Atlas Historique.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top left margin extended
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
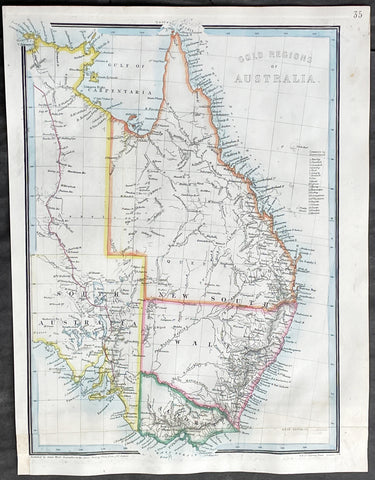
1855 James Wyld Scarce Antique Map of Australian Early Goldfields
- Title : Gold Regions of Australia
- Date : 1855
- Size: 13 1/2in x 10 1/2in (345mm x 270mm)
- Condition: (A+) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 27006
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique early Gold Fields map of Eastern Australia was published by James Wyld in 1855.
This scarce map was published very early on, in the discovery of gold in Australia, in 1851. Once gold was discovered by Hargraves, the number of discoveries made Australia, in a short period of time, one of the richest places on earth.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, blue, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13 1/2in x 10 1/2in (345mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 10 1/2in (345mm x 270mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Bottom section of map rejoined
Verso: - None
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
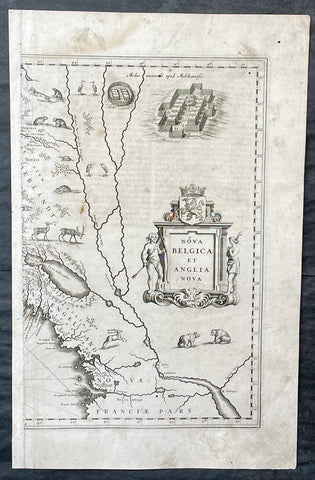
1635 Joan Blaeu Antique Half Page Map of New England, Nova Belgica et Anglia
- Title : Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova
- Date : 1635
- Size: 18 1/2in x 12in (470mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
- Ref: 16385
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique half right hand page map of New England & NE America by Joan Blaeu was published in the 1635 German edition of Atlas Novus.
This is the right hand, cartouche title section of this important map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 12in (470mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling, small worm hole top right margin
Plate area: - Light soiling, 4 small worm holes
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
This important map was one of the most attractive of the Americas published at the time. It is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript figurative map of Adriaen Block from 1614. Indeed it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way. This helped to create an accurate picture of the longitudinal scale of the coastline. His manuscript map is the first document to delineate an insular Manhattan; it also provides the earliest appearance of Manhates and Niev Nederland.
It has been noted that the time difference between 1614, the date of the manuscript, and Blaeus map whose first appearance is in 1635, appears long for such an important advance. It would seem highly feasible that Blaeu, who published many separately issued maps, would have wanted to produce one like this sooner. However, evidence points to the fact that it could not have been made before 1630. The Stokes Collection in New York possesses an example of the map on thicker paper without text on the reverse which could well be a proof issue of some kind.
There are features on Blaeus map that differ from the Block chart. Some of these could be accounted for by the fact that the surviving figurative map is not the original, and that the copyist omitted some place names that are referred to in the text of de Laets work. Block drew on Champlains map of 1612 for the depiction of the lake named after him, but it is here called Lacus Irocoisiensis. … The lack of interrelation between the Dutch or English colonies and the French, led for some time to the eastward displacement of this lake when its true position would be north of the Hudson River.
Some nomenclature has its origins in Blaeus second Paskaert of c.1630, and others, such as Manatthans, in de Laet. The colony of Nieu Pleimonth is identified. This and other English names along that part of the coast are largely derived from Smith\\\'s New England, 1616. Cape Cod is here improved over the Block manuscript by being reconnected to the mainland, the narrow strait having been removed. The coastline between here and Narragansett Bay, which can be clearly recognized, is not so accurate. Adriaen Blocx Eylandt leads us to the Versche Rivier, or Connecticut River, which Block ascended as far as was possible. t Lange Eyland is named; however, it is incorrectly too far east, being applied to what is possibly Fishers Island. De Groote bay marks Long Island Sound. The Hudson River is still not named as such, but is littered with Dutch settlements, and the failed Fort Nassau is here depicted renamed as Fort Orange. He does, however, improve on the direction of its flow. Blaeu separates the sources of the Hudson and Delaware Rivers which had been causing some confusion. Nieu Amsterdam is correctly marked as a fort at the tip of an island separated on the east side by Hellegat, or the East River. The coastline south of Sandy Hook also shows signs of improvement.
The whole map is adorned by deer, foxes, bears, egrets, rabbits, cranes and turkeys. Beavers, polecats and otters appear on a printed map for the first time. The Mohawk Indian village top right is derived from the de Bry-White engravings.
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of Victoria, Australia
- Title : Victoria The Gold Districts are coloured (sic yellow)
- Date : 1855
- Size: 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27096
Description:
This large hand coloured & scarce antique lithograph Goldfields Map of Victoria, Australia (with an inset map of the Mt Alexander & Castlemaine regions) by John Bartholomew was published in the 1855 edition of A & C Blacks General Atlas of The World
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of South Eastern Australia
- Title : Victoria. New South Wales and South Australia...Gold Deposits..
- Date : 1855
- Size: 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27097
Description:
This large hand coloured & scarce antique lithograph Goldfields Map of South Eastern Australia by John Bartholomew was published in the 1855 edition of A & C Blacks General Atlas of The World
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 12 1/2in (445mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
1855 John Bartholomew Large Antique Goldfields Map of Australia
- Title : Australia...Gold Areas marked thus....
- Date : 1855
- Size: 24in x 17 1/2in (610mm x 445mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50227
Description:
This large hand coloured & scarce antique lithograph Goldfields Map of Australia by John Bartholomew was published in the 1855 edition of A & C Blacks General Atlas of The World
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 17 1/2in (610mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 17 1/2in (610mm x 445mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The first gold rush in Australia began in May 1851 after prospector Edward Hargraves claimed to have discovered payable gold near Orange, at a site he called Ophir. Hargraves had been to the Californian goldfields and had learned new gold prospecting techniques such as panning and cradling. Hargraves was offered rewards by the Colony of New South Wales and the Colony of Victoria. Before the end of the year, the gold rush had spread to many other parts of the state where gold had been found, not just to the west, but also to the south and north of Sydney.
The Australian gold rushes changed the convict colonies into more progressive cities with the influx of free immigrants. These hopefuls, termed diggers, brought new skills and professions, contributing to a burgeoning economy. The mateship that evolved between these diggers and their collective resistance to authority led to the emergence of a unique national identity. Although not all diggers found riches on the goldfields, many decided to stay and integrate into these communities.
In July 1851, Victoria\'s first gold rush began on the Clunes goldfield. In August, the gold rush had spread to include the goldfield at Buninyong (today a suburb of Ballarat) 45 km (28 m) away and, by early September 1851, to the nearby goldfield at Ballarat (then also known as Yuille\'s Diggings) followed in early September to the goldfield at Castlemaine (then known as Forest Creek and the Mount Alexander Goldfield) and the goldfield at Bendigo (then known as Bendigo Creek) in November 1851. Gold, just as in New South Wales, was also found in many other parts of the state. The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854:
The discovery of the Victorian Goldfields has converted a remote dependency into a country of world wide fame; it has attracted a population, extraordinary in number, with unprecedented rapidity; it has enhanced the value of property to an enormous extent; it has made this the richest country in the world; and, in less than three years, it has done for this colony the work of an age, and made its impulses felt in the most distant regions of the earth.
When the rush began at Ballarat, diggers discovered it was a prosperous goldfield. Lieutenant-Governor, Charles La Trobe visited the site and watched five men uncover 136 ounces of gold in one day. Mount Alexander was even richer than Ballarat. With gold sitting just under the surface, the shallowness allowed diggers to easily unearth gold nuggets. In 7 months, 2.4 million pounds of gold was transported from Mount Alexander to nearby capital cities.
The gold rushes caused a huge influx of people from overseas. Australia\'s total population more than tripled from 430,000 in 1851 to 1.7 million in 1871. Australia first became a multicultural society during the gold rush period. Between 1852 and 1860, 290,000 people migrated to Victoria from the British Isles, 15,000 came from other European countries, and 18,000 emigrated from the United States. Non-European immigrants, however, were unwelcome, especially the Chinese.
The Chinese were particularly industrious, with techniques that differed widely from the Europeans. This and their physical appearance and fear of the unknown led to them to being persecuted in a racist way that would be regarded as untenable today.
In 1855, 11,493 Chinese arrived in Melbourne. Chinese travelling outside of New South Wales had to obtain special re-entry certificates. In 1855, Victoria enacted the Chinese Immigration Act 1855, severely limiting the number of Chinese passengers permitted on an arriving vessel. To evade the new law, many Chinese were landed in the south-east of South Australia and travelled more than 400 km across country to the Victorian goldfields, along tracks which are still evident today.
In 1885, following a call by the Western Australian government for a reward for the first find of payable gold, a discovery was made at Halls Creek, sparking a gold rush in that state.
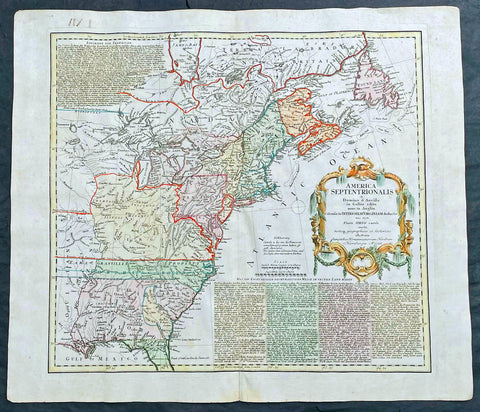
1756 Homann Antique Map Colonial United States North America French Indian War
- Title : America Septentrionalis a domino d Anville in Galiis edita nunc in Anglia coloniis in interiorem Virginiam deductis nec non fluvii Ohio cursu aucta notisq geographicis et historicis illustrata.....1756
- Ref #: 27018
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique 1st edition map of the Colonial United States, at the beginning of the French-Indian war, was engraved in 1756 - dated in cartouche - by the Homann firm, Germany.
This map has original margins and colour on heavy clean sturdy paper.
First edition Homann map of the English Colonies in North America prior to the start of the French and Indian War. The map stretches just west of the Mississippi River to the east and from James Bay through the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Although most of the text is in German, there is also much in English, including numerous place named annotations associated the French and Indian War, such as the locations of Fort Duquesne and Fort Necessity, both taken by the French in 1754. Thus although the cartographer credits D Anville for the basic cartography, it is clear he is drawing from English, not French, sources. Bottom right and upper left are notes offering the history of North America.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19in (535mm x 480mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light staining in lower margins, bottom margin centerfold rejoined with transparent archival tape
Plate area: - Light age toning along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The French and Indian War (1754–63) comprised the North American theatre of the worldwide Seven Years War of 1756–63. It pitted the colonies of British America against those of New France. Both sides were supported by military units from their parent countries, as well as by American Indian allies. At the start of the war, the French North American colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British North American colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on the Indians. The European nations declared war on one another in 1756 following months of localized conflict, escalating the war from a regional affair into an intercontinental conflict.
The name French and Indian War is used mainly in the United States. It refers to the two enemies of the British colonists, the royal French forces and their various American Indian allies. The British colonists were supported at various times by the Iroquois, Catawba, and Cherokee, and the French colonists were supported by Wabanaki Confederacy members Abenaki and Mikmaq, and Algonquin, Lenape, Ojibwa, Ottawa, Shawnee, and Wyandot.
British and other European historians use the term the Seven Years War, as do English-speaking Canadians. French Canadians call it La guerre de la Conquête (the War of the Conquest) or (rarely) the Fourth Intercolonial War.
Fighting took place primarily along the frontiers between New France and the British colonies, from Virginia in the south to Newfoundland in the north. It began with a dispute over control of the confluence of the Allegheny River and Monongahela River called the Forks of the Ohio, and the site of the French Fort Duquesne in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The dispute erupted into violence in the Battle of Jumonville Glen in May 1754, during which Virginia militiamen under the command of 22-year-old George Washington ambushed a French patrol.
In 1755, six colonial governors in North America met with General Edward Braddock, the newly arrived British Army commander, and planned a four-way attack on the French. None succeeded, and the main effort by Braddock proved a disaster; he lost the Battle of the Monongahela on July 9, 1755 and died a few days later. British operations failed in the frontier areas of Pennsylvania and New York during 1755–57 due to a combination of poor management, internal divisions, effective Canadian scouts, French regular forces, and Indian warrior allies. In 1755, the British captured Fort Beauséjour on the border separating Nova Scotia from Acadia, and they ordered the expulsion of the Acadians (1755–64) soon afterwards. Orders for the deportation were given by William Shirley, Commander-in-Chief, North America, without direction from Great Britain. The Acadians were expelled, both those captured in arms and those who had sworn the loyalty oath to His Britannic Majesty. Indians likewise were driven off the land to make way for settlers from New England.
The British colonial government fell in the region of modern Nova Scotia after several disastrous campaigns in 1757, including a failed expedition against Louisbourg and the Siege of Fort William Henry; this last was followed by Indians torturing and massacring their British victims. William Pitt came to power and significantly increased British military resources in the colonies at a time when France was unwilling to risk large convoys to aid the limited forces that they had in New France, preferring to concentrate their forces against Prussia and its allies in the European theater of the war. Between 1758 and 1760, the British military launched a campaign to capture the Colony of Canada (part of New France). They succeeded in capturing territory in surrounding colonies and ultimately the city of Quebec (1759). The British later lost the Battle of Sainte-Foy west of Quebec (1760), but the French ceded Canada in accordance with the Treaty of Paris (1763).
The outcome was one of the most significant developments in a century of Anglo-French conflict. France ceded to Great Britain its territory east of the Mississippi. It ceded French Louisiana west of the Mississippi River (including New Orleans) to its ally Spain in compensation for Spains loss to Britain of Florida. (Spain had ceded Florida to Britain in exchange for the return of Havana, Cuba.) Frances colonial presence north of the Caribbean was reduced to the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, confirming Great Britains position as the dominant colonial power in eastern North America.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1676 John Speed Antique Atlas Title Pages x 2 Empire of Great Britaine & World
- Title : The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine, A Prospect of the most famous Parts of the World by John Speed...London Thomas Bassett and Richard Chiswell 1676; The Achievement of our Soveraigne King Charles the 11D.
- Date : 1676
- Size: 22 1/2in x 17 1/2in (570mm x 445mm)
- Ref #: 42005/42006
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Price: $1250.00US
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured, copper plate engraved antique Title and Dedication Pages was published for the 1676 edition of John Speeds double atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine & Atlas A Prospect of the most Famous Parts of the World printed by Thomas Bassett and Richard Chiswell, London.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 17 1/2in (570mm x 445mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/4in x 9 3/4in (385mm x 250mm) each
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
John Speeds The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine was published in 1610/11 by John Sudbury and George Humble, and contained the first set of individual county maps of England and Wales besides maps of Ireland and a general map of Scotland. Most, but not all, of the county maps have town plans on them; those showing a Scale of Passes being the places he had mapped himself. The county maps were the first consistent attempt to show territorial divisions, such as boundaries of hundreds, but it was Speed’s town plans that were a major innovation and probably his greatest contribution to British cartography. The Theatre was an immediate success: the first print run of around 500 copies must have sold quickly because many editions followed. Sudbury and Humble realized, given the increasing popularity of both county and world atlases and in the light of the success of Abraham Ortelius’s Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, the potential demand for an English world atlas.
In 1627, two years before his death, Speed published Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World with 21 finely engraved maps, which was the first world atlas produced by an Englishman. There is a fascinating text describing the areas shown on the back of the maps in English, although a rare edition of 1616 of the British maps has a Latin text – this is believed to have been produced for the Continental market. Its maps are famous for their bordering panels of national characters in local costume and panoramic views depicting the areas of major towns and cities. Much of the engraving was done in Amsterdam at the workshop of Jodocus Hondius. The maps of the world and America show California as an island and are amongst the earliest ever printed to depict this seventeenth-century cartographic myth.
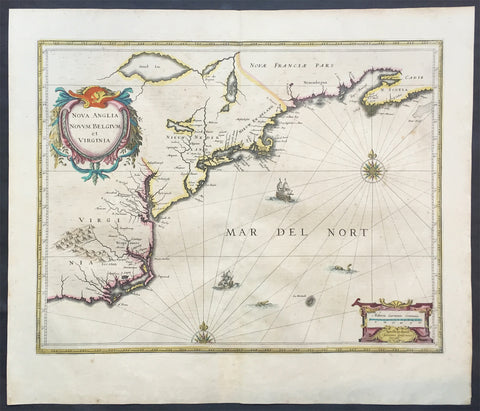
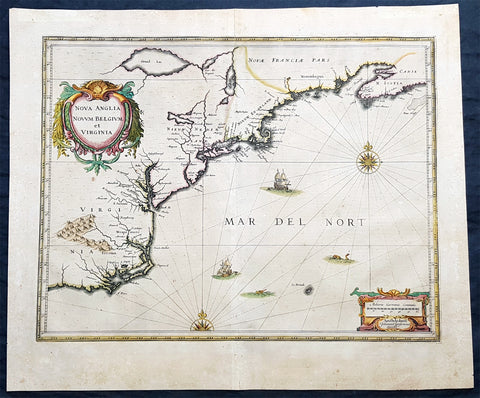
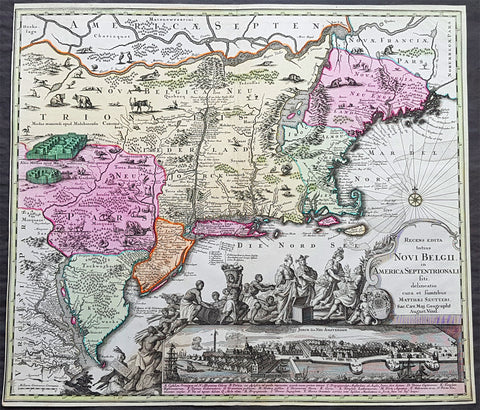
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America Virginia to New York to New England
- Title : Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Ref: 43134
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured, important original antique map of the north east regions of the United States from Virginia, Chesapeake Bay, to New York & New England by Jan Jansson was published in the 1639 French edition of the Jansson, Hondius Atlas.
A beautiful map with sturdy, clean paper original wide margins and beautiful original hand colouring.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light toning on margin edges
Plate area: - Very light offsetting
Verso: - None
Background:
A beautiful original 17th map of Virginia, New York and New England which was derived from the less well circulated Johannes de Laet map of 1630. This version is enlarged and expanded to the north and slightly east, with de Laets narrative on the verso (De Laets map is one of extreme importance, being the first printed to use the namesManbattes (Manhattan) and N. Amsterdam)
The nomenclature on this map is virtually identical to the De Laet map, with the few minor differences most likely owing to the engravers error. C of Feare is still depicted over 2° too far south. This is not Cape Fear we know of today but actually Cape lookout.
During the fiercely competitive decade of the 1630's the families of Blaeu and Jansson produced maps drawn directly from one another. Here, however, Jansson produces one that was not followed by Blaeu, relying upon the more restricted map of Nova Belgica to represent the land north of Chesapeake Bay. A sign of the Dutch influence here is that both atlas producers largely declined to include the advanced cartography of Champlain, thereby relegating it altogether.
There are three know states of this map, the first one published in 1636 - entitled Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia.
The second edition in which the title of the map was changed to Nova Belgium et Anglia Nova (to give more weight to Dutch claims in North America) within a new square cartouche was first published in 1647.
State 3 was published in 1694 by Schenk & Valk which included new regional demarcation and a latitude and longitude grid. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley; Burden; AMPR)
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America Virginia to New York to New England
- Title : Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 93508
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Description:
This magnificent original copper plate engraved antique landmark 1st edition map of the NE region of North America, the original colonial states from Virginia to New England, was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas
A magnificent early map of NE North America published only 19 years after the landing of the Pilgrims at Plymouth Rock, Massachusetts.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (505mm x 384mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning
Plate area: - Age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
This influential map is derived from the less well circulated Johannes de Laet map of 1630. Enlarged and expanded to the north and slightly east, it carries de Laets narrative on the reverse. De Laets map is one of extreme importance, being the first printed to use the names Manbattes (Manhattan) and N. Amsterdam. The nomenclature is virtually identical, with the few minor differences most likely owing to the engravers error. C of Feare is still depicted over 2° too far south. This is not Cape Fear we know of today but actually Cape lookout.
During the fiercely competitive decade of the 1630s the families of Blaeu and Hondius - Jansson of ten produced maps drawn directly from one another. Here, however, Jansson produces one that was not followed by Blaeu, the latter relying upon the more restricted map of Nova Belgica to represent the land north of Chesapeake Bay. A sign of the Dutch influence here is that both atlas producers largely declined to include the advanced cartography of Champlain, thereby relegating it altogether.
There are three know states of this map, this one first published in 1636, the second edition was published in 1647 renamed Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova within a new square cartouche. State 3 was published in 1694 by Schenk & Valk which included new regional demarcation and a latitude and longitude grid. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley; Burden)
1851-1891 Original Antique Virginian American Civil War Documents F. Beckham, M D Ball, D Coffman
-
Title :
1. The Commonwealth of Virginia
2. Fairfax County Va April 15th 1861.
3. State of West Virginia Green brier co. June 11th 1866.
4. United States Stamp for Special Tax Internal Revenue. - Date : 1851-1891
- Size: Please view description below
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
- Ref: 27090
Description:
We have on offer a group of 4 original antique documents, three of which relate directly to Virginia and the American Civil War dated 1851,1861, 1866. The first two documents concern Fontaine Beckham & Mottrom Dulany Ball with the third relating to Daniel Coffman. These three are very interesting and scarce items.
The fourth document relates to the Internal Revenue Service in 1891. Details, descriptions and conditions below.
1. Printed court summons signed by Fontaine Beckham (1788-1859) as justice of the peace, Jefferson County, Virginia, 8 January 1851. Printed sheet completed in manuscript, signed 'F Beckham'.
Fontaine Beckham was mayor of Harpers Ferry during the raid by John Brown in 1859 with Beckham infamously shot and killed during the raid, making him possibly one of the first casualties of the American Civil War.
Condition: Mounted on red-velvet-covered thick card mount, sheet torn at lower right-hand corner not affecting text. Condition Good. - 7in x 53/4in (18 x 14.6 cm)
Fontaine Beckham (1788-1859) was mayor of Harpers Ferry, Virginia, and local agent for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. He was shot and killed in the famous raid on the small outpost by abolitionist John Brown, today seen as a major event in the build-up to the American Civil War.
...... Beckham was the most prominent man killed during John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry, being the town's mayor, a county magistrate (in which capacity he signs this document), and a station agent for the B & O Railroad. Despite being a slave owner himself, Beckham was quite well-liked and considered by most to be a friend and benefactor of black men. He maintained a close friendship with his former slave Heyward Shepard, who also died during the raid.. After Shepard's death, some accounts state the mayor exposed himself to fire due to his clouded judgment. After Beckham's death, the infuriated town's people seized one of John Brown's imprisoned men, riddling his body with bullets. Yet Beckham's death also resulted in the only lasting freeing of slaves accomplished by the raid, as his will stipulated the freeing of five of his slaves......)
2. Manuscript receipt for the purchase of 'negro slaves Dennis and Belinda', Fairfax County, Virginia, signed by a member of a prominent local family, Mrs. M C(sic) Ball, dated 15 April 1861. We believe this to a transaction by Mary Ball, the mother of the first Governor of Alaska, Mottrom Dulany Ball, who at the time was have been fighting for the confederacy. The verso of the receipt is marked for Dulany, (as he was sometimes known) who would have been considered the head of the family after the death of his farther in 1859. Single bifolium of heavy woven paper, 10 lines, written on one side only, conjugate leaf docketed 'Dulany'
Condition: Damp-stained, creased from folding, loss to upper inner corner. Although stained the parchment is stable and heavy. Condition Good.
- 7 1/2in x 53/4in (18.2 x 13.8 cm)
Mottrom Dulany Ball, of Fairfax County, Fairfax Court House, and Alexandria, Virginia, was a musician, poet, teacher, lawyer, soldier and a founding father of the State of Alaska. Mottrom Dulany Ball, who was known variously as Mott, M.Dulany, or M.D., was born at Oak Mount, the home of his grandfather, Daniel French Dulany, in Fairfax County, Virginia on June 23, 1835.
Mott was the son of Spencer Mottrom Ball and Mary L. Dulany. Both parents were from prominent Virginia families. President George Washington is included among their many distinguished relatives. Mott’s early years were spent at his grandfather, Mottrom Ball’s, plantation, Woodberry, near Lewinsville, Fairfax County, Virginia. The elder Mottrom Ball was a physician who was educated at the University of Glasgow, in Scotland. TheBall family estate, Woodberry, consisted of 1,200 acres of land, rectangular in shape, extending north from the Lewinsville Presbyterian Church all the way to the to the Potomac River. 2, 3 The extensive plantation included a grist mill, Ball’s Mill, which stood on Scott’s Run. The location is today known as Swink’s Mill.4 Modern day Ball’s Hill Road traces the path of a farm road which ran through the center of Woodberry ending at the family home, Elmwood, on Ball’s Hill, also known as Prospect Hill, just south of Georgetown Pike.5 Politically, Mott’s father, Spencer Mottrom Ball, was an Anti-Jacksonian. As the name implies, this party was opposed to the authoritarian policies of President Andrew Jackson and his Democratic party. Several anti-Jacksonian factions came together to form the Whig party in 1834. Whigs supported the supremacy of Congress over the presidency.....)
3. Contemporary manuscript copy of two affidavits, one the same sheet, confirming Daniel Coffman to have been a loyal man during the rebelion [sic]', Greenbrier County, West Virginia, 1866.
Single sheet of lined paper written recto only, small embossed stamp depicting the Capitol Building and with text 'Congress' various inconsistencies in spelling.
Condition: Old folds, central fold just splitting at head, nicked along inner edge. Condition Good.
- 9in x 7in (23.5 x 17.8 cm)
First affidavit.
State of West Virginia Greenbrier Co. June 1866.
Personelly (sic) apparent before me a justice of the Peace John Sydenrtrleker (sic) and made oath that he knew Daniel Coffman to have been a loyal man during the rebellion and consider him the same use (sic) to this time Signed and sworn to before me in my township of fort spring this june 11th 1866...D Coffman JPS.....
Second affidavit.
State of West Virginia Greenbrier Co. June 1866.
Personell (sic) apparent before me a justice of the Peace H H Brackman and made oath that he knew Daniel Coffman to have been a loyal man during the rebellion and he invest (sic) himself the same now and I believe what he said to me
Signed and sworn to befor (sic) me in my township of fort spring...D Coffman JPS.....
The Coffman family have lived in Greenbrier county since the Rev Isaac Coffman 1741 - 1824, buried in the Coffman Cemetery, Ronceverte, West Virginia.
4. Internal Revenue receipt 'for special tax on the business of retail liquor dealer', paid by R. D. Burns of Lynchburg, Virginia, 9 December 1891 Engraved receipt in red and black, completed in manuscript.
Condition: Aged, small hole to lower left, upper right corner chipped. Condition Good. - 9 3/4in x 7 1/4in (24.5 x 18 cm)
General Definitions:
Please view description above
Imperfections:
Please view description above
1751 D Anville Very Large Antique Map The West Coast of Africa, Slave Coast
- Title : Carte Particuliere De La Cote Occidentale De L'Afrique Depusi le Cap Blanc jusqu'au Cap De Verga et du Cours Des Rivieres De Senega et de Gambie . .MDCCLI
- Ref #: 22009
- Size: 42in x 33in (1.07m x 840mm)
- Date : 1751
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large finely engraved, highly detailed original antique map of of the west coast of Africa covering Gambia and Senegal was engraved in 1751 - dated in the tile cartouche - and was published in Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D'Anville's large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
Description: D' Anville's maps have a clarity and a directness that is very 'modern'. He incorporated as much known information into his maps as he could. Map extent is from Cap Blanc in the north to Cap de Verga in the south.
Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster's Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 42in x 33in (1.07m x 840mm)
Plate size: - 40 1/2in x 28in (1.02m x 710mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light text offsetting
Verso: - None
1755 (1768) Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique 2nd edition Map of Colonial United States
- Title : Partie De L Amerique Septentrionale, qui Comprend Le Cours De L Ohio...Par le Sr Robert de Vaugondy
- Date : 1755 (1768)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93514
- Size: 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured, scarce 2nd edition antique map of the east coast of the United States, illustrating the course of the Ohio River and stretching from New England to the Carolinas, north to the Great Lakes and south to the Mississippi - with an inset map of The Carolinas - was published in 1768 - dated 1755 in the cartouche - by Robert Du Vaugondy in his Atlas Universal.
This map is all original with hand colour on age toned heavy paper with original margins with a heavy dark ink denoting an early pressing.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Second state of the early de Vaugondy map of the British colonies, with changes after the 1763 Treaty of Paris, with Virginia & Carolina extended to the Mississippi and Pennsylvania extended to Lake Erie. The majority of geographical information is based upon John Mitchells great map of North America from the mid 1750s, also drawing from Lewis, Evans on the Middle British Colonies and Joshua Frys and Peter Jeffersons map of Virginia and Maryland. The Mitchell map was the culmination of many years of British surveying in the North American Colonies and was considered one of the best maps of the continent available to Europeans and Americans in the mid-eighteenth century.
De Vaugondys rendition does not copy the full scope of Mitchells map but instead focuses on the colonies stretching from southern Maine to the Carolinas. In the top left corner is an inset of South Carolina and Georgia. De Vaugondy also pays special attention to the river systems and settlements. This map shows some of the earliest accurate information of the trans-Allegheny regions (the Ohio River, Kentucky, Tennessee and Parts of Ohio) and inland areas to the southeast of the Great Lakes and interior of New England.
Maine is still part of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. During this era. The dispute between New Hampshire and New York over who controlled the area which is now Vermont has been resolved. The outbreak of the French & Indian War (Seven Years War) briefly suspended interest in the disputed area, and it was not until 1764 that the British crown upheld New Yorks claim to Vermont. Included is a beautiful title cartouche in the Rococo style. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1778 John Mitchell & Antonio Zatta 12 Sheet Antique Map of North America - Rare
- Title : Le Colonie Unite dell' America Settentrle. di Nuova Projezione Ass. Ee. Li Signori Riformatori dello Studio di Padova. Venezia 1778, Presso Antonio Zatta, con Privilegio dell' Eccellentissimo Senato.
- Ref #: 93528
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 52 1/2in x 51in (1.33m x 1.30m)
- Date : 1778
Description:
This impressive very large twelve-sheet joined, original hand coloured important antique map is Antonio Zattas version of John Mitchells 1755 landmark map of North America, published first in 1778. This map is one of a few to be released during the late 18th century copying Mitchells map, in an effort to explain the rapidly changing political & economic situation in North America. Zatta has included many additional notes relating to both the Treaty of 1763 and events in the Revolutionary War. Most importantly, it is the first printed map devoted to the thirteen states, and to use the a name distinguishing them from their previous status as British Colonies. The name United Colonies was used in the Declaration of Independence and was not officially replaced until the Articles of Confederation adopted the name The United States of America.
This is an incredibly important and rare map, especially joined, in excellent condition with original colour. With John Mitchells map is now almost now impossible to find, with the last known sale in 2011 of $175,000US, this map is now one of the few, of that period, that is avaialble.
Zatta published these twelve separate sheets of Mitchells Map of North America, plus three other maps: Il Canada, Le Isole di Terra Nuova e Capo Breton, and La Baja D Hudson in the atlas Atlante Novissimo published from 1779-1785, with a second edition of the Zatta/Mitchell map published in 1791. Zattas version does not cover the far western portions of Mitchells map stretching to the Mississippi. An image of Mitchells map has been included as a point of reference.
Because Mitchells map was immediately recognized as seminal, it was exceedingly popular. Events leading up to the American Revolution only increased that demand. During the midst of the colonists on-going struggle for liberation from England, Zatta published this version which included some additional place names and information on early battles of the American Revolution.
The maps of Venetian publisher Antonio Zatta are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 52 1/2in x 51in (1.33m x 1.30m)
Plate size: - 49 1/2in x 49 1/4in (1.26m x 1.25m)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - Light creasing
Background:
A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America by John Mitchell Map is a landmark map by John Mitchell (1711–1768), which was reprinted several times during the second half of the 18th century, in France, Italy & Germany. The Mitchell Map was used as a primary map source during the Treaty of Paris for defining the boundaries of the newly independent United Colonies. The Mitchell Map is the most comprehensive map of eastern North America made during the colonial era, measuring 6.5 feet (2.0 m) wide by 4.5 feet (1.4 m) high.
Mitchell started compiling a first draught map in 1750 from information acquired in London, both in official & private archives. This proved to be inadequate & George Montagu-Dunk, 2nd Earl of Halifax, accordingly ordered the governors of the 13 British colonies to survey and compile new maps, which most did. These became the basis, along with cartographical information of the French geographer Guillaume Delisle, of his landmark map. Late in 1754, Halifax was using one manuscript copy of Mitchells second map to successfully promote his political position (no compromise with the French) within the British cabinet in the build-up to the Seven Years War, also know as the French and Indian War. Halifax also permitted Mitchell to have the map published: it appeared in April 1755, engraved by Thomas Kitchin and published by Andrew Millar.
The published map bore the title A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America. It bore the copyright date of 13 February 1755, but the map was probably not sold to the public until April or even May. Minor corrections to the maps printing plates were made probably during the printing process (for example, the name and address of the publisher were corrected).
The geographer John Green criticized Mitchell and his map soon after it appeared, emphasizing two failings with respect to Nova Scotia (an area of particular dispute with the French). Mitchell, Green noted, had used neither the astronomical observations for latitude and longitude made by Marquis Joseph Bernard de Chabert in the 1740s nor a 1715 chart of the Nova Scotia coast. In response, Mitchell released a new version of his map, now with two large blocks of text that described all of his data sources; the new version of the map also adjusted the coastline in line with Chaberts work but rejected the 1715 chart as deeply flawed. This version of the map, which Mitchell referred to as the second edition, is commonly thought to have appeared sometime in 1757, but advertisements in the (London) Public Advertiser and Gazetteer and London Daily Advertiser on 23 April 1756 clearly indicate that this new map appeared at that time.
Mitchells map was printed in eight sheets; when assembled, it measures 136 cm by 195 cm (4 feet 6 inches by 6 feet 5 inches; height x width). The initial impressions printed in 1755 have a consistent coloring outlining British colonial claims. Mitchell extended the southern colonies across the entire continent, even over established Spanish territory west of the Mississippi. Mitchell divided up the Iroquois territories (as he understood them, reaching from Lake Champlain [Lac Irocoisia] to the Mississippi, and north of Lake Superior) between Virginia and New York, leaving only a much-reduced territory to the French.
Mitchells map was expensive but it spawned many cheaper variants that trumpeted Halifax and Mitchells powerful colonial vision to the British public. One of these, published in December 1755 by a Society of Anti-Gallicans, restricted the French even further just to Quebec.
The map is liberally sprinkled with text describing and explaining various features, especially in regions that were relatively unknown or which were subject to political dispute. Many notes describe the natural resources and potential for settlement of frontier regions. Others describe Indian tribes. Many Indian settlements are shown, along with important Indian trails.
Since Mitchells main objective was to show the French threat to the British colonies, there is a very strong pro-British bias in the map, especially with regard to the Iroquois. The map makes clear that the Iroquois were not just allies of Britain, but subjects, and that all Iroquois land was therefore British territory. Huge parts of the continent are noted as being British due to Iroquois conquest of one tribe or another. French activity within the Iroquois claimed lands is noted, explicitly or implicitly, as illegal.
In cases where the imperial claims of Britain and France were questionable, Mitchell always takes the British side. Thus many of his notes and boundaries seem like political propaganda today. Some of the claims seem to be outright falsehoods.
The Mitchell Map remained the most detailed map of North America available in the later eighteenth century. Various impressions (and also French copies) were used to establish the boundaries of the new United States of America by diplomats at the 1783 Treaty of Paris that ended the American Revolutionary War. The maps inaccuracies subsequently led to a number of border disputes, such as in Maine.[clarification needed] Its supposition that the Mississippi River extended north to the 50th parallel (into British territory) resulted in the treaty using it as a landmark for a geographically impossible definition of the border in that region. It was not until 1842, when the Webster-Ashburton Treaty resolved these inconsistencies with fixes such as the one that created Minnesotas Northwest Angle, that the U.S.–Canada border was clearly drawn from Maine to the Oregon Country.
Similarly, during the drafting of the Northwest Ordinance, the maps inaccuracy in depicting where an east–west line drawn through the southernmost point of Lake Michigan would intersect Lake Erie led to a long dispute over the Ohio–Michigan border that culminated in the Toledo War.
Zatta, Antonio fl. 1757-1797
Antonio Zatta was a prominent Italian editor, cartographer, and publisher. Little is known about his life beyond his many surviving published works. It is possible that he was born as early as 1722 and lived as late as 1804. He lived in Venice and his work flourished between 1757 and 1797. He is best known for his atlas, Atlante Novissimo (1779-1785), and for his prolific output of prints and books that were both precisely made and aesthetically pleasing. Zatta clearly had a large network from which to draw information; this is how he was able to publish the first glimpse of the islands visited by Captain Cook in the Atlante Novissimo.
Zattas maps are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. His re-engraving and publication of John Mitchells famous map of North America A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America in 1778, is considered one of the best re-issues of this seminal, landmark map .
......He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.... (Portinaro & Knirsch, The Cartography of North America, 1500-1800, p. 319).
Zatta was among the leaders in the eighteenth-century revival of fine printing in Italy and his choice of the text of Raynal to support his re-issue of Mitchells Map, is not surprising. Anne Palms Chalmers describes Zatta as a sardonic writer with the focus of a certain amount of political controversy (Venetian Book Design in the Eighteenth Century, The Metropolitan Museum of Art Bulletin, New Series, Vol. 29, No. 5, January 1971, pp. 226-235). Chalmers describes Zattas printing and design as harmonious in composition with ornament unified by style, quality of line, and tone of printing.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1696 Jaillot Large Antique Map Norway Sweden Finland Denmark - Latvia & Estonia
- Title : La Scandinavie...Hubert Jaillot 1696
- Size: 37in x 24in (940mm x 610mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1696
- Ref #: 70329
Description:
This very large, beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Scandinavia, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Denmark along with Latvia & Estonia was engraved in 1696 - dated in cartouche - and was published by Alexis Hubert Jaillot in his monumental Atlas Nouveau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, pink, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 37in x 24in (940mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 35in x 23in (890mm x 585mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Several small repairs to margins, no loss
Plate area: - Horizontal fold, light soiling and creasing
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Before the fifteenth century the people of Southern Europe had little geographical knowledge of the Scandinavian World except from sketchy detail shown in the Catalan Atlas (1375) and on a number of \" portolani\" embracing Denmark and the southern tip of Norway. It was not until 1427 that a manuscript map prepared about that time by Claudius Clavus (b.1388) a Dane who spent some time in Rome, made available to scholars a tolerable outline of the northern countries and Greenland. That was to remain the best map available for the rest of the century and it was used as the basis for maps of Scandinavia in early printed editions of Ptolemy. Others by Nicolaus Cusanus (1491) and Ehrhard Etzlaub (c. 1492) followed but, needless to say, these are extremely rare; even the later maps by Olaus Magnus and Marcus Jordan, where they have survived at all , are known only by a very few examples. In fact, apart from the rare appearance of an early Ptolemy map, the oldest of Scandinavia which a collector is likely to find are those of Munster\'s Cosmograhy first published in 1544. In the following centuries the few maps and charts complied in Scandinavia were usually published in Amsterdam, Antwerp, Paris or Nuremberg, the most important maps often being incorporated in the major Dutch, French & German Atlases. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1639 Henricus Hondius Original Antique Map of the German State of Thuringia
- Title : Thuringia Lantgraviatus
- Date : 1639
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
- Ref #: 23434
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original antique map of the German State of Thuringia or Thüringen in central Germany was published by Henricus Hondius in the 1639 edition of Mercators Atlas.
The map centers on the city of Erfurt and alos includes major cities of Gotha, Weimar, Schwartzburg, Halle, Jena, Mulhausen and others
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19in (570mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in (520mm x 420mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold,
Verso: - Small repair to bottom left margin
Background:
Named after the Thuringii tribe who occupied it around AD 300, Thuringia came under Frankish domination in the 6th century.
Thuringia became a landgraviate in 1130 AD. After the extinction of the reigning Ludowingian line of counts and landgraves in 1247 and the War of the Thuringian Succession (1247–1264), the western half became independent under the name of \"Hesse\", never to become a part of Thuringia again. Most of the remaining Thuringia came under the rule of the Wettin dynasty of the nearby Margraviate of Meissen, the nucleus of the later Electorate and Kingdom of Saxony. With the division of the house of Wettin in 1485, Thuringia went to the senior Ernestine branch of the family, which subsequently subdivided the area into a number of smaller states, according to the Saxon tradition of dividing inheritance amongst male heirs. These were the \"Saxon duchies\", consisting, among others, of the states of Saxe-Weimar, Saxe-Eisenach, Saxe-Jena, Saxe-Meiningen, Saxe-Altenburg, Saxe-Coburg, and Saxe-Gotha; Thuringia became merely a geographical concept.
Thuringia generally accepted the Protestant Reformation, and Roman Catholicism was suppressed as early as 1520; priests who remained loyal to it were driven away and churches and monasteries were largely destroyed, especially during the German Peasants\' War of 1525. In Mühlhausen and elsewhere, the Anabaptists found many adherents. Thomas Müntzer, a leader of some non-peaceful groups of this sect, was active in this city. Within the borders of modern Thuringia the Roman Catholic faith only survived in the Eichsfeld district, which was ruled by the Archbishop of Mainz, and to a small degree in Erfurt and its immediate vicinity.
1632 Henricus David Large Antique Portrait of Cartographer Giovanni A Magini
- Title : Io. Antonius Maginus Pat. Mathemat. In Bonon. Gymn. Profess
- Date : 1632
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 80766
- Size: 17 1/2in x 11in (445mm x 280mm)
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique portrait of the Italian Cartographer Giovanni Antonio Magini was engraved by Henricus David in 1632 - date is engraved below portrait.
Giovanni Antonio Magini (1555-1617) was an Italian mathematician, cartographer and Professor of Astronomy in Bologna. He is responsible for publishing an edition ofPtolemy's Geographia in 1596 that contained 27 maps of the ancient world drawn from the text of Claude Ptolemy, along with 27 contemporary or modern maps. His maps were used by Blaeu in 1640. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Fresh
Paper size: - 17 1/2in x 11in (445mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 12n x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light dis-colouration in top margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1662 Joan Blaeu Complete Set of 9 Antique Maps of North America from Atlas Major, 1st Edition
- Titles:
1. Extrema Americae....Terra Nova Francia;
2. Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova;
3. Nova Virginiae Tabula;
4. Virginiae partis australis, et Floridae;
5. Nova Hispania;
6. Yucatan...Guatimala;
7. Insulae Americanae;
8. Canibales Insulae;
9. Mappa Aestivarum Insularum Alias Barmudas - Sizes: 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)ea
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date: 1662
- Ref #: BlaeuNA 1662
Description:
This is a unique opportunity to acquire a complete set of 9 maps of North America published by Joan Blaeus in the monumental & rare 1st 1662 Latin edition of Atlas Major. The maps cover the geographical detail of Canada, North America, Mexico, The Caribbean & Central America. Please see the background section below for details of each map. All maps have wide original margins & colour on strong sturdy paper.
Joan Blaeus 11 volumes of Atlas Major, is considered by many to be the greatest atlas set ever published. It excels in comprehensiveness, engraving, color, and overall production. The first edition was published in Latin in 1662 and was subsequently published in French, Dutch, German, and Spanish over the next 10 years.
On the 23rd of February 1672, a fire broke out in central Amsterdam, that ended the reign of one of the greatest & most prolific publishers of printed maps and atlases in publishing history. The Blaeu family had reached its zenith 10 years previously, with the publication of its greatest achievement, the Atlas Major or Great Atlas, consisting of 11 volumes, with geographical detail reflecting many of the achievements of the Golden Age of the United Netherlands. Blaeus Atlas Major were the most expensive books printed in the 17th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - Various, pls see below
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm) min
Imperfections:
Margins: - Pls see below
Plate area: - Pls see below
Verso: - Pls see below
Background:
1. Extrema Americae ( Eastern Canada) - Rare only published in Atlas Major. Derived mainly from the Samuel de Champlain Nouvelle France map of 1632, this map reflects the growing financial importance of the waters of New France to Europe.
Plate: 22 1/2in x 17 3/4in.
Condition: Age toning, text show-through & browning to image.
2. Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova (New England) - NE America, centering on New York and Manhattan from Virginia to the St Lawrence River. This map is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript figurative map of Adriaen Block from 1614. Indeed it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way.
Plate: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in
Condition: Age toning, text show-through & browning to image.
3. Nova Virginiae Tabula (John Smiths Virginia & Chesapeake Bay) This map was printed from a plate engraved by Dirk Grijp from a previous plates by Henricus Hondius.
Plate: 19in x 15in
Condition: Light age toning
4. Virginiae partis australis, et Floridae Virginia, the Carolinas & Georgia.
Plate: 20in x 15in
Condition: Light age toning
5. Nova Hispania et Nova Galicia Western Mexico
Plate: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
6. Yucatan...Guatimala (Yucatan, Central America) Rare only published in Atlas Major.
Plate: 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
7. Insulae Americana (GOM, Caribbean)
Plate: 20 1/2in x 15in
Condition: Light age toning
8. Canibales Insulae (Lesser Antilles Islands) Rare, printed only in Atlas Major
Plate: 21in x 16 1/2in
Condition: Age toning
9. Mappa Aestivarum Insularum Alias Barmudas Dictarum Bermuda. Like all 17th century maps of Bermuda this map is based ultimately on the survey made by John Norwood, of the Bermuda Company, in 1618 in the form as published by the English map-maker John Speed in 1627.
Plate: 21in x 16in
Condition: Light age toning
1787 Samuel Dunn Large Antique Double Hemisphere World Map w/ Scientific anno.
- Title : A General Map of the World, or Terraqueous Globe with all the New Discoveries and Marginal Delineations, Containing the Most Interesting Particulars in the Solar, Starry and Mundane System...1787
- Date : 1787
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 80778
- Size: 49 1/2in x 41in (1.25m x 1.020mm)
Description:
This monumental very large original copper-plate engraved antique double hemisphere world map, with scientific annotations, by Thomas Dunn, with cartographic material based on information by J. B. B. D Anville, was engraved by Thomas Kitchin in 1787 - dated - and published by Robert Sayer as plate nos. 1-2 in the 1790 edition of General Atlas.
Samuel Dunns General Map of the World, or Terraqueous Globe, is a general world map with all the new discoveries and marginal delineations, containing interesting information relating to the solar, starry and mundane systems, star charts, a map of the Moon, the Solar System, and numerous other features. Dunns large map has an insurmountable amount of general & scientific detail.
This map is one of the most popular and recognizable large maps of the world from the period, having been the map of choice for a number of atlases published by Jefferys, Sayer and Bennett & Laurie and Whittle over a 30 year period. The map was revised several times..
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 49 1/2in x 41in (1.25m x 1.020mm)
Plate size: - 49 1/2in x 41in (1.25m x 1.020mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin cropped close to plate-mark
Plate area: - Bottom left Analemma globe restored and backed
Verso: - Some folds strengthened with archival tape
Background:
The double hemisphere globes are surrounded on all sides by detailed scientific calculations and descriptions as well as Northern and Southern Hemisphere star charts, a map of the Moon, a latitude and longitude analemma chart, a map of the Solar System, a mercator projection of the world, an analemma projection, a seasonal chart, a universal scale chart, and numerous smaller diagrams depicting planets and mathematical systems. All text is in English. The survey of this map starts in North America, much of which was, even in 1794, largely unknown.
North America, this map follows shortly after the explorations of captain James Cook in the Arctic and Pacific Northwest, so the general outline of the continent is close to complete. However, when this map was made, few inland expeditions had extended westward in America, beyond the Mississippi. This map notes two separate speculative courses for the apocryphal river of the west, a northern route extending from lake Winnipeg and a southern route passing south of Winnipeg through Pike\'s lake. The River of the West was hopeful dream of French and English explorers who were searching for a water passage through North America to the Pacific. In concept, should such a route be found, it would have become an important trade artery allowing the British and French, whose colonies dominated the eastern parts of North America, to compete with the Spanish for control of the lucrative Asia-Pacific trade. These earlier speculative cartographers didn\'t realize that the bulk of the Rocky Mountains stood between them and their plans. The kingdom of Quivira, which is one of the lands associated with Spanish legends of the Seven Cities of Gold is located slightly south of the western rivers. In this area we can also find Drake\'s Harbor or Port de la Bodega and Albion. Drake\'s Harbor is where Sir Francis Drake supposedly landed during his circumnavigation of the globe in 1580. Drake wintered in this harbor and used the abundant resources of the region to repair his ships. He also claimed the lands for England dubbing them New Albion. Although the true location of Drake\'s port is unknown, most place it much further to the north. By situating it and consequently New Albion further to the south, Dunn is advocating a British rather than Spanish claim to this region. On the Eastern coast of North America we find a fledgling United States extending from Georgia to Maine. Dunn names Boston, New York, Charleston, Long Island, and Philadelphia, as well as the important smaller towns of Jamestown, Williamsburg and Edonton.
South America, exhibits a typically accurate coastline and limited knowledge of the interior beyond Peru and the populated coastlands. A few islands are noted off the coast, including the Galapagos, which are referred to as the Inchanted Islands. The Amazon is vague with many of its tributaries drawn in speculatively. Dunn and d\'Anville have done away with the popular representation of Manoa or El Dorado in Guyana, but a vestigial Lake Parima is evident. Further south, the Laguna de los Xarayes, another apocryphal destination, is drawn at the northernmost terminus of the Paraguay River. The Xaraiés, meaning Masters of the River were an indigenous people occupying what are today parts of Brazil\'s Matte Grosso and the Pantanal. When Spanish and Portuguese explorers first navigated up the Paraguay River, as always in search of El Dorado, they encountered the vast Pantanal flood plain at the height of its annual inundation. Understandably misinterpreting the flood plain as a gigantic inland sea, they named it after the local inhabitants, the Xaraies. The Laguna de los Xarayes almost immediately began to appear on early maps of the region and, at the same time, almost immediately took on a legendary aspect as the gateway to El Dorado.
Across the Atlantic in Africa we find the situation in South America mirrored - that is, the coasts are well defined by the interior is vague. The Nile River follows the Ptolemaic course with a presumed source in two lakes at the base of the \'Mountains of the Moon.\' Further east, the Niger River is well mapped but gets lost as it flows inland. There is no suggestion of its outlet into the Gulf of Guinea, which at the time had not been considered. In the southern part of Africa we fine an elongated lake without a northern border labeled Massi. This is probably an embryonic form of Lake Malawi. Also in this area, we encounter the Kingdom of Monomatapa and the mountain range called the \'Backbone of the World.\' This region of Africa held a particular fascination for Europeans since the Portuguese first encountered it in the 16th century. At the time, this area was a vast empire called Mutapa or Monomotapa that maintained an active trading network with faraway partners in India and Asia. As the Portuguese presence in the area increased in the 17th century, the Europeans began to note that Monomatapa was particularly rich in gold. They were also impressed with the numerous well crafted stone structures, including the mysterious nearby ruins of Great Zimbabwe. This combination led many Europeans to believe that King Solomon\'s Mines, a sort of African El Dorado, must be hidden in this region. Monomotapa did in fact have rich gold mines in the 16th and 17th centuries, but most of these had been exhausted by the 1700s.
Asia is exceptionally well mapped reflecting the most recent information available in Europe - especially regarding the explorations of Vitus Bering and Tschirikow in the Siberian Arctic. Notes Macau, Formosa (Tay-oan), numerous silk route cities, the straits of Sin Capura (Singapore), Beijing (Peking), Edo (Tokyo) and Bombay.
Australia appears in full as New Holland or Terra Australis. Names numerous points along the coast with associated notes regarding the activities of various explorers. Van Diemen\'s Land or Tasmania is curiously attached to the mainland - an error that many earlier maps had long ago corrected. Further east New Zealand is exceptionally well formed. Most of the region has been thoroughly mapped by Cook, though several of the cartographic errors perpetuated by Quiros are present. There is little trace of either Antarctica or the Great Southern continent, though Bouvet\'s Island does appear as \'Sandwich Land.\'
Throughout the map we can also find the routes of numerous important explorers including Middleton, Anson, Bougainville, Cook, the Resolution, the Spanish Galleon Carlos, Bouvet, and others. Often their landings and important discoveries are also noted.
Dunn, Samuel d. 1794
Samuel Dunn was a British mathematician and amateur astronomer.
He was a native of Crediton, Devonshire. His father died at Crediton in 1744. He wrote in his will:.....
In 1743, when the first great fire broke out and destroyed the west town, I had been some time keeping a school and teaching writing, accounts, navigation, and other mathematical science, although not above twenty years of age; then I moved to the schoolhouse at the foot of Bowdown [now Bowden] Hill, and taught there till Christmas 1751, when I came to London.....
The schoolhouse was the place where the English schoo\\\" was kept previously to its union with the blue school in 1821. In London, Dunn taught in different schools, and gave private lessons.
In 1757, he came before the public as the inventor of the universal planispheres, or terrestrial and celestial globes in plano, four large stereographical maps, with a transparent index placed over each map.....
whereby the circles of the sphere are instantaneously projected on the plane of the meridian for any latitude, and the problems of geography, astronomy, and navigation wrought with the same certainty and ease as by the globes themselves, without the help of scale and compasses, pen and ink.....
He published an account of their Description and Use, 2nd edition, octavo, London, 1759. From the preface, it appears that in 1758 Dunn had become master of an academy for boarding and qualifying young gentlemen in arts, sciences, and languages, and for business, at Chelsea. It was at Ormond House, where there was a good observatory.
On 1 January 1760, he made the observation of a remarkable comet; other discoveries he communicated to the Royal Society. Towards the close of 1763, he gave up the school at Chelsea, and fixing himself at Brompton Park, near Kensington, resumed once more his private teaching. In 1764 he made a short tour through France. In 1774, when residing at 6 Clements Inn, near Temple Bar, he published his excellent New Atlas of the Mundane System, or of Geography and Cosmography, describing the Heavens and the Earth. … The whole elegantly engraved on sixty-two copper plates. With a general introduction, folio, London. About this time his reputation led to his being appointed mathematical examiner of the candidates for the East India Company\\\'s service.
Under the companys auspices he was enabled to publish in a handsome form several of his more important works. Such were:
1. A New and General Introduction to Practical Astronomy, with its application to Geography … Topography, octavo, London, 1774.
2. The Navigators Guide to the Oriental or Indian Seas, or the Description and Use of a Variation Chart of the Magnetic Needle, designed for shewing the Longitude throughout the principal parts of the Atlantic, Ethiopic, and Southern Oceans, octavo, London (1775).
3. A New Epitome of Practical Navigation, or Guide to the Indian Seas, containing the Elements of Mathematical Learning, used … in the Theory and Practice of Nautical affairs; the Theory of Navigation. ..; the Method of Correcting and Determining the Longitude at Sea …; the Practice of Navigation in all kinds of Sailing (with copper plates), octavo, London, 1777, and
4. The Theory and Practice of the Longitude at Sea … with copper plates, octavo, London, 1778; second edition, enlarged, quarto, London, 1786.
He also methodised, corrected, and further enlarged a goodly quarto, entitled A New Directory for the East Indies … being a work originally begun upon the plan of the Oriental Neptune, augmented and improved by Mr. Willm. Herbert, Mr. Willm. Nichelson, and others, London, 1780, which reached a fifth edition the same year. Dunn was living at 8 Maiden Lane, Covent Garden, in July 1777, but by September 1780 had taken up his abode at 1 Boar\\\'s Head Court, Fleet Street, where he continued for the remainder of his life.
He died in January 1794. His will, dated 5 January 1794, was proved at London, on the 20 January by his kinsman, William Dunn, officer of excise of London (registered in P.C.C., 16, Holman). Therein he describes himself as teacher of the mathematics and master for the longitude at sea, and desires to be buried in the parish church belonging to the place where I shall happen to inhabit a little time before my decease. He names seven relations to whom he left £20 each; but to his wife, Elizabeth Dunn, who hath withdrawn herself from me near thirty years, the sum only of ten pounds. No children are mentioned.
He also requested the corporation of Crediton to provide always and have a master of the school at the foot of Bowden Hill residing therein, of the church of England, but not in holy orders, an able teacher of writing, navigation, the lunar method of taking the longitude at sea, planning, drawing, and surveying, with all mathematical science. For this purpose he left £30 a year. Six boys were to be taught, with a preference to his own descendants. The stock thus bequeathed produced in 1823 dividends amounting to £25 4/- per annum, the school being known by the name of Dunn\\\'s School.
Dunn contributed nine papers to the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, of which body, however, he was not a fellow. On the title-page of his Atlas he appears as a member of the Philosophical Society at Philadelphia, America. A few of his letters to Thomas Birch are preserved, and one to Emanuel Mendes da Costa
1755 JB D Anville Large Original Antique Map of North America, Great Lakes, Indian Wars
- Title : Canada Louisiane et Terres Anglois Par Le Sr. D Anville...MDCCLV
- Ref #: 61140
- Size: 52in x 38in (1.32m x 960mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This magnificent, scarce, very large (52in x 38in) & highly detail map of North America was engraved in 1755 - dated in the title cartouche - by George De La Haye and was published by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D Anville in his large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
Geopolitically this map is extremely significant drawn as war between the Global Powers of the day, France, England & Spain, was breaking, known in Europe as the Seven Year War known in North America as the French & Indian war. (Please see below for more detail)
This map rivals John Mitchells "A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America published in 1755" - considered to be one of the most significant maps of North America published in the 18th & 19th centuries (a 1st edition of Mitchells map is currently for sale for $165,000).
I have included an image of the Mitchell map for comparison. The D Anville map is considered by many to be cartographically superior to the Mitchell map, at a fraction of the price.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 52in x 38in (1.32m x 960mm)
Plate size: - 45in x 35in (1.12m x 890mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light ceasing along folds
Verso: - Very small worm holes
Background: This extraordinary map of the eastern half of North America extends from Newfoundland, Canada to St. Augustine, Florida, stretching westward beyond the Mississippi as far as modern day Texas. The map includes both the original colonial colonies along the Atlantic seaboard from Maine to Georgia and the French claims in Louisiana (the Mississippi Valley) and modern day Canada. Florida is acknowledged as a Spanish enclave. Elevation is rendered in profile with fortifications, towns, and American Indian villages identified. A large inset map centres on the course of the St. Lawrence River from the Isle Aux Coudres to Lake Ontario.
The is a very significant map, drawn from a definitive French perspective, defining the territorial alignments and claims within North America shortly following the outbreak of the French and Indian War, considered to be a New World reflection of the European Seven Years War. It is however notable that it began before the larger hostilities in Europe and most of the major battles involved primarily parties only loosely aligned with the French or English - most specifically American Indians and lawless frontiersman, who had their own political agenda.
The war began with French incursions into western Pennsylvania and other territories claimed simultaneously by the French, English and American Indian forces. Just prior to the war, the French, in the interest of broadening their hold on the lucrative fur trade, established a series of forts, all of which are here noted, along the length of the Mississippi and further east, including Fort Duquesne (here Fort de Quene, Pittsburgh), Fort de la Presquisle, and for Le Beouf (here, Fort de la Riv Jaus Beufs).
The map also recognizes British claims, only inland as far as the Appalachian Mountains, beyond which place names take on a noticeably French character. These last three forts occupied particularly contested territory under the control of the powerful British allied Iroquois League. The most contested of these was Fort Duquesne (modern day Pittsburgh) in direct opposition to another fort then being constructed by the Ohio Company, a trading and land speculation firm established by prominent Virginia colonials, including George Washington. The Virginian colonial governor responded to Duquesne by sending then Lieutenant George Washington and a band of Virginia militiamen to harass the French. The resulting Jumonville Affair, in which Washington oversaw an attack on a French Canadian diplomatic forces led by Joseph Coulon de Villiers de Jumonville, to warn the Ohio Company fort builders away from French claimed territory. The slaying of Jumonville and several other French diplomats prompted a response from French forces at Fort Duquesne, leading to Washingtons retreat and construction of Fort Necessity, really little more than a palisaded shack, marked here just south of Fort Duquesne. These events, all of which occurred in May of 1754, were said to have increased hostilities in Europe and led to the start of the Seven Year War in 1755.
Beyond the political agenda of this map, is the map itself, being one of the finest and most heavily detailed maps of North America published in the mid 18th century. Ranking alongside the large 1755 Mitchell map in detail but judged by many as cartographically superior. Drawing on both French and British cartographical detail, D Anville identifies countless American Indian tribes, many of which, like the Sioux and Missouri, the British had only vague knowledge. Moreover, he also includes detail such as swamps, rapids, fords, abandoned villages, and even the ancient remnants of mound builder culture in the Ohio Valley. D Anville notably does not include Mitchells fictional Lake Superior islands.
This map was originally published to accompany the pamphlet entitledMemoire sur la carte intitulee: Canada, Louisiane, & Terres angloises and was also published in four parts for D Anvilles Atlas General.
These large maps are hard to find in such good condition and make fantastic historical reference tools due to the size and high level of detail as with all D Anvilles work. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1730 Georg Seutter Antique Map of New England & New York City - Rare 2nd State
- Title : Recens edita totius Novi Belgii, in America Septentrionali siti, delineatio cura et sumtibus Matthaei Seutteri, Sac. Caes Maj. Geographf. August. Vind
- Size: 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1730
- Ref #: 43001
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the NE region of colonial North America, with the famous Restitutio inset birds-eye view of 17th century New York city, was engraved & published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730.
This is the rare second state, identified by the omission of Chalcographi Augustani from the title and the blank shaded are directly below the title (text was added to the shaded area in the 3rd to 6th states) The cartouche and city view are uncoloured as was intended by Seutter along with the beautiful original map colouring.
This map is in exceptional condition with beautiful original colour, with heavy engraving (denoting an early pressing) on clean heavy sturdy paper. The top and left borders have been professionally extended, with no impact on the image.
There are, at the time of listing, nine of these maps for sale online, of states 2 to 6. Of the 9 only 2 are of the rare 2nd state. The average asking price of the nine maps is $4897US.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - T & L margins extended
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The map is based upon the Jansson-Visscher New England series of maps, first published by Visscher in 1651. Seutter replaces the original Restitutio view of New York City with a new view of New York entitled Neu Jorck sive Neu Amsterdam, with a key to the view below in Latin. Above the view is an elaborate scene depicting natives, slaves & allegorical deities presenting tributes to the English monarch, George II. The course of the Delaware and Hudson are separated, unlike early editions of the map.
This is the first map in the series to show distinct drawn boundaries between Massachusetts, New England, New York, New Jersey and Pennsylvania, as earlier examples had previously left the delineation of the boundaries to the colorist. Philadelphia is now shown as a set of houses in relief, rather than a ground plan. The map is richly embellished with many animals and other decorations and is without doubt, one of the most decorative 18th century maps of the region.
1725 John Senex Large Twin Hemisphere World Antique Map Isaac Newton & Ed Halley
- Title : A Map of The World Corrected from the Observations communicated to the Royal Societys of London and Paris....Sold by Jogn Senex at the Globe....1725
- Ref #: 27015
- Size: 43 1/2in x 24 1/4in (1.105m x 615mm)
- Date : 1725
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This very large original hand coloured, magnificent and extremely scarce copper-plate engraved antique Twin Hemisphere World Map drawn & engraved by John Senex in 1725 - dated below the title - was published for John Senexs Elephant Folio Atlas
This is the second edition of the large World Map. There were three states in 1711, 1725 and 1750.
Due to their size, these large scale maps are scarce. As they are hard to store and protect damage and loss over time was frequent. It is estimated that there are less than a 10% survival rate for these larger maps. To help improve its longevity, this map has been professionally mounted on archival board.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 43 1/2in x 24 1/4in (1.105m x 615mm)
Plate size: - 43in x 23 1/2in (1.090m x 595mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom right & top left corner professionally restored. Cropped to plate mark
Plate area: - Light creasing, folds as issued
Verso: - Mounted to archival board
Background:
This map illustrates the change in the approach to cartography, aiming to highlight the importance of scientific endeavours and discoveries. In the case of this early map John Senex has included theories of tides, sea currents and winds by two of the foremost scientists of the day Sir Isaac Newton and Dr Edmund Halley. This text, surrounding the map is some of the earliest theories of the modern age, to explain the affect of tides, sea currents and winds on the oceans and the world in general.
It is noted by Whitfield... that this map represents the complete ascendancy of scientific taste in the eighteenth century twin hemisphere world map; the maps borders are filled with neither the classical motifs or the scientific motifs, but with scientific texts, long and detailed passages from two of the foremost scientists of the day (Isaac Newton and Edmund Halley) on the Theory of Tides from Newton and An Attempt to assign the Physical cause of the Trade Winds and Monsoons by Halley. This map epitomises the thirst for scientific curiosity that encompassed the world of the 18th century.
Senex has been geographically restrained with many unknowns, such as the debate on California as an Island - shown here as a peninsular. The search for a northern passage to Asia still abounds as does the lack of definitive knowledge of the Pacific NW. But he gives no guesses or half truths only sticking to what is known at the time. Senex remarks in text above California...These parts as yet being undiscovered, us not certain yet whether America joins to the North Eastern Part of Tartary, where hence it is most probable that it was peopled being supposed to be separated if at all but by narrow straits.
He also remarks in text north of Hudson's Bay keeping open the possibility of a NW passage...This way a northwest passage to China has several times been attempted without success.
In the Caribbean Senex notes..The Caribbean Isles in or near the month of August are dreadfully afflicted with furious storms called Hurricanes much as it were particular to them.
He has also been objective in his depiction of the known coastlines of Australia and New Zealand and has followed popular thinking on the connection of New Guinea to Australia. He engraves dire notes regarding New Holland..The soil of Hollandia Nova is barren and desert no fresh but some salt water rivers, no four footed beasts except an Amphibious one as big as a dog with Sea Cows and innumerable quantities of Rats as great as cats; also black swans and Parrots; the natives are black and go naked: the coast is low, foul and rocky, the inland parts high. Here abound oysters, lobsters and crabs and vast numbers of troublesome flies. (Mr. Witsen Phil Trans. No 245)
This is an incredibly important and rare map with many text passages. (Ref: Tooley; Whitfield; M&B)
Sir Isaac Newton PRS ( 1642 – 1727) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a natural philosopher) widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists of all time and among the most influential scientists. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus.
Dr. Edmund Halley FRS ( 1656 - 1742) was an English astronomer, geophysicist, mathematician, meteorologist, and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, Halley catalogued the southern celestial hemisphere and recorded a transit of Mercury across the Sun. He realised that a similar transit of Venus could be used to determine the distances between Earth, Venus, and the Sun. Upon his return to England, he was made a fellow of the Royal Society, and with the help of King Charles II, was granted a masters degree from Oxford.
Halley encouraged and helped fund the publication of Isaac Newtons influential Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (1687). From observations Halley made in September 1682, he used Newtons laws of motion to compute the periodicity of Halleys Comet in his 1705 Synopsis of the Astronomy of Comets. It was named after him upon its predicted return in 1758, which he did not live to see.
Beginning in 1698, Halley made sailing expeditions and made observations on the conditions of terrestrial magnetism. In 1718, he discovered the proper motion of the fixed stars.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1646 Jan Jansson Antique Heptarchy Map of Great Britain & Ireland - Christianity in England
- Title : Britannia prout divisa suit temporibus Anglo-Saxonum præsertim durante illorum Heptarchia
- Ref #: 82076
- Size: 23 1/2in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1646
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Britain during the reign of the Saxon Kings between 500 - 700AD - know as the Heptarchy Era - was published by Jan Jansson in his 1646 edition of Atlas Nouvs, blank verso.
Of the three iterations of this map by John Speed, Joan Blaeu and Jansson, this is considered by many to be the most accomplished. It is distinguishable from the others with the inclusion of compass roses & rhumb lines, sailing ships and the Irish escutcheon.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 16 3/4in (520mm x 425mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins, old ink price top right
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Splendid map of Anglo-Saxon Britain flanked by intricately rendered portraits of the kings through the 5th through 7th centuries. The monarchs to the left are those of the pre-Christian era, while those on the right are depicted receiving Christianity or being martyred for its sake.
This is often called the Heptarchy Map, as it presents England during the time following the Anglo Saxon conquest of southern England, approximately 500 to 850 A.D. known as the Heptarchy Era. (The word itself refers to the seven kingdoms that would eventually combine to form the Kingdom of England in the 10th century.)
To the left are the seven full length figures of the first aspiring Saxon Kings with their escutcheons, armies or townships;
1. Hengist - Kent 456AD
2. Ella - South Saxon 478AD
3. Cherdin - West Saxon 519AD
4. Erkenwin - East Saxon 527AD
5. Ida - Northumberland 582AD
6. Uffa - East Angle 546AD
7. Creda - Mercian 575AD
On the right there are scenes showing the conversion of Saxon sovereigns to Christianity:
1. Ethelbert - Kent 595AD receiving religious instruction from St Augustine
2. Sebert - East saxon604AD re-consecrating the temples of Diana and Apollo that later become St Pauls London and St Peters Westminster
3. Epenwald - East Angle 624AD embracing baptism by the armed exhortation of King Edwin of Northumberland
4. Edwin - Northumberland 627AD stirred by a vision to receive the faith
5. Kengils West Saxon 635AD converted by the preaching of St Berinus
6. Peada Mercia 650 receiving the Faith by the persuasion of King Osway of Northumberland but also being murdered by his own mothers, some say his wifes, procurement.
7. Ethenwolfe South Saxon 662AD being baptised at Oxford by St Berinus (Ref Shirley, Tooley, M&B)
1595 Gerard Mercator Original True Rare 1st Edition Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Africa Ex Magna orbis terra descriptione Gerardi Mercatoris desumpta. Studio & industria GM Iunioris
- Size: 21in x 16 1/4in (535mm x 415mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1595
- Ref #: 27016
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original, true rare 1st edition* antique map, of Africa by Gerard Mercator was published in the 1595 Latin edition of Mercators Atlas, Atlas Sive Cosmographicae Meditationes Illustrissimi Ducis.
* True 1st edition identified on the verso of the map, according to Koemans Atlantes Neerlandica, illustrating the letter "C" under the title "Africa".
As indicated in the title Cartouche, this map this is a reduction by Gerard Mercator Junior of Africa, compiled from Gerard Mercators world map of 1569. This rendition was drawn by Mercators grandson (also named Gerard) in 1595.
The map is typical of 16th century cartography of Africa containing some fantastical detail especially in regards to the interior. The depiction of the Nile is based on Ptolemys geography with some complex modifications from various sources, including Abyssinian monks. The source of the Nile is shown as a series of lakes located in the Lune Montes just north of the Tropic of Capricorn. Another branch of the Nile flows from the west, with this system rambling through what is the Sahara Desert. Mercator adds a lake named Sac. Haf lac, from the 1507 Waldseemuller world map. This lake feeds both the Zambere River and the Nile. In Abissini, the legendary Christian King Prester John sits on his throne. The boldly engraved oceans, beautiful calligraphy, and strapwork cartouche (surmounted by two satyrs) make this a decorative masterpiece.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 16 1/4in (535mm x 415mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 15in (470mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Age toning, small rejoin in bottom right margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Age toning, left & top margin re-enforced
Background:
Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster\'s Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d\'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century.
1880s Alphonse & Jules Lebegue 21in x 12in Diameter Antique Desk Globe
- Title : Globe Terrestre J Lebegue & Cie Editeurs 36 Rue Nenve, 36 Bruxelles
- Size: 12in (305mm) Diameter Globe/Standing 21in (530mm)
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
- Date : 1880s
- Ref #: 30072
Description:
This fantastic original antique 12in (305mm) Diameter Desk Globe, standing 21in (530mm), was made by the French Publishing Company of Alphonse & Jules Lebegue, Belgium & Paris in the 1880s.
Globes that have survived are rare, as most globes constructed in history have either been damaged or literally thrown away. The globe itself has sustained some damage but is overall stable and sturdy. The wooden stand along with the globe brass ring are in excellent condition. The specific damage to the globe is:
- Dent and damage between Indonesia and Japan
- Dent and damage off the coast of western South America
- Small dent in mid Pacific
- Light abrasion at north Pole
- Overall browning.
But even with the above this is a wonderful piece of cartographic history.
Total Dimensions;
Globe Diameter: 12in (305mm
Standing Complete: 21in (530mm)
Width of Stand: 19in (480mm)
Weight: 5.5kg
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in (305mm) Diameter Globe/Standing 21in (530mm)
Plate size: - 12in (305mm) Diameter Globe/Standing 21in (530mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see description above
Plate area: - Please see description above
Verso: - Please see description above
Background:
A globe is a spherical model of Earth, of some other celestial body, or of the celestial sphere. Globes serve similar purposes to maps, but unlike maps, do not distort the surface that they portray except to scale it down. A globe of Earth is called a terrestrial globe. A globe of the celestial sphere is called a celestial globe.
A globe shows details of its subject. A terrestrial globe shows land masses and water bodies. It might show nations and prominent cities and the network of latitude and longitude lines. Some have raised relief to show mountains. A celestial globe shows stars, and may also show positions of other prominent astronomical objects. Typically it will also divide the celestial sphere up into constellations.
The word globe comes from the Latin word globus, meaning sphere. Globes have a long history. The first known mention of a globe is from Strabo, describing the Globe of Crates from about 150 BC. The oldest surviving terrestrial globe is the Erdapfel, wrought by Martin Behaim in 1492. The oldest surviving celestial globe sits atop the Farnese Atlas, carved in the 2nd century Roman Empire.
The sphericity of the Earth was established by Greek astronomy in the 3rd century BC, and the earliest terrestrial globe appeared from that period. The earliest known example is the one constructed by Crates of Mallus in Cilicia (now Çukurova in modern-day Turkey), in the mid-2nd century BC.
No terrestrial globes from Antiquity or the Middle Ages have survived. An example of a surviving celestial globe is part of a Hellenistic sculpture, called the Farnese Atlas, surviving in a 2nd-century AD Roman copy in the Naples Archaeological Museum, Italy.
Early terrestrial globes depicting the entirety of the Old World were constructed in the Islamic world. According to David Woodward, one such example was the terrestrial globe introduced to Beijing by the Persian astronomer, Jamal ad-Din, in 1267.
The earliest extant terrestrial globe was made in 1492 by Martin Behaim (1459–1537) with help from the painter Georg Glockendon. Behaim was a German mapmaker, navigator, and merchant. Working in Nuremberg, Germany, he called his globe the Nürnberg Terrestrial Globe. It is now known as the Erdapfel. Before constructing the globe, Behaim had traveled extensively. He sojourned in Lisbon from 1480, developing commercial interests and mingling with explorers and scientists. In 1485–1486, he sailed with Portuguese explorer Diogo Cão to the coast of West Africa. He began to construct his globe after his return to Nürnberg in 1490.
Another early globe, the Hunt–Lenox Globe, ca. 1510, is thought to be the source of the phrase Hic Sunt Dracones, or Here be dragons. A similar grapefruit-sized globe made from two halves of an ostrich egg was found in 2012 and is believed to date from 1504. It may be the oldest globe to show the New World. Stefaan Missine, who analyzed the globe for the Washington Map Society journal Portolan, said it was part of an important European collection for decades. After a year of research in which he consulted many experts, Missine concluded the Hunt–Lenox Globe was a copper cast of the egg globe.
A facsimile globe showing America was made by Martin Waldseemueller in 1507. Another remarkably modern-looking terrestrial globe of the Earth was constructed by Taqi al-Din at the Constantinople Observatory of Taqi ad-Din during the 1570s.
The worlds first seamless celestial globe was built by Mughal scientists under the patronage of Jahangir.
In the 1800s small pocket globes (less than 3 inches) were status symbols for gentlemen and educational toys for rich children.
Traditionally, globes were manufactured by gluing a printed paper map onto a sphere, often made from wood.
The most common type has long, thin gores (strips) of paper that narrow to a point at the poles, small disks cover over the inevitable irregularities at these points. The more gores there are, the less stretching and crumpling is required to make the paper map fit the sphere. This method of globe making was illustrated in 1802 in an engraving in The English Encyclopedia by George Kearsley .
Modern globes are often made from thermoplastic. Flat, plastic disks are printed with a distorted map of one of the Earths Hemispheres. This is placed in a machine which molds the disk into a hemispherical shape. The hemisphere is united with its opposite counterpart to form a complete globe.
Usually a globe is mounted so that its spin axis is 23.5° from vertical, which is the angle the Earths spin axis deviates from perpendicular to the plane of its orbit. This mounting makes it easy to visualize how seasons change.
Lebegue, Alphonse Nicolas 1814 - 1885
Jules Lebegue (son)
Lebègue was a publisher of maps, plans as well as terrestrial and celestial globes, in Paris & Brussels. He was born in Paris in 1814 & died on December 12th 1885 in Brussels. He was the son of the Parisian printer and bookseller Jean Lebègue, with business on the Rue des Noyers, Paris.
In 1854 he established a printing press and publishing house in Brussels, Belgium and becoming A. N. Lebegue and C (ie), becoming one of the best-known publishing houses in the Belgian capital. His business launched a weekly newspaper in 1858, with an Advertising Office that became one of the most popular organs of the local Liberal Partywhile specialising in the works of Pierre Joseph Proudhon . At this time, Lebègue expanded his publishing business into maps, plans and globes. Beside his publishing business, Lebègue wrote several books, often novels of a historical nature and during the second empire, became close to the French publisher Hetzel
Alphonse was the uncle to both Alphonse-Nicolas Lebègue (1856-1938) the French paleographer and Ernest Lebègue (1862-1943) the French historian. He died on December 12, 1885 in Brussels, leaving his business to his son Jules Lebègue.
1815 Swoboda & Hartl Large Old, Antique Map of Australia, Ulimaroa New Zealand - Rare
- Title : Generalcharte von Australien nach dem entwurfe des H.Joseph Marx Freiherrn v. Liechtenstern
- Date : 1815
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 16258
- Size: 27 1/4in x 22in (695mm x 560mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original & scarce antique map of New Holland also named Ulimaroa, New Zealand and the South Pacific by Franz Swoboda and Martin Hartl was published in Vienna in 1815 - dated.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27 1/4in x 22in (695mm x 560mm)
Paper size: - 27in x 20 3/4in (685mm x 525mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (7mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Vertical crease right image
Verso: - None
This map is typical of the affect of Cooks discoveries on European cartography. Australia regularly became a focus on regional maps. The name "Ulimaroa" was often used, mainly by German & Austrian cartographers, at this time. It was term Cook learned from the New Zealand Maoris before discovering the east coast of Australia during his first voyage of discovery. When this map was printed there was a strong belief that the Australian continent was possibly divided by an internal sea strait, separating the east from the west coasts. It was explorers such as Flinders and Baudin who set out to find this elusive passage and if so the possible point at which a ship could enter.
Only a few years before in 1798 Flinders and Bass had proved that there was a strait dividing Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) from the rest of the continent so now the race was on to find the other passage. On Swoboda’s map a line has been drawn from the bottom of Carpentaria to the eastern part of present day Victoria. This line represented two things, the potential shape of the eastern landmass split by the sea and the extent to English territory in the newly settled colonies, only 17 years old. The Southern Coastline is not shown as even though Flinders had by 1803 mapped the entire region he was in 1805 still under house arrest on the islands of Mauritius by the French, he would not publish his discoveries until 1814. Therefore this map shows Australia at a pivotal point in its history when most of the continent was still open for settlement by other nations and the coastlines and mysteries were still to be confirmed. (Ref: Clancy; M&B; Tooley)
1723 William Dampier 2 Volumes of World Voyages to America Australia Asia - 20 x Maps & Plates
- Title : Nouveau Voyage Autour Du Monde...Ou l on decrite en particular l Isthme de l Amerique, plusieurs côtes et isles des Indes Occidentales...1723
- Size: 8vo
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1723
- Ref #: 93005
Description:
These two beautiful leather bound volumes of William Dampiers voyages to America, New Holland (Australia) and the East Indies, contains 5 titles with 20 maps & plates (some folding) and was published in Amsterdam by David Paul Marret in 1723 (dated)
These 2 volumes are the French translation of the voyages of the English explorer, ex-pirate and navigator, William Dampier, who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavigate the world three times between 1679 & 1711. He has also been described as Australia\'s first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the British Admiralty with his book, A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in western Australia, but was court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage, he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crew mate who may have inspired Daniel Defoe\'s Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Lord Nelson, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 8vo
Plate size: - 8vo
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see below for condition report
Plate area: - Please see below for condition report
Verso: - Please see below for condition report
Background:
The two volumes contain the following 5 titles with 20 maps & plates.
Volume 1.
1. Nouveau Voyage Autour Du Monde...Ou l\'on decrite en particular l\'Isthme de l\'Amerique, plusieurs côtes et isles des Indes Occidentales, les Isles du Cap Verd, le passage par la Terre del Fuego, les côtes meridionales du Chili, du Perou & du Mexique; l\'Isle de Guam, Mindanao, & des autres Philippines, les isles orientales qui sont prés de Cambodie; de la Chine; Formosa; Luçon, Celebes, &c., la Nouvelle Hollande, les Isles de Sumatra, de Nicobar & de Sainte Helene & le Cap de Bonne Esperance...Ou l\'on traite des differens terroirs de tous ces pays, de leurs ports, des plantes, des fruits & des animaux qu\'on y trouve; de leurs habitans, de leurs coûtumes, de leur religion, de leur gouvernement, de leur negoce, &c....1723
This volume refers to Dampiers voyages to North & South America, East Indies, SE Asia, China, Australia & Africa.
Contains Title page, 8 maps & plates total of 340 pages.
a) Mappe-Monde - World map with Dampiers tracks.
b) Maps of the Isthmus of Panama and Central America
c) Print of Natives gathering fruit
d) Print of Dampier loading Gold from the New World
e) Voyage au tour du Monde title page
f) Map of Mexico & southern North America
g) Print of a battle in the East indies
h) Print of a coconut palm in East Indies
2. Suite du Voyage Autour du Monde... Avec un Traite Des Vents qui regnent dans toute..LA ZONE TORRIDE Enrichi de Cartes & de Figures..1723
This volume refers to the contuinuation of Dampiers voyages to North & South America, East Indies, SE Asia, China, Australia & Africa along with a description of global winds and tides.
Contains title page along with 6 maps & plates, 227 pages.
a) Engraved Voyage au Tour Du Monde
b) Print of ships offshore from the city of Manila in the Phillippines
c) View of Manila
d) 2nd print of ships offshore from the city of Manila in the Phillippines
e) Map of the Philippines islands of Banshee
f) Map of Pulocondor, Malayia
g) Print of Dampiers ship and compass rose
3. Traits des Vents Aliisez ou Reglez des Vents Frais ...1715
This volume refers again to globle winds & tides.
Contains title page 2 maps & 148 pages
a) Description of winds and tides in the eastern hemisphere
b) Description of winds and tides in the eastern hemisphere
Volume 2.
1. Voyage Autour Du Monde... Contenant une Description d\'Achin,
Ville de Sumatra, du Royaume de Tonquin & autres Places des Indes,
& de la Baye de Campeche. Ou l\'on traite des differens terroirs de tous ces pays, de leurs ports, des plantes, des fruits & des animaux qu\'on y trouve; de leurs
habitans, de leurs coûtumes, de leur religion, de leur gouvernement,
de leur negoce, &c...1723
This volume refers to the continuation of Dampiers travels in East Indies, SE Asia & Mexico
Contains title page, 4 maps & plates, 264 pages.
a) Royalty in Vietnam
b) Map of central & north America
b) Print of Vietnam
c) Map of Australia & East Indies
2. Voyages de Guillaume Dampier a la Baye de Campeche...1714
This volume refers to Dampiers travel to Campeche, Mexico.
Contains title page and 197 pages.
Condition Report: Two volumes bound in full leather with five raised bands to spines, and title label. Couple of minor chips to top of both spines. The leather is scuffed and little pitted/worn (see photos). Internally there are a couple of small chips to inner edges of front and rear end-papers. Inscription to front end-papers (Gift of W. Wood 1745) and bookplate to inside front board (Lord Sandys). The title page of volume III and following four or so leaves have damp staining, and there is light damp staining throughout Volume I & II. The damp staining has caused the leaves to become softer and little chipped, with some nicks/tears and chips. There is a tear/crease to top inner edge and chip to bottom corner of title page of volume I. Scattered pale foxing/browning. Several of the plates have occasional creases. Four leaves of volume III are gently detaching and two leaves of volume I are missing. A few leaves are a little faded. Overall VG, in readable with firm binding.
1722 G. Delisle and Covens & Mortier Antique Map of North America - 5th State
- Title : Carte Du Mexique et de la Floride des Terres Angloises et des Isles Antilles du Cours...1722
- Date : 1722
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70814
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 545mm)
Description:
In the world of early 18th century American cartography, no one published as many landmark maps of North America as the French family firm of Delisle. This large original copper-plate engraved scarce map of North America became one of the most copied map of the next 100 years by the likes of Homann, Seutter, Lotter, Sanson and many others.
Re-engraved and published by Covens & Mortier in Amsterdam, this map is the 5th state of seven, published in the Atlas Nouveau.
The 7 states outlined by Tooley are:
- State 1 (1703): De LIsles first address on Rue Des Canettes.
- State 2 (1703): address changed to Quai de lHorloge Couronne de Diamans and the imprint of Renard.
- State 3 (1708): Couronne de Diamans is erased and se trouve a Amsterdam chez L. Renard Libraire prez de la Bourse is added
- State 4 (1708): A Paris Chez L Auteur sur le Quai de l Horloge is added and Couronne de Diamans and Renards imprint are removed and the engravers name (Simoneau) appears below the cartouche.
- State 5 (1722): A Amsterdam Chez Jean Covens & Corneille Mortier avec Privilege 1722 Re-engraved and published by Covens & Mortier in Atlas Nouveau
- State 6 (1745): Philippe Buache imprint added below neatline at right.
- State 7 (1783): Title altered to Carte du Mexique et des Etas Unis d Amerique, Partie Meridionale, issued by Dezauche, showing US States and boundaries.
Condition Report
Paper thickness and quality: - Very heavy and stable
Paper colour: - Off white
Age of map colour: - Original & later
Colours used: - Yellow, green, pink, blue
General colour appearance: - Fresh
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 19 1/2in (610mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in bottom margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The importance of this landmark map by Guillaume Delisle cannot be overstated. It was the first map to accurately depict the course and mouth of the Mississippi River. Much of the map was drawn from reports brought back to France from the survivor's of the La Salle expedition into the interior of North America and from information derived from the explorations of Bienville and d'Iberville. In the year preceding the publication of the map, Delisle utilised his position with the King of France to gain access to the best available information from the new world.
During this time, he compiled the geographical data from the reports of the French Jesuit Missionaries and explorer's in North America, along with Spanish manuscript maps (often copied by the Missionaries while they were acting in the service of the Spanish as spiritual guides and gaining their confidence). The result of this work were a series of 4 landmark maps of America, including his map of North America (L'Amerique Septentrionale, 1700), Canada and the Great Lakes (Carte du Canada ou de la Nouvelle France 1703) and the Mississippi Valley & Gulf Coast (Carte de la Louisiane et du Cours du Mississipi 1708) and of course this map.
Carl Wheat called this map a "towering landmark along the path of Western cartographic development." De L'Isle's map also inlcuded greater accuracy in the Great Lakes region and in its depiction of English settlements along the East Coast. Excellent detail of the Indian villages in East Texas, based upon the reports of Iberville and the Spanish missionaries. The best depiction of the Southwest to date, with early trails & Indian tribes. Cumming described the map as "profoundly influential. This is a beautifully engraved and hand coloured map by one of the finest French cartographers of the 18th century. (Ref: Cummings; M&B; Tooley)
1720 Guillaume Delisle Large Antique Map of America, New Zealand, Pacific Ocean
- Title : Hemisphere Occidental Dresse en 1720 pour l usage
- Date : 1720
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93081
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Description:
This very large 1st edition beautifully hand coloured original antique Map of America by Guillaume Delisle, was engraved by J De la Haye in 1720, dated, and was was published in the Atlas Nouveau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 19in (490mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - Uniform age toning
Verso: - Uniform age toning
Background:
Guillaume de L isle was responsible for some of the most accurate maps of America avaialble in the early 18th century. Delisle did away with most of the speculative cartography especially of North America and researched his information in finite detail. This can be seen in many ways. The most oblivious is showing California as a Peninsular - which some cartographers did not believe until the 1740\'s - and the NW region has been left blank, free of speculation. Another noticeable difference is the accurate depiction of the Great Lakes.
As with all Delisle\'s map this is finely engraved with amazing detail and hand colour. The map includes the tracks of many explorers up until 1710. These include Magellan 1520, Halley 1700, de Quiros 1605, de Mendana 1595, de la Maire 1616, Tasman, Halley and others. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1708 Guillaume Delisle Large Antique Map of North America - 4th State, rare
- Title : Carte Du Mexique et de la Floride des Terres Angloises et des Isles Antilles du Cours et des Environs de la Riviere Mississipi . . .Chez L Auteur sue le Quaide de l Horlage Privilege du Roy po. 20 ana 1703
- Date : 1708
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93525
- Size: 29 1/4in x 20 1/2in (750mm x 520mm)
Description:
In the world of early 18th century American cartography, no one published as many landmark maps of North America as the French family firm of Delisle. This large original copper-plate engraved scarce map of North America became one of the most copied map of the next 100 years by the likes of Homann, Seutter, Lotter, Sanson and many others. Engraved by Charles Simoneau, this map is the 4th state of seven (identified with the date 1703 in the cartouche with Delisles address in Paris erased) was published by Guillaume Delisle in the <i>Atlas Nouveau.</i>
The 7 states outlined by Tooley are:
- State 1 (1703): De LIsles first address on Rue Des Canettes.
- State 2 (1703): address changed to Quai de lHorloge Couronne de Diamans and the imprint of Renard.
- State 3 (1708): Couronne de Diamans is erased and <i>se trouve a Amsterdam chez L. Renard Libraire prez de la Bourse</i> is added
- State 4 (1708): <i>A Paris Chez L Auteur sur le Quai de l Horloge</i> is added and <i>Couronne de Diamans and Renards</i> imprint are removed and the engravers name (Simoneau) appears below the cartouche.
- State 5 (1722): <i>A Amsterdam Chez Jean Covens & Corneille Mortier avec Privilege 1722</i> Re-engraved and published by Covens & Mortier in Atlas Nouveau
- State 6 (1745): Philippe Buache imprint added below neatline at right.
- State 7 (1783): Title altered to Carte du Mexique et des Etas Unis dAmerique, Partie Meridionale, issued by Dezauche, showing US States and boundaries.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29 1/4in x 20 1/2in (750mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 19 1/2in (660mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This map, which is one of the three great maps of regional North America conceived by Delisle during the first quarter of the eighteenth century, identifies the colonial affiliations that defined the destiny of North America by the end of the century. As is often the case, the British North American Colonies are shown hemmed in by the Appalachians and crowding the Atlantic coast. The status of present-day South Carolina is dubious, the coloring implying that it may belong to Spain. To the north and west of New England, Canada confines the British colonies even further. In the Southwest, French Floride extends to the Rio Grande and south to present-day Brownsville. The northern boundary of Floride is indicated, except that it abuts Canada, thereby giving France possession of the entire middle part of the continent. Various remarks and locations for Native American tribes are shown, indicating, for example, the locations of the Apache Vaqueros, the Apache Navaio, and the Tiguas. In the French possessions many tribes and their villages are indicated, for example, the famous Cenis in Texas, the Apalache in Georgia and Florida, and the Kicapou near the Great Lakes (their original location before they were pushed all the way to Mexico). Delisles debts to Ibervilles explorations are frequently shown on this map.
The map was compiled from the reports brought back to France from the survivors of the La Salle expedition into the interior of North America and from the information derived from the explorations of Bienville and dIberville. In the year preceding the publication of the map, De LIsle utilized his position with the King of France to gain access to the best available information from the new world. During this time period he assiduously compiled the geographical data from the reports of the French Jesuit Missionaries and Explorers in North America, along with Spanish manuscript maps (often copied by the Missionaries while they were acting in the service of the Spanish as spiritual guides and gaining their confidence).
The result of this work were a series of landmark maps of the North America, including his map of North America ( LAmerique Septentrionale, 1700), Canada and the Great Lakes ( Carte du Canada ou de la Nouvelle France 1703), and the Mississippi Valley & Gulf Coast ( Carte de la Louisiane et du Cours du Mississipi 1708).
The map has been a towering landmark along the path of Western cartographic development. De LIsles map also includes greater accuracy in the Great Lakes region and in its depiction of English settlements along the East Coast. Excellent detail of the Indian villages in East Texas, based upon the reports of dIberville and the Spanish missionaries. The best depiction of the Southwest to date, with early trails & Indian tribes. Cumming described the map as profoundly influential.
Many have suggested that Claude Delisle, father of Guillaume, was the one who conducted the research on the maps, whereas Guillaume was the one who actually drew the maps and engraved the plates. Obviously the maps were a collaborative effort of the Delisle firm.
1812 Conrad Malte Brun Large Quatro Antique World Atlas with 75 Maps
- Title : Atlas Complet du précis de la Geographie universelle. Dressé conformément au Texte de cet Ouvrage et sous les Yeux de L'Auteur, par M. Lapie. (Cet Atlas est formé de 75 Cartes)
- Size: Large Quarto - 14 1/2in x 11in (370mm x 280mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1812
- Ref #: 31573
Description:
This original large quatro, antique 1st edition atlas by Conrad Matle-Brun Atlas Complet du précis de la Geographie universelle containing 75 hand coloured maps, as called for, was published by Francois Buisson in 1812.
This fine world atlas contains 3 double page and 72 single page maps with original hand colouring on clean heavy paper with a heavy impression. The binding & spine is tight, with worn boards. A beautiful intact clean atlas, now how to find.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 14in (510mm x 355mm) double page maps
Plate size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm) single page maps
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Malte-Brun, Conrad 1775 - 1826
Malte-Brun was born Malthe Conrad Bruun - sometimes referred to simply as Malte-Brun - was a Dano-French geographer and journalist. His second son, Victor Adolphe Malte-Brun, was also a geographer. Today he is perhaps best remembered for coining the name for the geographic region Oceania (French Oceanie) around 1812.
Born in Thisted to an administrator of Danish crown lands, Malte-Brun was originally destined for a career as a pastor, but chose instead to attend classes at the University of Copenhagen, and became a supporter of the French Revolution and an activist in favor of freedom of the press. Following the harsh censorship laws instituted by the Danish ruler crown prince Frederick in September 1799, he was indicted because of his many pamphlets which contained outright criticism of the government, which the new censorship laws forbade. A particular cause for offence was a pamphlet he published in 1795 entitled Catechism of the Aristocrat.
The case of Peter Andreas Heiberg, who for similar crimes had been sentenced to exile at Christmas of 1799, did not make Malte-Brun optimistic about his prospects. He had already left the country prior to the court sentence (which was first carried late 1800) and had settled first in Sweden, later in the Free City of Hamburg.
At some point during his exile, he started using his Danish first name, Malthe, as part of his surname, Bruun.
Malte-Brun arrived in France in November 1799, and began work on a geography treatise meant as a gift to his adoptive country. A poem on the death of Andreas Peter Bernstorff which he published during his exile procured for him permission to return to Denmark. But another pamphlet against the aristocracy subjected him to a new prosecution, and he left his country, and finally took up his residence in Paris. In December 1800, the Danish courts pronounced sentence of perpetual banishment against him, which was rescinded about the time of his death. Malte-Brun\'s geography treatise was written with the help of Edme Mentelle, a professor at the Ale Normale; together, they produced Gaographie mathamatique, physique et politique de toutes les parties du monde (6 vols., published between 1803 and 1812).
He was a regular contributor to Journal des dabats. At first opposed the consular government, but subsequently became a zealous imperialist, and after the fall of Napoleon an equally zealous monarchist, publishing in 1824 Traita de la lagitimita considae comme base du droit public de l Europe chratienne.
Aside from his political writings, he devoted himself especially to geographical studies. He was the founder of Les Annales des Voyages (in 1807) and Les Annales des Voyages, de la Gaographie et de l Histoire (in 1819), which encouraged observations and reports as a basis for research. He became well known after contributing Tableau de la Pologne, a treatise on the geography of Poland (in 1807) as the First Empire troops established French tutelage in the region). In 1822-1824, he served as the first general secretary of the newly founded Sociata de Gaographie. Malte-Brun was the first person to suggest importing camels into Australia. See Australian feral camel.
He died in Paris in 1826 as he was drafting the final version of his major work, the Pracis de Gaographie Universelle ou Description de toutes les parties du monde. This appeared in eight volumes (1810 - 29), the last two volumes being by Huot. Malte-Bruns name was given to streets in both Paris (20th arrondissement) and Thisted.