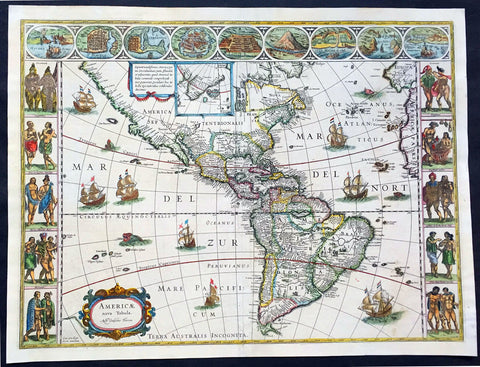
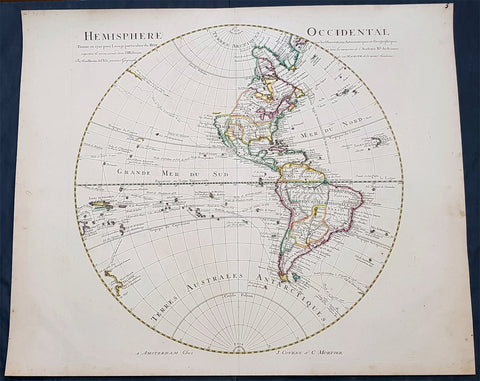
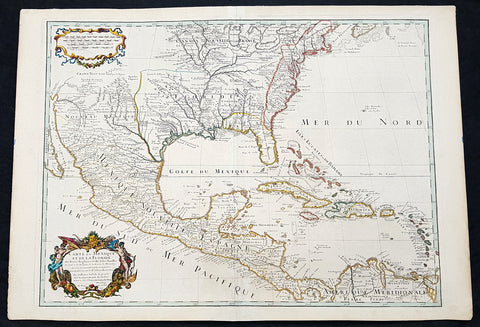
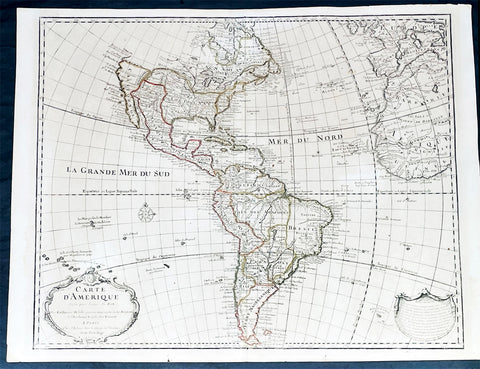
America (177)
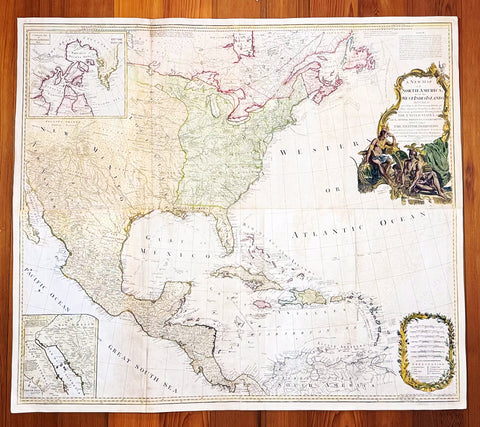
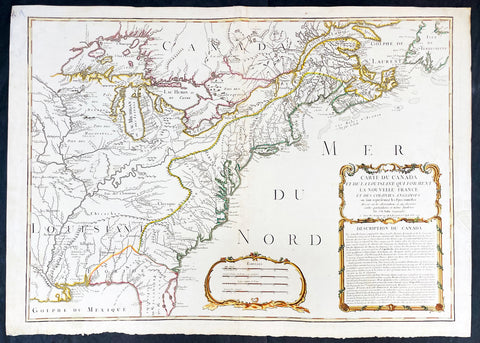
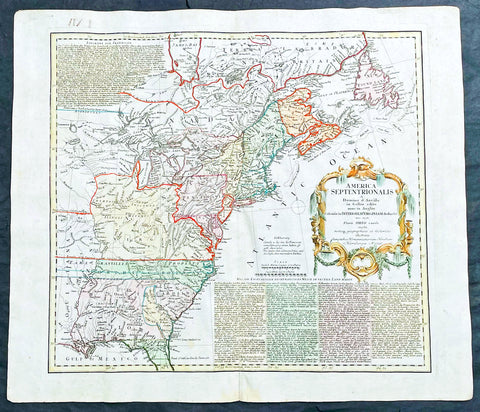
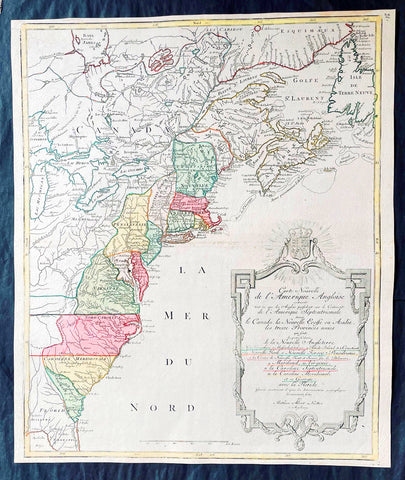
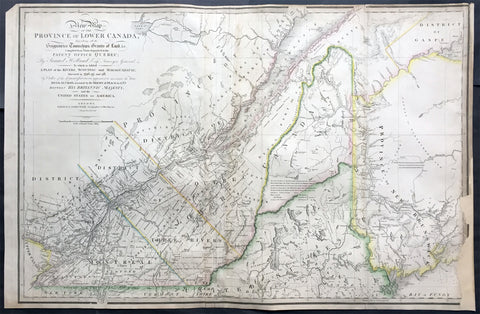
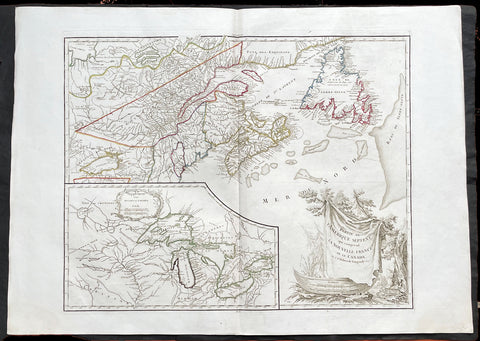
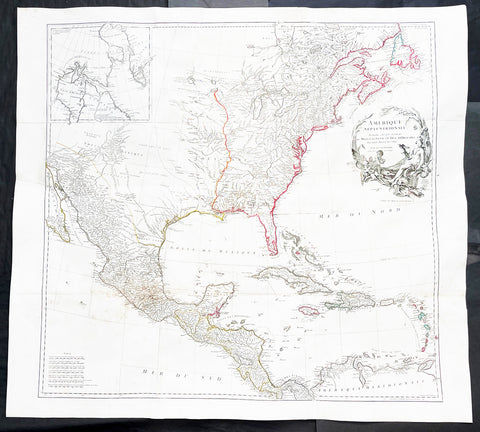
1794 Thomas Pownall & Kitchin Large Post Revolutionary War Map of North America
- Title : A New Map of North America with the West India Islands, divided according to the Preliminary Articles of Peace, Singed at Versailles, 20, jan 1783, wherein are particularly Distinguished The United States, and the Several Provinces, Governments & ca which Compose the British Dominions, Laid down according to the Latest Surveys, and Corrected from the Original Materials of Goverr. Pownall, Membr. of Parlimt....1794
- Size: 47in x 41in (1.20m x 1.050m)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1794
- Ref #: 35672
Description:
A large, extraordinary important, original rare copper-plate engraved map of North America by Governor Thomas Pownell, was engraved & updated by Thomas Kitchin in 1794 - dated in cartouche - and published in A general atlas, describing the whole universe: being a complete collection of the most approved maps extant; corrected with the greatest care, and augmented from the latest discoveries by Laurie and Whittle (active 1794 - 1858) London.
This map was first issued by Emmanuel Bowen and John Gibson in 1755 and went through numerous iterations over the next 40 years. This edition was issued shortly after the end of the American Revolutionary War and the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The map details the newly formed United States of America in Green, the British & French dominions in Canada in Red, plus the extensive Spanish territories of from Florida, Louisiana Mexico and Central America. As one might expect from a map of this size, the detail throughout is extraordinary.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 47in x 41in (1.20m x 1.050m)
Plate size: - 46in x 40in (1.10m x 990mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light toning & offsetting
Verso: - Age toning.
Background:
This monumental 1794 map of North America by Governor Thomas Pownell was issued shortly after the end of the American Revolutionary War. The United States at this time extended from the Pacific to the Mississippi River and from Georgia to the Great Lakes and Maine. The early state boundaries roughly conform to their original colonial charters. Virginia, North Carolina, and South Carolina are drawn with indefinite western borders, suggesting claims to further unexplored land beyond the Appellation Mountains. By this time most of the boundary issues in the New England states had been resolved, though there remained some vagaries regarding the Massachusetts Connecticut border and, though Vermont is noted textually, its boundaries are not drawn in. At this time there were also some unresolved issues regarding the national borders between Maine and Nova Scotia. In Pennsylvania, the western border displays some surveying confusions that would not be resolved until the early 1800s and the creation of Ohio.
It is beyond the old colonial centers where this map really gets interesting. Pownall offers copious notations on the lands and territories between the Appellation range and this Mississippi River. In some cases he offers commentary on the various indigenous tribes including the Creeks, Chickasaws, Chocktaws, Senekas, Eriez, Delawares, Shawnee, Iroquois, Algonquians, Ottawas and others. The cartographer was clearly concerned with the development of these western regions and offers copious commentary on fit sites for factories, the alliances and temperaments of tribes, and the navigability of various river systems, particularly the Mississippi and Ohio.
The Great Lakes are mapped with considerable accuracy though several apocryphal islands do appear in Lake Superior. The most notable of these are Phelipeaux and Pontchartrain. Phelipeaux Island first appeared in French maps of this region in the 1740s. Later it was mentioned as a boundary marker in the 1783 Treaty of Paris which ended the American Revolutionary War. The nonexistence of these islands was not conclusively proven until about 1820.
To the west of the Mississippi we pass into the largely unknown lands of the Great Plains. In what is roughly modern day Missouri, between Memphis and St. Louis, there is an interesting note suggesting that this region is Full of Mines, with a secondary note suggesting that these mines gave rise to the Mississippi Scheme of 1719. This refers to the Mississippi Company (Compagnie du Mississippi) or, as it was more commonly known the Indies Company (Compagnie d Occident). This organization was part of a French investment plan comparable to the South Seas Company which was developing contemporaneously in England. The Mississippi Companys charter was to trade the riches of the Louisiana Territory. The main proponent of the Mississippi Company, John Law, greatly exaggerated the wealth of Louisiana by describing a rich mining region easily accessible along the Mississippi from New Orleans. This resulted in a stock buying rush which disproportionately overvalued Mississippi Company stock, resulting in one of the world\'s first Bubble Economies.
Further North, along the northern border between the United States and British America (Canada), Rain Lake, the Lake of the Woods, and Lake Winnepeg are noted. This region was a hotbed of exploration throughout the 18th century. French and English concerns in the New World were desperate for access to the Pacific and the rich Asian markets. These markets had long been dominated by the Spanish who had easy access to the Pacific via Mexico and South America. The French and English set their hopes on a Northwest Passage. By the late 18th century the search for a route through the high Arctic had long been abandoned. Instead, explorers and theoretical cartographers believed that a water route might be found among the elaborate network of lakes and rivers that meandered through central Canada. Our map shows evidence of some of this exploration, particularly the travels of the Quebec born Pierre de La Verendrye and his sons around Lake Alimipigon, the Lake of the Woods (Lake Minitti) and Lake Winnipeg (Lake Ouinipigon).
As we progress even further west, passing out of Louisiana into the Spanish holdings we begin to see significant mapping - both conjectural and factual. The Spanish had long been passively active in the exploration of New Mexico. Though no concerted effort had been put forth to map the region, various missionaries and territorial governors had, over roughly 200 years of occupation added considerable data, both fact and fiction to the cartographic picture. Numerous American Indian groups are noted including the Pimas, the Apaches ,the Navajo and others. Along the Rio del Norte or upper Rio Grande there are a quantity mission stations including the regional capital of Santa Fe.
Just to the west of these missions we begin to enter more mythical territory and both Cibola and Teguayo are noted. Cibola and Teguayo are both associated with the legendary Seven Cities of Gold. It was believed that in 1150 when Merida, Spain, was conquered by Moors ,the city\'s seven bishops fled to unknown lands taking with them much of the city\'s riches. Each Bishop supposedly founded a great city in a far away place. With the discovery of the New World and the fabulous riches plundered by Cortez and Pizarro, the Seven Cities became associated with New World legends. Coronado, hearing tales of the paradise-like mythical Aztec homeland of Azatlan somewhere to the north of Mexico , determined to hunt for these cities in what is today the American southwest. In time indigenous legends of rich and prosperous lands became attached to the seven cities. Two of these appear on our map - Cibola and Teguayo.
The gulf of Mexico, the West Indies, and the Caribbean are charted with considerable and typical accuracy. Notes numerous offshore shoals, reefs, and other dangers - especially around the Bahamas. Also describes several important shipping routes, particularly the former routes of Spanish galleons from Veracruz to Havana, the route from Cartagena to Havana, and the route from Cartagena to Europe.
There are also two particularly interesting insets. The first, in the upper left quadrant, depicts the Canadian arctic, particularly the Hudson and Baffin Bays. Notes all of the most recent discoveries in this region and offers interesting notes such as If there is Northwest Passage it appears to be through one of these inlets. In the northwestern quadrant of this inset, the supposed discoveries of Admiral de Fonte are included, despite a notation that they are Imaginary.
The second inset of interest in located in the lower left quadrant. This smaller maps depicts the northern parts of the Gulf of California and the Colorado River Delta based upon the explorations of the Jesuit Father Eusebius Francis Kino. The actual cartography of this region has been vague since the mid 17th century when it was postulated that California must be an Island. It was not until Kino\'s historic expedition, recorded here, that Baja California was conclusively proven to be a peninsula.
A magnificent title cartouche appears in the upper right quadrant. The cartouche, which angles around Bermuda, depicts two stylized American Indians surrounded by the presumed flora and fauna of the new world. These include a small monkey, a parrot, and a jaguar. Above the cartouche is a textual quotation from Article III of the Treaty of Paris, affirming the rights of the United States to access the rich cod fields of Newfoundland\'s Grand Banks.
The Treaty of Paris, signed in Paris by representatives of King George III of Great Britain and representatives of the United States of America on September 3, 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War. The treaty set the boundaries between the British Empire in North America and the United States, on lines exceedingly generous to the latter. Details included fishing rights and restoration of property and prisoners of war.
This treaty and the separate peace treaties between Great Britain and the nations that supported the American cause—France, Spain, and the Dutch Republic—are known collectively as the Peace of Paris. Only Article 1 of the treaty, which acknowledges the United States existence as free, sovereign, and independent states, remains in force.
Thomas Pownall 1722 - 1805 was a British scholar, statesman and soldier active in the colonial administration of North America just prior to the American Revolutionary War. Pownell was born in England and educated at Trinity College, Cambridge. After graduation he was employed by his brother, John Pownall, at the office of the Lords Commissioners of Trade and Plantations, which oversaw British economic interests in its North American colonies. In 1753, Pownall was appointed secretary to the governor of New York, Sir Danvers Osborne. Osborne, himself having be only recently appointed to the position, committed suicide shortly after taking office. Despite this setback, Pownall remained in America and devoted himself to studying and researching the colonies. In the process Pownall became close lifelong friends with Benjamin Franklin and other New World luminaries. He also published several notable works on the colonial administration of North America. In 1757 Pownall was appointed Governor of the Massachusetts Bay colony. In this position he frequently found himself at odds with the restrictive policies of the Board of Trade. It was not long before he was pushed out of office and, declining the governorship of Jamaica, reassigned to South Carolina. Despite nominally holding the governorship of South Carolina, Pownall never visited the colony. Instead he returned to England where he eventually became a member of Parliament. In Parliament, he advocated for reduced taxes towards the colonies - had he been heeded, the American Revolution may have never happened. Pownall retired from public life around 1780, but continued to pursue his scholarly interests. Pownalls research contributed significantly to several important maps and scholarly work on North America.
Laurie and Whittle 1794 - 1858 based in London, were map and atlas publishers active in the late 18th and early 19th century. Generally considered to be the successors to the Robert Sayer firm, Laurie and Whittle was founded by Robert Laurie (c. 1755 - 1836) and James Whittle (1757-1818). Robert Laurie was a skilled mezzotint engraver and is known to have worked with Robert Sayer on numerous projects. James Whittle was a well-known London socialite and print seller whose Fleet Street shop was a popular haunt for intellectual luminaries. The partnership began taking over the general management of Sayers firm around 1787; however, they did not alter the Sayer imprint until after Sayers death in 1794. Apparently Laurie did most of the work in managing the firm and hence his name appeared first in the Laurie and Whittle imprint. Together Laurie and Whittle published numerous maps and atlases, often bringing in other important cartographers of the day, including Kitchin, Faden, Jefferys and others to update and modify their existing Sayer plates. Robert Laurie retired in 1812, leaving the day to day management of the firm to his son, Richard Holmes Laurie (1777 - 1858). Under R. H. Laurie and James Whittle, the firm renamed itself Whittle and Laurie. Whittle diedin 1818, and thereafter the firm continued under the imprint of R. H. Laurie. After Lauries death the publishing house and its printing stock came under control of Alexander George Findlay, who had long been associated with Laurie and Whittle. Since, Laurie and Whittle has passed through numerous permeations, with part of the firm still extant as an English publisher of maritime or nautical charts, Imray, Laurie, Norie and Wilson Ltd. The firm remains the oldest surviving chart publisher in Europe.
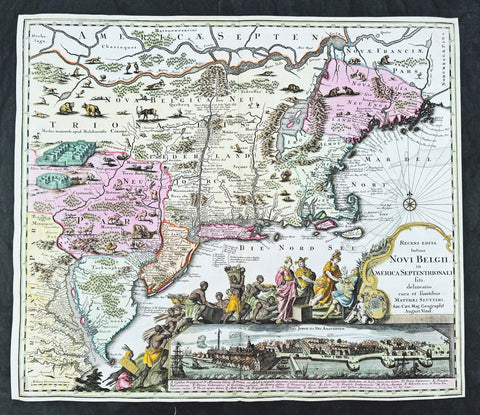
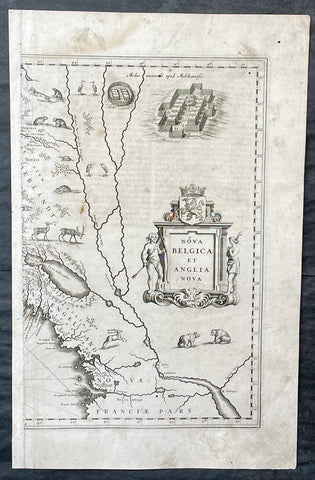
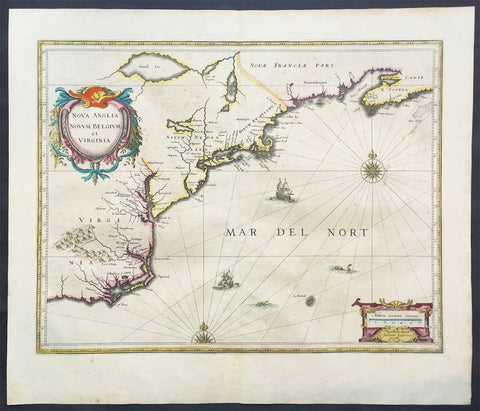
1730 Georg Seutter Antique Map of New England & New York City - Rare 2nd State
- Title : Recens edita totius Novi Belgii, in America Septentrionali siti, delineatio cura et sumtibus Matthaei Seutteri, Sac. Caes Maj. Geographf. August. Vind
- Size: 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1730
- Ref #: 43001
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the NE region of colonial North America, with the famous Restitutio inset birds-eye view of 17th century New York city, was engraved & published by Georg Mattraus Seutter in 1730.
This is the rare second state, identified by the omission of Chalcographi Augustani from the title and the blank shaded are directly below the title (text was added to the shaded area in the 3rd to 6th states) The cartouche and city view are uncoloured as was intended by Seutter along with the beautiful original map colouring.
This map is in exceptional condition with beautiful original colour, with heavy engraving (denoting an early pressing) on clean heavy sturdy paper. The top and left borders have been professionally extended, with no impact on the image.
There are, at the time of listing, nine of these maps for sale online, of states 2 to 6. Of the 9 only 2 are of the rare 2nd state. The average asking price of the nine maps is $4897US.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 20 1/4in (585mm x 515mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - T, R & L margins extended
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The map is based upon the Jansson-Visscher New England series of maps, first published by Visscher in 1651. Seutter replaces the original Restitutio view of New York City with a new view of New York entitled Neu Jorck sive Neu Amsterdam, with a key to the view below in Latin. Above the view is an elaborate scene depicting natives, slaves & allegorical deities presenting tributes to the English monarch, George II. The course of the Delaware and Hudson are separated, unlike early editions of the map.
This is the first map in the series to show distinct drawn boundaries between Massachusetts, New England, New York, New Jersey and Pennsylvania, as earlier examples had previously left the delineation of the boundaries to the colorist. Philadelphia is now shown as a set of houses in relief, rather than a ground plan. The map is richly embellished with many animals and other decorations and is without doubt, one of the most decorative 18th century maps of the region.
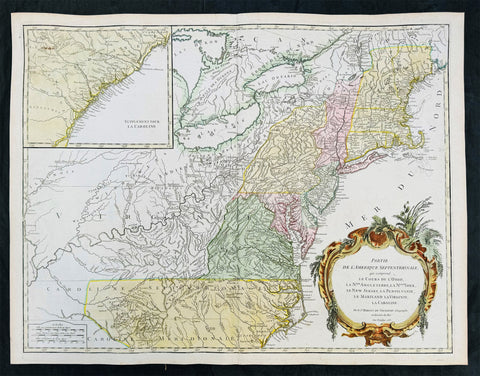
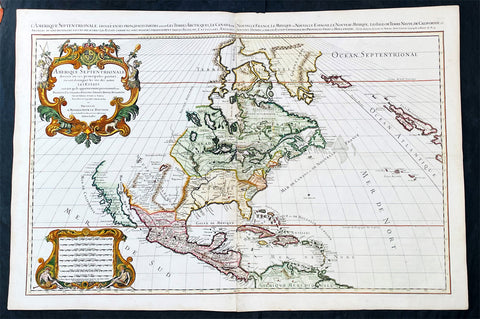
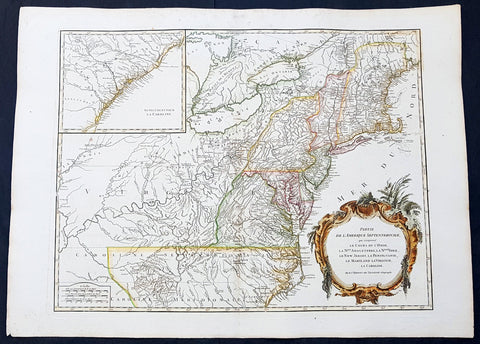
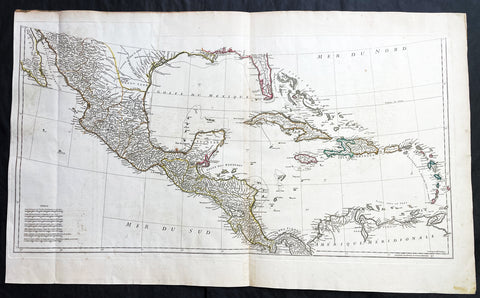
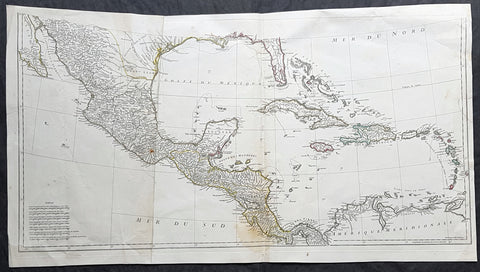
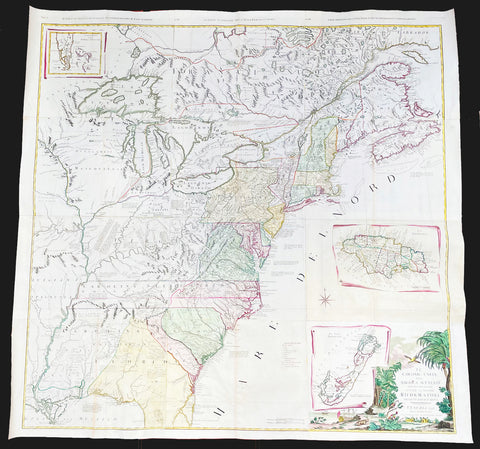
1755 (1768) Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique 2nd edition Map of Colonial United States
- Title : Partie De L Amerique Septentrionale, qui Comprend Le Cours De L Ohio...Par le Sr Robert de Vaugondy
- Date : 1755 (1768)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93514
- Size: 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured, scarce 2nd edition antique map of the east coast of the United States, illustrating the course of the Ohio River and stretching from New England to the Carolinas, north to the Great Lakes and south to the Mississippi - with an inset map of The Carolinas - was published in 1768 - dated 1755 in the cartouche - by Robert Du Vaugondy in his Atlas Universal.
This map is all original with hand colour on age toned heavy paper with original margins with a heavy dark ink denoting an early pressing.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26in x 20 1/2in (660mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Second state of the early de Vaugondy map of the British colonies, with changes after the 1763 Treaty of Paris, with Virginia & Carolina extended to the Mississippi and Pennsylvania extended to Lake Erie. The majority of geographical information is based upon John Mitchells great map of North America from the mid 1750s, also drawing from Lewis, Evans on the Middle British Colonies and Joshua Frys and Peter Jeffersons map of Virginia and Maryland. The Mitchell map was the culmination of many years of British surveying in the North American Colonies and was considered one of the best maps of the continent available to Europeans and Americans in the mid-eighteenth century.
De Vaugondys rendition does not copy the full scope of Mitchells map but instead focuses on the colonies stretching from southern Maine to the Carolinas. In the top left corner is an inset of South Carolina and Georgia. De Vaugondy also pays special attention to the river systems and settlements. This map shows some of the earliest accurate information of the trans-Allegheny regions (the Ohio River, Kentucky, Tennessee and Parts of Ohio) and inland areas to the southeast of the Great Lakes and interior of New England.
Maine is still part of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. During this era. The dispute between New Hampshire and New York over who controlled the area which is now Vermont has been resolved. The outbreak of the French & Indian War (Seven Years War) briefly suspended interest in the disputed area, and it was not until 1764 that the British crown upheld New Yorks claim to Vermont. Included is a beautiful title cartouche in the Rococo style. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1723 William Dampier 2 Volumes of World Voyages to America Australia Asia - 20 x Maps & Plates
-
Title : Nouveau Voyage Autour Du Monde...Ou l on decrite en particular l Isthme de l Amerique, plusieurs côtes et isles des Indes Occidentales...1723
(New Voyage around the world. In which are described in particular the Istmus of America, several Coasts & Islands of the West Indies, the Islands of Cape Verde, the passage through the Land of Fuego, the Southern Coasts of Chili, Peru, & Mexico. . - Size: 8vo
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1723
- Ref #: 93005
Description:
French edition of William Dampier's account of his voyages around the World, in 2 volumes, especially to the South Seas in the years 1683 to 1691. Dampier first sailed to Sierra Leone and from there to the Falkland Islands, Cape Horn, Peru, Guatemala, Mexico, Philippines, Vietnam, China, Indonesia and onto New Guinea. He then went ashore in northern Western Australia, in the Broome region, the region later named after him and then sailed onto Sumatra, the Cape of Good Hope and back to Europe.
Although John Brooke was probably shipwrecked on the Australian coast in 1621, without knowing where exactly he was, Dampier became the first Englishman to set foot in Australia, in the Broome NW region. Even though Dampier spent a good deal of his time as a Buccaneer, he wrote these accounts of his adventures without sensation, concentrating on the hydrographic, geographic and scientific details. This helped him establish his legitimacy, bringing immediate academic acclaim rather than condemnation as a pirate.
Dampier was first person to circumnavigate the world three times between 1679 & 1711. He has also been described as Australias first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the British Admiralty with his book, A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in western Australia, but was court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage, he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crew mate who may have inspired Daniel Defoes Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Lord Nelson, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace.
These two leather bound Volumes, contain 20 maps & plates (some folding) and was published in Amsterdam by David Paul Marret in 1723 (dated)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 8vo
Plate size: - 8vo
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see below for condition report
Plate area: - Please see below for condition report
Verso: - Please see below for condition report
Background:
The two volumes contain the following titles with 20 maps & plates.
Volume 1.
1. Nouveau Voyage Autour Du Monde...Ou l\'on decrite en particular l\'Isthme de l\'Amerique, plusieurs côtes et isles des Indes Occidentales, les Isles du Cap Verd, le passage par la Terre del Fuego, les côtes meridionales du Chili, du Perou & du Mexique; l\'Isle de Guam, Mindanao, & des autres Philippines, les isles orientales qui sont prés de Cambodie; de la Chine; Formosa; Luçon, Celebes, &c., la Nouvelle Hollande, les Isles de Sumatra, de Nicobar & de Sainte Helene & le Cap de Bonne Esperance...Ou l\'on traite des differens terroirs de tous ces pays, de leurs ports, des plantes, des fruits & des animaux qu\'on y trouve; de leurs habitans, de leurs coûtumes, de leur religion, de leur gouvernement, de leur negoce, &c....1723
This volume refers to Dampiers voyages to North & South America, East Indies, SE Asia, China, Australia & Africa.
Contains Title page, 8 maps & plates total of 340 pages.
a) Mappe-Monde - World map with Dampiers tracks.
b) Maps of the Isthmus of Panama and Central America
c) Print of Natives gathering fruit
d) Print of Dampier loading Gold from the New World
e) Voyage au tour du Monde title page
f) Map of Mexico & southern North America
g) Print of a battle in the East indies
h) Print of a coconut palm in East Indies
2. Suite du Voyage Autour du Monde... Avec un Traite Des Vents qui regnent dans toute..LA ZONE TORRIDE Enrichi de Cartes & de Figures..1723
This volume refers to the continuation of Dampiers voyages to North & South America, East Indies, SE Asia, China, Australia & Africa along with a description of global winds and tides.
Contains title page along with 6 maps & plates, 227 pages.
a) Engraved Voyage au Tour Du Monde
b) Print of ships offshore from the city of Manila in the Phillippines
c) View of Manila
d) 2nd print of ships offshore from the city of Manila in the Phillippines
e) Map of the Philippines islands of Banshee
f) Map of Pulocondor, Malayia
g) Print of Dampiers ship and compass rose
3. Traits des Vents Aliisez ou Reglez des Vents Frais ...1715
This volume refers again to globe winds & tides.
Contains title page 2 maps & 148 pages
a) Description of winds and tides in the eastern hemisphere
b) Description of winds and tides in the eastern hemisphere
Volume 2.
1. Voyage Autour Du Monde... Contenant une Description d\'Achin,
Ville de Sumatra, du Royaume de Tonquin & autres Places des Indes,
& de la Baye de Campeche. Ou l\'on traite des differens terroirs de tous ces pays, de leurs ports, des plantes, des fruits & des animaux qu\'on y trouve; de leurs
habitans, de leurs coûtumes, de leur religion, de leur gouvernement,
de leur negoce, &c...1723
This volume refers to the continuation of Dampiers travels in East Indies, SE Asia & Mexico
Contains title page, 4 maps & plates, 264 pages.
a) Royalty in Vietnam
b) Map of central & north America
b) Print of Vietnam
c) Map of Australia & East Indies
2. Voyages de Guillaume Dampier a la Baye de Campeche...1714
This volume refers to Dampiers travel to Campeche, Mexico.
Contains title page and 197 pages.
Condition Report: Two volumes bound in full leather with five raised bands to spines, and title label. Couple of minor chips to top of both spines. The leather is scuffed and little pitted/worn (see photos). Internally there are a couple of small chips to inner edges of front and rear end-papers. Inscription to front end-papers (Gift of W. Wood 1745) and bookplate to inside front board (Lord Sandys). The title page of volume III and following four or so leaves have damp staining, and there is light damp staining throughout Volume I & II. The damp staining has caused the leaves to become softer and little chipped, with some nicks/tears and chips. There is a tear/crease to top inner edge and chip to bottom corner of title page of volume I. Scattered pale foxing/browning. Several of the plates have occasional creases. Four leaves of volume III are gently detaching and two leaves of volume I are missing. A few leaves are a little faded. Overall VG, in readable with firm binding.
Dampier, William 1651 - 1715
Dampier was an English explorer, navigator & buccaneer who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavigate the world three times. He has also been described as Australias first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Sir Walter Raleigh and James Cook.
After impressing the Admiralty with his book A New Voyage Round the World, Dampier was given command of a Royal Navy ship and made important discoveries in western Australia, before being court-martialled for cruelty. On a later voyage he rescued Alexander Selkirk, a former crewmate who may have inspired Daniel Defoes Robinson Crusoe. Others influenced by Dampier include James Cook, Horatio Nelson, Charles Darwin.
In 1679, Dampier joined the crew of the buccaneer Captain Bartholomew Sharp on the Spanish Main of Central America, twice visiting the Bay of Campeche, or Campeachy as it was then known, on the north coast of Mexico. This led to his first circumnavigation, during which he accompanied a raid across the Isthmus of Darién in Panama and took part in the capture of Spanish ships on the Pacific coast of that isthmus. The pirates then raided Spanish settlements in Peru before returning to the Caribbean.
Dampier made his way to Virginia, where in 1683 he was engaged by the privateer John Cooke. Cooke entered the Pacific via Cape Horn and spent a year raiding Spanish possessions in Peru, the Galápagos Islands, and Mexico. This expedition collected buccaneers and ships as it went along, at one time having a fleet of ten vessels. Cooke died in Mexico, and a new leader, Edward Davis, was elected captain by the crew.
Dampier transferred to the privateer Charles Swans ship, Cygnet, and on 31 March 1686 they set out across the Pacific to raid the East Indies, calling at Guam and Mindanao. Spanish witnesses saw the predominantly English crew as not only pirates and heretics but also cannibals. Leaving Swan and 36 others behind on Mindanao, the rest of the privateers sailed on to Manila, Poulo Condor, China, the Spice Islands, and New Holland. Contrary to Dampiers later claim that he had not actively participated in actual piratical attacks during this voyage, he was in fact selected in 1687 to command one of the Spanish ships captured by Cygnets crew off Manila.
On 5 January 1688, Cygnet anchored two miles from shore in 29 fathoms on the northwest coast of Australia, near King Sound. Dampier and his ship remained there until March 12, and while the ship was being careened Dampier made notes on the fauna and flora and the indigenous peoples he found there. Among his fellows were a significant number of Spanish sailors, most notably Alonso Ramírez, a native of San Juan, Puerto Rico Later that year, by agreement, Dampier and two shipmates were marooned on one of the Nicobar Islands. They obtained a small canoe which they modified after first capsizing and then, after surviving a great storm at sea, called at Acheen (Aceh) in Sumatra.
Dampier returned to England in 1691 via the Cape of Good Hope, penniless but in possession of his journals. He also had as a source of income a slave known as Prince Jeoly (or Giolo), from Miangas (now Indonesia), who became famous for his tattoos (or paintings as they were known at the time). Dampier exhibited Jeoly in London, thereby also generating publicity for a book based on his diaries.
The publication of the book, A New Voyage Round the World, in 1697 was a popular sensation, creating interest at the Admiralty. In 1699, Dampier was given command of the 26-gun warship HMS Roebuck, with a commission from King William III (who had ruled jointly with Queen Mary II until her death in 1694). His mission was to explore the east coast of New Holland, the name given by the Dutch to what is now Australia, and Dampiers intention was to travel there via Cape Horn.
The expedition set out on 14 January 1699, too late in the season to attempt the Horn, so it headed to New Holland via the Cape of Good Hope instead. Following the Dutch route to the Indies, Dampier passed between Dirk Hartog Island and the Western Australian mainland into what he called Shark Bay on 6 August 1699. He landed and began producing the first known detailed record of Australian flora and fauna. The botanical drawings that were made are believed to be by his clerk, James Brand. Dampier then followed the coast north-east, reaching the Dampier Archipelago and Lagrange Bay, just south of what is now called Roebuck Bay, all the while recording and collecting specimens, including many shells. From there he bore northward for Timor. Then he sailed east and on 3 December 1699 rounded New Guinea, which he passed to the north. He traced the south-eastern coasts of New Hanover, New Ireland and New Britain, charting the Dampier Strait between these islands (now the Bismarck Archipelago) and New Guinea. En route, he paused to collect specimens such as giant clams.
By this time, Roebuck was in such bad condition that Dampier was forced to abandon his plan to examine the east coast of New Holland while less than a hundred miles from it. In danger of sinking, he attempted to make the return voyage to England, but the ship foundered at Ascension Island on 21 February 1701. While anchored offshore the ship began to take on more water and the carpenter could do nothing with the worm-eaten planking. As a result, the vessel had to be run aground. Dampiers crew was marooned there for five weeks before being picked up on 3 April by an East Indiaman and returned home in August 1701.
Although many papers were lost with Roebuck, Dampier was able to save some new charts of coastlines, and his record of trade winds and currents in the seas around Australia and New Guinea. He also preserved a few of his specimens. In 2001, the Roebuck wreck was located in Clarence Bay, Ascension Island, by a team from the Western Australian Maritime Museum. Because of his widespread influence, and also because so little exists that can now be linked to him, it has been argued that the remains of his ship and the objects still at the site on Ascension Island – while the property of Britain and subject to the island governments management – are actually the shared maritime heritage of those parts of the world first visited or described by him. His account of the expedition was published as A Voyage to New Holland in 1703.
The War of the Spanish Succession had broken out in 1701, and English privateers were being readied to act against French and Spanish interests. Dampier was appointed commander of the 26-gun ship St George, with a crew of 120 men. They were joined by the 16-gun Cinque Ports with 63 men, and sailed on 11 September 1703 from Kinsale, Ireland. The two ships made a storm-tossed passage round Cape Horn, arriving at the Juan Fernández Islands off the coast of Chile in February 1704. While watering and provisioning there, they sighted a heavily armed French merchantman, which they engaged in a seven-hour battle but were driven off.
Dampier succeeded in capturing a number of small Spanish ships along the coast of Peru, but released them after removing only a fraction of their cargoes because he believed they would be a hindrance to his greater designs. The greater design he had in mind was a raid on Santa María, a town on the Gulf of Panama rumoured to hold stockpiles of gold from nearby mines. When the force of seamen he led against the town met with unexpectedly strong resistance, however, he withdrew. In May 1704, Cinque Ports separated from St George and, after putting Alexander Selkirk ashore alone on an island for complaining about the vessels seaworthiness, sank off the coast of what is today Colombia. Some of its crew survived being shipwrecked but were made prisoners of the Spanish.
It was now left to St George to make an attempt on the Manila galleon, the main object of the expedition. The ship was sighted on 6 December 1704, probably Nuestra Señora del Rosario. It was caught unprepared and had not run out its guns. But while Dampier and his officers argued over the best way to mount an attack, the galleon got its guns loaded and the battle was joined. St George soon found itself out-sized by the galleons 18- and 24-pounders, and, suffering serious damage, they were forced to break off the attack.
The failure to capture the Spanish galleon completed the break-up of the expedition. Dampier, with about thirty men, stayed in St George, while the rest of the crew took a captured barque across the Pacific to Amboyna in the Dutch settlements. The undermanned and worm-damaged St George had to be abandoned on the coast of Peru. He and his remaining men embarked in a Spanish prize for the East Indies, where they were thrown into prison as pirates by their supposed allies the Dutch but later released. Now without a ship, Dampier made his way back to England at the end of 1707.
In 1708, Dampier was engaged to serve on the privateer Duke, not as captain but as sailing master. Duke beat its way into the South Pacific Ocean round Cape Horn in consort with a second ship, Duchess. Commanded by Woodes Rogers, this voyage was more successful: Selkirk was rescued on 2 February 1709, and the expedition amassed £147,975 (equivalent to £19.9 million today) worth of plundered goods. Most of that came from the capture of a Spanish galleon, Nuestra Señora de la Encarnación y Desengaño, along the coast of Mexico in December 1709.
In January 1710, Dampier crossed the Pacific in Duke, accompanied by Duchess and two prizes. They stopped at Guam before arriving in Batavia. Following a refit at Horn Island (near Batavia) and the sale of one of their prize ships, they sailed for the Cape of Good Hope where they remained for more than three months awaiting a convoy. They left the Cape in company with 25 Dutch and English ships, with Dampier now serving as sailing master of Encarnación. After a further delay at the Texel, they dropped anchor at the Thames in London on 14 October 1711.
Dampier may not have lived to receive all of his share of the expeditions gains. He died in the Parish of St Stephen Coleman Street, London. The exact date and circumstances of his death, and his final resting place, are all unknown. His will was proven on 23 March 1715, and it is generally assumed he died earlier that month, but this is not known with any certainty. (Ref Tooley M&B)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
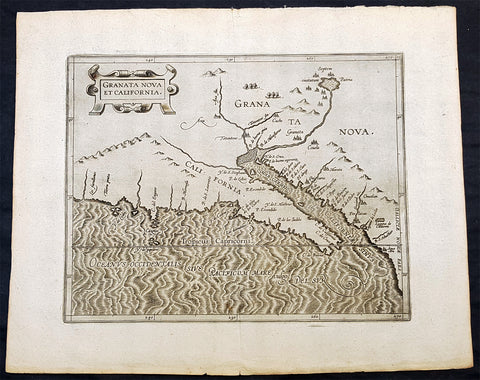
1597 Cornelis Wytfliet Antique Map Early Important Map of California & SW America
- Title : Granata Nova et California
- Size: 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1597
- Ref #: 41716
Description:
A fine original antique, and incredibly important map the first to focus on California & the SW was published by Cornelis van Wytfliet in the 1597 edition of Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum.
The first printed map devoted to California and the south-west of the present day United States. One of the most interesting features is the depiction of so many fabled places largely from Spanish sources. Most notable amongst these are the seven cities of Cibola. The seven cities originated from the narrative of Fray Marcos de Niza in 1539. Some of the other nomenclature originates from Coronados epic exploration. The outline map is fairly accurate and is derived largely from Petrus Plancius large world map of 1592. The main coastal irregularity is the westward slant of the Californian coastline. Bearing in mind that it would be shown as part of an island in twenty five years, this is quite forgivable. No other states of the map are known and all issues are without text on the back (Burden 106).
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 15in x 12in (380mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/4in x 9 1/4in (285mm x 235mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
In 1597 Cornelis van Wytfliet published his Augmentum to Ptolemys Geography. Dedicated to Philip III of Spain it is a history of the New World to date, recording its discovery, natural history etc. For the book Wytfliet had engraved nineteen maps, by whom we do not know, one of the world and eighteen regional maps of the Americas. As such this book can be truly called the first atlas of the New World, America.
Wytfliet, Cornelis van d. 1597
Cornelius Wytfliet or Cornelis van Wytfliet was a geographer from Leuven in the Habsburg Netherlands, best known for producing the first atlas of the Americas.
Cornelius was the son of Catherine Huybrechts and her husband, Gregorius Wytfliet, who was advocate fiscal of Leuven University from 1557 to 1594. After graduating Licentiate in Laws from the University of Leuven, Wytfliet moved to Brussels and became secretary to the Council of Brabant. He died in or shortly after 1597, when his Descriptionis Ptolemaicae Augmentum (a work adding new discoveries to Ptolemys description of the world) was published
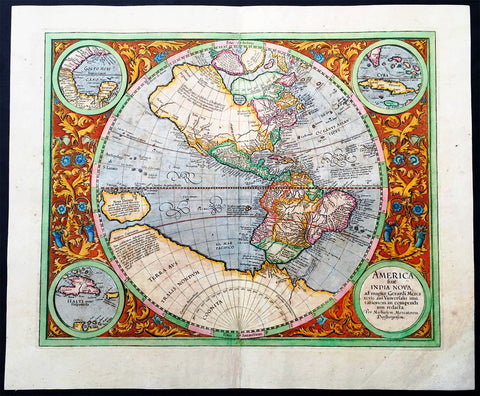
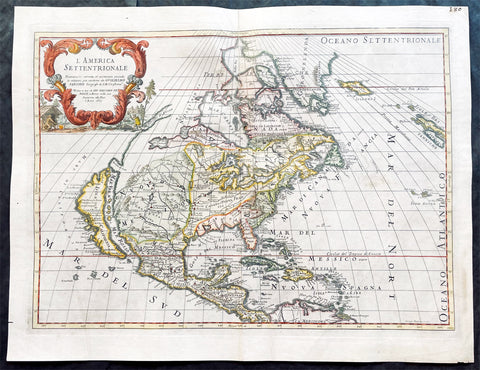
1639 Henricus Hondius Antique 1st Edition Map of North America California Island
- Title : America Septentrionalis
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43161-1
- Size: 23in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Description:
This magnificent original copper-plate engraved antique rare 1st state map of North America, with California as an Island, by Henricus Hondius was published in the 1639 French edition.
There were only 3 publications of this map by Hondius in the 1630s & 40s with Jan Jansson replacing the map with his signature in 1641.
The now seldom seen first state of an important, early Dutch map of North America. It one of the first Dutch atlas maps to show California as an island, preceded only by the Hondius Hondius world map of 1633. A note on the map recounting the story of the origin of the California-as-an-island refers to a Dutch captain who obtained a map of California depicted as an island from a captured Spanish ship. The note even provides the dimensions of the island. The Hondius map was an important conduit for bringing the island myth into the cartographic mainstream. Further, Tooley noted the map was also first attempt in Holland to add lakes connected to the St. Lawrence. One of these lakes on the map is in the approximate shape and position of Lake Ontario.
This was also one of a very few, early Dutch maps specifically of North America (as opposed to the entire Western Hemisphere). Aside from the rare De Jode map of 1593, this is the only folio-sized map of North America produced during the entire Dutch Golden Age.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 20in (595mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 19in (500mm x 470mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin extended from plate-mark
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Henricus Hondius beautifully engraved map of North America had significant influence in perpetuating the theory of California as an island. This was of the influence of his powerful Dutch publishing house with no earlier maps representing California as an island maps having such a wide audience. The 1630s were a decade of constant development in the houses of Blaeu, Hondius & Jansson. It is interesting to note that Blaeu never produced a single sheet map of North America; producing a map of just the whole American continent, first produced in 1617. Also during this decade Joannes Janssonius became an active partner of Hondius, and although this map does not bear his mark, it is believe it was his creation, based on the very similar South American, at the same time, displaying his name.
Cartographically this map is a careful composition of many different sources. The depiction and nomenclature of the west, along with that of California, derive directly from the Henry Briggs The North Part of America, 1625. A legend placed strategically over the north-west coastline offers the opportunity to discontinue a coastline least understood. An unnamed lake still feeds a Rio del Norto flowing incorrectly south-west into what should be the headwaters of the Gulf of California. On the east bank of this river is Real de Nueua Mexico, or Santa Fe. The Gulf of Mexico and the Florida peninsula originate from the Hessel Gerritsz chart of c.1631.
The east coast, however, is harder to define; the south-east appears to be quite generic in form. It is the area north of here that does not appear to be from a particular source. The Chesapeake Bay area is defined in about as much detail as the scale and style of the map will allow, Iames Towne being clearly identified. NOVUM BELGIUM is unlike any other before it, the area between the Zuitt Reuier (Delaware River) and the Noort R (Hudson River) being greatly elongated on a north-east to south-west axis. New Amsterdam is curiously not designated although Fort Orange is present. For New England just a select few names have been chosen from John Smiths map of the area, 1616. The Gulf of St. Lawrence appears to follow de Laet more than Champlain. The latter is used to depict a single great Lake; however, its name, Lac des Iroquois, is borrowed from one nearby. Interestingly the author chose not use Champlains more recent 1632 map but the earlier 1612 Carte Geographique De La Nouvelle France; To avoid unknown territory he does not venture the river system further west, unlike Champlain. Along the Atlantic coast of Labrador we find for the first time much Dutch Nomenclature, reflecting their increased whaling activities in these waters. Hudson Bay is clearly derived from Briggs, 1625, except for the west coast where he introduces the cartography of Thomas James, 1633. The addition of a fox here could be seen as a veiled reference to Luke Foxe, whose own map of the previous year bears just such an animal.
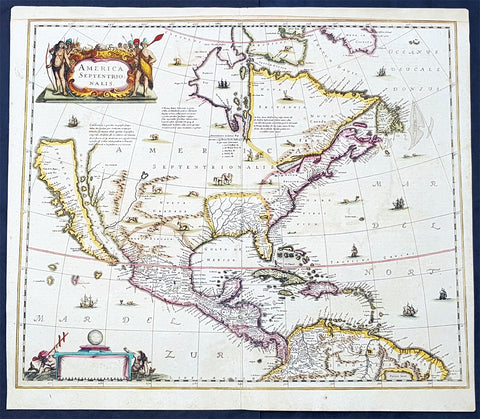
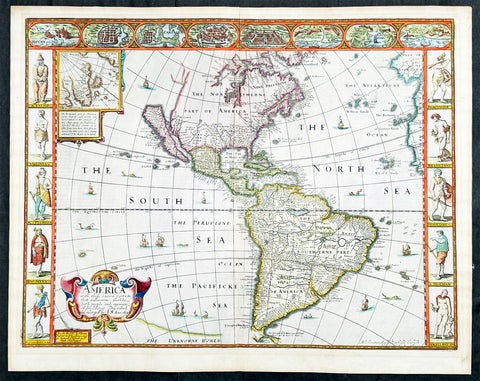
1626 (1676) John Speed Antique Map of America - Beautiful Condition
- Title : America with those known parts in that unknowne world both people and manner of buildings discribed and inlarged by I.S. Ano 1626.
- Date : 1626 (1676)
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 430mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35654
Description:
This original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of America by John Speed was published in the 1676 Bassett & Chiswell edition of Speeds famous atlas Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World.
One of the best examples of this map I have seen. Beautiful original condition with original hand colour, clean heavy impression on sturdy clean paper with original margins, which is very rare.
This 1626 map of America is the fourth or 1676 state and is one of the most iconic maps of America, surrounded by decorative vignettes illustrating the indigenous peoples and cities of the Americas. This map is both beautiful and important. It features a number of first, including being the first atlas map to depict California as an island and to accurately depict the east coast of North America. Cartographically it follows on the earlier maps of the Dutchman Abraham Goos, the engraver, with updates to reflect the 1625 Briggs vision of an insular California
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17in (545mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/4in x 15 1/2in (515mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 3/4in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Old archival hinge paper top of verso, not affecting the map.
Background:
This is the first atlas map to represent California as an island. The idea of an insular California first appeared as a work of fiction in Garci Rodriguez de Montalvo's c. 1510 romance Las Sergas de Esplandian, where he writes
.....Know, that on the right hand of the Indies there is an island called California very close to the side of the Terrestrial Paradise; and it is peopled by black women, without any man among them, for they live in the manner of Amazons.....
Baja California was subsequently discovered in 1533 by Fortun Ximenez, who had been sent to the area by Hernan Cortez. When Cortez himself traveled to Baja, he must have had Montalvo's novel in mind, for he immediately claimed the 'Island of California' for the Spanish King. By the late 16th and early 17th century ample evidence had been amassed, through explorations of the region by Francisco de Ulloa, Hernando de Alarcon and others, that California was in fact a peninsula. However, by this time other factors were in play. Francis Drake had sailed north and claimed 'New Albion' (identified here on the northwest coast of California Island) near modern day Washington or Vancouver for England. The Spanish thus needed to promote Cortez's claim on the 'Island of California' to preempt English claims on the western coast of North America. Henry Briggs, an English mathematician, began promoting the idea of an insular California in 1622, citing the journals of Friar Antonio de la Ascension, who accompanied the 1602-03 Sebastian Vizcaino expedition. The significant influence of the Spanish crown on European cartographers caused a major resurgence of the Insular California theory. Just before this map was made Eusebio Kino, a Jesuit missionary, traveled overland from Mexico to California, proving conclusively the peninsularity of California. Even so, it was ultimately a 1747 royal decree from King Ferdinand VII of Spain that finally forced cartographers to give up on the alluring idea.
Other elements of interest in North America are the complete absence of the Great Lakes - which in 1626 had yet to be conceived of by any European cartographers. The Straits of Anian appear tenuously in the extreme northwest, just above California. Just east of the 'o' in 'California', on the continental mainland, there is a curious ghosted in lake called the 'Lagueo de Oro.' We have found no references or explanation for this. None of the legendary kingdoms of gold, Quivara, Teguayo, Cibola, etc. are noted. The western portions of the Hudson Bay are unmapped - suggestive of their unexplored status. The addition of Long Island and Boston, in notably darker print, are important updates over the earliest editions.
South America offers much of interest including the mythical Lake Parimia, in Guiana. The legend of Parima is associated with the English adventurer Sir Walter Raleigh's search for El Dorado. Believing El Dorado to lie in the northern part of the Amazon, Raleigh sailed down the Orinoco River just before the onset of the rainy season. Reaching a remote tribal village, Raleigh noted canoes arriving bearing gold, silver, and other treasures. Asked where the gold came from, the natives replied, 'Manoa', the term for the tribe to which the river traders belonged. Manoa, the natives claimed could be reached following a long river voyage southward to a Great Lake, called Parima. Raleigh and his associates immediately associated Manoa and Lake Parima with the golden kingdom of El Dorado, though they never visited the city or lake. Subsequent maps, including this one, mapped el Dorado and Lake Parima in this location for several hundred years. Both Raleigh and the natives were describing an actual event known to occur annually in the region. Rains would annually swell the Amazon and Orinoco river systems creating a linkage in the Rupununu flood plain, which, during heavy rains, can resemble a massive lake. The Manoa were a large and populous trading nation active in pre-colonial days whose vast empire, based in the Amazon Basin, extended form the Andes to the Orinoco. Curiously, in addition to noting the city of Manoa on Lake Parima, D'Anville also correctly maps the center of the ancient Manoan civilization between the Amazon tributaries Rio Negro and Rio Yapura. Sadly the Manoa and many of the other populous South American indigenous nations noted by the earliest explores to the region vanished, brought low by European epidemics.
Another mythical lake, Eupana, appears further south connecting the Rio de la Plata and the Paraguay River to the R. Real, thus turning eastern Brazil into an island. This is a update over many earlier maps which connected Eupana directly to the Amazon. Far in the south Speed presents us ith another anomaly, the Straits of Le Maire, which separates Tierra de Fuego from another mysterious stretch of land labeled 'States Land.' The is in fact the modern island of Isla de los Estados, the southeastern most point in South America. Jacob le Maire and his pilot Willem Schouten passed to between this island and Tierra del Fuego on their 1615 voyage around Cape Horn and into the Pacific.
In the high Arctic, near Iceland and Greenland, the supposed islands of Frisland and Brasil are noted. Frisland is little more than a double mapping of Iceland. Brasil, also known as Hy-Brasil, is a phantom island north Atlantic just west of Ireland. In Irish myths it was said to be cloaked in mist, except for one day every seven years, when it became visible but still could not be reached. Little is known of this origins of this myth, but it appears on maps in various forms from about 1325. The last known appearance was in 1865 when it appeared on a nautical chart as 'Brasil Rock.' Some speculate that it may be an early reference to Porcupine Bank, a shoal in the Atlantic Ocean about 200 kilometres (120 mi) west of Ireland.
Speed's map of America is especially noteworthy for its surrounded vignettes. To either side of the map proper there are various vignettes illustrating the indigenous peoples of the America. These includes natives of Greenland, Virginia, Florida, Mexico, New England, Peru, Brazil, and Tierra del Feugo.n Along the top of the map there are eight city views: Havanna, Santo Domingo, Cartagena, Mexico City, Cuzco, the isle of Moca, Rio de Janeiro, and Olinda.
This map was engraved for John Speed by Abraham Goos. It is the fourth state of the map issued by Thomas Bassett of Fleet Street and Richard Chiswell of St. Paul's Churchyard. Bassett, Chiswell, and others continued to republish Speed's work well after his death. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman, Burden)
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
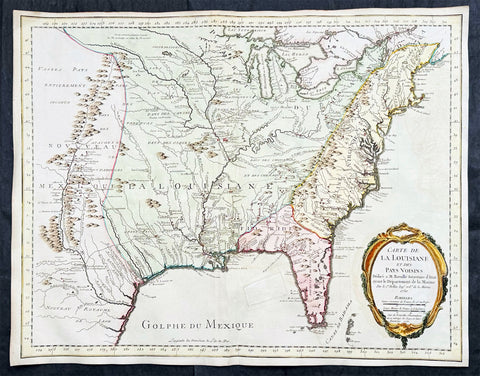
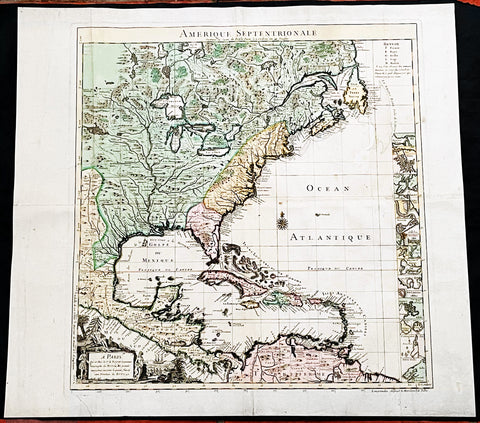
1750 (1755) Nicolas Bellin Very Scarce Large Antique Map of North America
- Title : Carte de La Louisiane et Des Pays Voisins Dediee a M. Rouille Secretairr 'd Etat ayant le Departement de la Marine . . . 1750 . . . Sur de Nouvelle Observations on a corrigee les Lacs, et leurs Enviorns. 1755.
- Date : 1750 (1755)
- Size: 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35661
Description:
This large original very scarce hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of North America by Nicolas Bellin, in 1750 - dated - and updated in 1755, was published as a single map by Nicolas Bellin in Paris.
Extremely important, large and scarce 1755 map of North America issued at the outbreak of the French and Indian War (1754 - 1763). Centered on the vast Mississippi Valley, the map covers from the Rio Grande to the Atlantic Seaboard and from Lake Superior to the Florida Keys. While first issued in 1750, the present map has been updated considerably to represent French, English, and Spanish claims at the outbreak of the French and Indian War. Most of the most important battle sites are forts are noted, including Fort Duquesne, Fort Necessity, Fr. Le Boeuf, Fort Presqu'Isle, and Fort St. Frederic, among others.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early & later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Small professional restoration in GOM
Verso: - None
Background:
The map presents the much of the modern United States as the French understood it at the outbreak of the war. Spanish territory is red, English territory is yellow, and French territory is green. The British are here restricted to the coastal lands east of the Appalachian Mountains, and bounded on the south by the Altamaha River, which forms the boundary with Spanish Florida. French Territorial claims are expansive, encompassing roughly 2/3rds of the land and controlling the most valuable waterways, including the Great Lakes, the Ohio, and the Mississippi. Forts, mission settlements, mines, and trading posts dot the Mississippi Valley, but in truth, most of these were, by this time, only loosely manned or altogether abandoned - hardly an argument for effective occupation.
This map features a wealth of cartographic information drawn in part from the Guilaume de L'Isle map of 1718, but has been expanded considerably with new information from the the Chaussegros de Lery manuscripts and Pierre-Francois-Xavier de Charlevoix s Histoire et description generale de la Nouvelle France. Of note is the curious mountain range running through Michigan.
The inclusion of Fort Necessity is significant, as it suggests this map was issued just months after the construction of the fort and George Washington's disastrous defeat there. It underscores how quickly information moved - even through the outback of the New World and active war. For this map to have been made, news of the events, as well as cartographic reconnaissance, would have had to move rapidly from Fort Duquesne, down the Ohio River, then down the full length of the Mississippi, then across the Atlantic to Paris. There Bellin would have had to study the work, reconcile it with his older maps, update and re-engrave them accordingly, and then get the map to the presses for distribution. The whole is a remarkable accomplishment, but may explain somewhat this maps scarcity, as in a short time, much of the data he would be irreverent.
The map is dedicated to Antoine-Louis Rouillé, comte de Jouy (1689 - 1761). Rouillé replaced Jean-Frédéric Phélypeaux, 1st Count of Maurepas (1701 - 1781), Bellin's former patron, as Secretary of State for the Navy (Ministère de la Marine) on July 24, 1754, just in time for the French and Indian War. Bellin, who worked under the Navy Department, would have been highly motivated to engender Rouillé patronage and good well, making the dedication unsurprising.
The map was separately published in Paris, France by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin. It is dedicated to M. Rouillé. It represents the second state of the map, 1755, issued during the French and Indian War. Examples are extremely scarce. We have identified only three examples, including this map, in the last 20 years of market history. The map is further not identified in Cumming, Karpinski, Ehrenberg, or Phillips. The OCLC notes examples in 8 institutions, but upon closer inspection many of these appear to be digital resources and do not represent any actual holdings.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
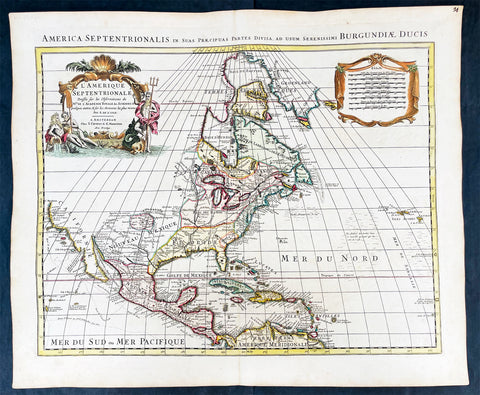
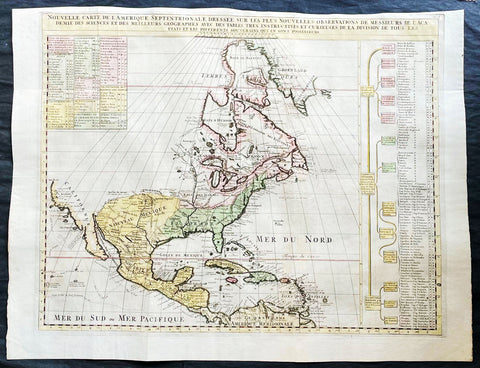
1730 Delisle and Covens & Mortier Foundation Antique Map of North America
- Title : L Amerique Septentrionale dressee sur les Observations de Mrs. De L Academie Royale des Sciences & quelques autres & sur les Memoires les plus recens Par G De L Isle A. Amsterdam Chez I Covens & C Mortier Avec Privilege.
- Ref #: 93501-1
- Size: 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 540mm)
- Date : 1700 (1730)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This is without doubt one of the most important foundation maps, of North America, published in the early to mid 18th century. This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map by Johannes Covens & Pierre Mortier, after Guillaume Delisle, that was published in 1730 in Atlas nouveau de dicerses cartes choisies des Meilleurs Geographes comme Sanson, G De Lisle &c....A Amsterdam.....
The first edition of this map was mistakenly dedicated to Nicolas Sanson, in the title. This oversight was corrected to Delisle in this 1730 edition.
This map is beautiful with original borders beautiful hand colouring on heavy stable paper.
Covens & Mortier (fl 1721-1866) was an eighteenth century cartographic publishing house. The company was founded by Johannes Covens (1697-1774) and Cornelis Mortier (1699-1783) and was located in Vijgendam in Amsterdam .
The collaboration between the two men began after the death of Pieter Mortier (1661-1711), son of a French political refugee. In 1690, Mortier obtained the privilege of distributing maps and atlases from French publishers, in the Netherlands . His widow continued business until his death in 1719 . His son Cornelis took over the business, under the name of his father.
In November 1721 Cornelis Mortier founded a company with Johannes Covens I. He was married in the same year to Corneliss sister. Thus the company of Covens & Mortier was born.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25 1/2in x 21 1/2in (650mm x 540mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
There are many reasons why this rare 1st edition foundation map is important. It contains detail of radical changes both to the interior of North America and helps debunk many fundamentally held ideas of the coastlines. Some of these ideas included The Great lakes, California as an island and previously invented ideas of the interior, NW & NE coastlines.
Specifically the shape of the Great Lakes are changed based on information from the great Italian cartographer Vincenzo Coronelli.
The Mississippi valley is well developed with recent French settlement of d\\\'Iberville at Bilochy and the forts at Bon Secours and St Louis. The map also corrects the error of the western swing of the lower part of the Mississippi River, moving its mouth to essentially its correct position on the Gulf of Mexico.
Delisle has also corrected longitude positions and was the first to revert to a peninsular form for California. He stops his western coast at Cape Mendocin and is the first map to show the Saragossa Sea.
The map also illustrates the routes of explorers such as Cortez, Drake, D\\\'Olivier, Gaeten and Mendana, and indicates the locates of a number of Indian tribes, including the Apaches.
As this is a French map we see many of the French strong points in the NE such as Tadousac, Quebec, Fort Sorel, Montreal & Fort Frontenac included. The English settlements are confined to the east of the Alleghenies, with Fort and River Kinibeki as the border between New England and Arcadia.
Such was the improvement of this map, and the sterling reputation of Delisle, that within a few years other publishers issued their own copies of the map, which continued to appear until the 1780s. The importance of this map cannot be overstated in the progression of American cartography. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1756 J B Nolin Large Rare Antique Map of North America, Great Lakes, French Indian War (1754-63)
- Title : Carte Du Canada et de La Louisiane Qui Forment La Nouvelle France et Des Colonies Anglois . . . 1756
- Date : 1756 (dated)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 93505
- Size: 30in x 21 1/2in (760mm x 555mm)
Description:
This large, magnificent and very rare original copper plate engraved antique pre-revolutionary French Indian war map of North America was engraved by Jean Baptist Nolin in 1756, dated in cartouche.
This is an important and rare pre-revolutionary French Indian war map, which focuses on the territorial claims of France and Great Britain. Highly detailed showing many early towns and cities, some forts, Indian villages, and tribal territory. Includes the following French text describing the territories claimed by France, Great Britain & Spain in North America: Description du Canada below the cartouche,
This highly detailed map focuses on the territorial claims of France and Great Britain during the French Indian War (1754-63) highly detailed, with a heavy emphasis on the mapping of the Great Lakes. A must for any collector of maps of North America.
We have found records of only 7 sales of this map since 1983, and currently there is only one other to be found for sale.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 21 1/2in (760mm x 555mm)
Plate size: - 28in x 20 1/2in (720mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repair to left margin, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Old small repair to top centerfold
Verso: - Re-enforce along centerfold
Background:
The French and Indian War (1754–63) comprised the North American theatre of the worldwide Seven Years War of 1756–63. It pitted the colonies of British America against those of New France. Both sides were supported by military units from their parent countries, as well as by American Indian allies. At the start of the war, the French North American colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British North American colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on the Indians. The European nations declared war on one another in 1756 following months of localized conflict, escalating the war from a regional affair into an intercontinental conflict.
The name French and Indian War is used mainly in the United States. It refers to the two enemies of the British colonists, the royal French forces and their various American Indian allies. The British colonists were supported at various times by the Iroquois, Catawba, and Cherokee, and the French colonists were supported by Wabanaki Confederacy members Abenaki and Mikmaq, and Algonquin, Lenape, Ojibwa, Ottawa, Shawnee, and Wyandot.
British and other European historians use the term the Seven Years War, as do English-speaking Canadians. French Canadians call it La guerre de la Conquête (the War of the Conquest) or (rarely) the Fourth Intercolonial War.
Fighting took place primarily along the frontiers between New France and the British colonies, from Virginia in the south to Newfoundland in the north. It began with a dispute over control of the confluence of the Allegheny River and Monongahela River called the Forks of the Ohio, and the site of the French Fort Duquesne in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The dispute erupted into violence in the Battle of Jumonville Glen in May 1754, during which Virginia militiamen under the command of 22-year-old George Washington ambushed a French patrol.
In 1755, six colonial governors in North America met with General Edward Braddock, the newly arrived British Army commander, and planned a four-way attack on the French. None succeeded, and the main effort by Braddock proved a disaster; he lost the Battle of the Monongahela on July 9, 1755 and died a few days later. British operations failed in the frontier areas of Pennsylvania and New York during 1755–57 due to a combination of poor management, internal divisions, effective Canadian scouts, French regular forces, and Indian warrior allies. In 1755, the British captured Fort Beauséjour on the border separating Nova Scotia from Acadia, and they ordered the expulsion of the Acadians (1755–64) soon afterwards. Orders for the deportation were given by William Shirley, Commander-in-Chief, North America, without direction from Great Britain. The Acadians were expelled, both those captured in arms and those who had sworn the loyalty oath to His Britannic Majesty. Indians likewise were driven off the land to make way for settlers from New England.
The British colonial government fell in the region of modern Nova Scotia after several disastrous campaigns in 1757, including a failed expedition against Louisbourg and the Siege of Fort William Henry; this last was followed by Indians torturing and massacring their British victims. William Pitt came to power and significantly increased British military resources in the colonies at a time when France was unwilling to risk large convoys to aid the limited forces that they had in New France, preferring to concentrate their forces against Prussia and its allies in the European theater of the war. Between 1758 and 1760, the British military launched a campaign to capture the Colony of Canada (part of New France). They succeeded in capturing territory in surrounding colonies and ultimately the city of Quebec (1759). The British later lost the Battle of Sainte-Foy west of Quebec (1760), but the French ceded Canada in accordance with the Treaty of Paris (1763).
The outcome was one of the most significant developments in a century of Anglo-French conflict. France ceded to Great Britain its territory east of the Mississippi. It ceded French Louisiana west of the Mississippi River (including New Orleans) to its ally Spain in compensation for Spains loss to Britain of Florida. (Spain had ceded Florida to Britain in exchange for the return of Havana, Cuba.) Frances colonial presence north of the Caribbean was reduced to the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, confirming Great Britains position as the dominant colonial power in eastern North America.
1719 Alexis Jaillot Large Antique Map of North America, Final Scarce Edition
Antique Map
- Title : Amerique septentrionale divisee en ses principales parties, ou sont distingues les vns des autres les estats suivant qu'ils appartiennent presentemet aux Francois, Castillans, Anglois, Suedois, Danois, Hollandois, tiree des relations de toutes ces nations par le S. Sanson, Geographe Ordinaire du Roy...1719
- Date : 1719
- Size: 37 1/2in x 25in (950mm x 635mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35647
Description:
Alexis Hubert Jaillot first published this map of North America in 1674 in the middle of a centuries old argument as to whether California was indeed an Island or Peninsula. The map was to publish again in 1685, 1690, 1692 & 1695, with very little change to the plate. But in 1719 the plate was re-engraved making significant changes to the eastern seaboard, The Great Lakes, Mississippi River and California. But unlike many publishers of the time, Jaillot did not depict California as a peninsula but straddled both arguments, showing California neither as an Island but also not joined to the mainland, separated quite clearly by the Mer Rouge.
The 1719 date of this map places its publication as first hand information is becoming increasingly undeniable that California is not an Island, but this was at odds with the established idea, that California is an Island. Hence the reason for the change but the obvious resistance to depict California truly as part of the American mainland.. (Ref: Shirley; Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 37 1/2in x 25in (950mm x 635mm)
Plate size: - 34 3/4in x 23in (885mm x 541mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background: Although California was depicted as a Peninsula in the early maps of North America by Mercator in 1531, Ortelius in 1570 and Wytfliet in 1597, this in-fact changed after Father Antonio Ascension mistakenly reported the possiblity of a great opening in the west coast, found by Spanish explorers, that led to a vast inland sea north of Cape Medocin. Father Ascension drew a map depicting his idea of California as an Island in 1620, which he duly sent to the King of Spain. The ship carrying this map and his report was captured by the Dutch and taken to Amsterdam, one of the main centres of European cartography.
California as an Island was first published on a map in 1622 by Herrera but it was the English who first populised the idea with Henry Biggs in 1625 and John Speed in 1626-7. The Dutch followed with Hondius in 1631, De Laet 1633, Blaeu 1635, Visscher 1636 & Jansson in 1638. Such was Visschers and Janssons influence that it was sufficient to swing the whole of European Geography behind them, lasting until well into the 18th century.
One of the first to correct the misconception was Guillaume Delisle at the beginning of the 18th century. He was confident enough to leave blank his maps where real knowledge was deficient. Father Eusebio Kino was the first known European to cross the mainland to the peninsula of Califorina and in 1705 printed a map debunking the misconception. His view though was rejected by many of the time including Moll, Senex, Overton, De Fer Chatelain, Keulen, Homann & Seutter. The latter publishing his map of America with California as an Island up until 1750. Between 1715-30 Van Der Aa tried to have it both ways publishing separate maps with California as both an Island & Peninsula. Finally in 1747 King Ferdinand VII by a Royal Decree declared "California is not an Island" after a voyage along the west-coast by Father Consag in 1746.
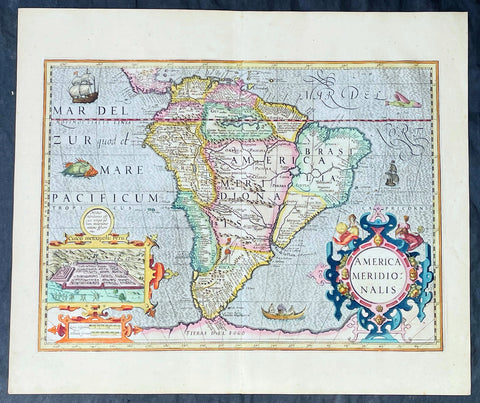
1628 Henricus Hondius Antique Map of South America, inset of Cusco - Beautiful
Antique Map
- Title : America Meridionalis
- Date : 1628
- Size: 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35645
Description:
This superb, original antique hand coloured folio map of South America, was engraved by Jodocus Hondius & published by his son Henricus for the continuation of Gerard Mercators 1628 French edition of Atlas.
This map is in superb condition with beautiful hand colouring, a deep heavy imprint denoting an early pressing on clean, heavy paper. Original margins, one of the best I have seen for sometime.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22in x 18 1/2in (560mm x 470mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 14 1/4in (495mm x 363mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The interior of the map is dominated by the large mythical lake Parime Lacus straddling the equator below Venezuela along with an interesting & mythical continental river system. The huge Rio de la Plata river flows south from the conjectural Eupana Lacus in Brazil, while the R. Grande flows north from the same lake, ostensibly making Brazil an island.
The Strait of Magellan is represented, but Tierra del Fuego (Fogo) is named as part of the mythical Great Southern Land instead of an island.
The map is beautifully engraved with a stippled wave pattern Pacific & Atlantic Oceans, filled with Spanish & English ships, sea monsters and native canoe. The continent is flanked by two elaborate Baroque cartouches; title to the right and a large inset plan of the Capital of the Ancient Incan Empire, Cuzco. A sole representation of the conquered Native Americans is engraved as a lone Indian with a bow and arrow in the interior of Patgonia.
Between 1452 and 1493, a series of papal bulls (Dum Diversas, Romanus Pontifex, and Inter caetera) paved the way for the European colonization and Catholic missions in the New World. These authorized the European Christian nations to \"take possession\" of non-Christian lands and encouraged subduing and converting the non-Christian people of Africa and the Americas.
In 1494, Portugal and Spain, the two great maritime powers of that time, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas in the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west. Through the treaty they agreed that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly between the two countries. The treaty established an imaginary line along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37\' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (which is now known to include most of the South American soil), would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. Because accurate measurements of longitude were not possible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
In 1498, during his third voyage to the Americas, Christopher Columbus sailed near the Orinoco Delta and then landed in the Gulf of Paria (Actual Venezuela). Amazed by the great offshore current of freshwater which deflected his course eastward, Columbus expressed in his moving letter to Isabella I and Ferdinand II that he must have reached heaven on Earth (terrestrial paradise):
Great signs are these of the Terrestrial Paradise, for the site conforms to the opinion of the holy and wise theologians whom I have mentioned. And likewise, the [other] signs conform very well, for I have never read or heard of such a large quantity of fresh water being inside and in such close proximity to salt water; the very mild temperateness also corroborates this; and if the water of which I speak does not proceed from Paradise then it is an even greater marvel, because I do not believe such a large and deep river has ever been known to exist in this world.
Beginning in 1499, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it into colonies.
European diseases (smallpox, influenza, measles and typhus) to which the native populations had no resistance were the overwhelming cause of the depopulation of the Native American population. Cruel systems of forced labor (such as encomiendas and mining industry\'s mita) under Spanish control also contributed to depopulation. Lower bound estimates speak of a decline in the population of around 20–50 per cent, whereas high estimates arrive at 90 per cent.[42] Following this, African slaves, who had developed immunity to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their American subjects to Christianity and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end. However, most initial attempts at this were only partially successful; American groups simply blended Catholicism with their traditional beliefs. The Spaniards did not impose their language to the degree they did their religion. In fact, the missionary work of the Roman Catholic Church in Quechua, Nahuatl, and Guarani actually contributed to the expansion of these American languages, equipping them with writing systems.
Eventually the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a Mestizo class. Mestizos and the Native Americans were often forced to pay unfair taxes to the Spanish government (although all subjects paid taxes) and were punished harshly for disobeying their laws. Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers. This included a great number of gold and silver sculptures, which were melted down before transport to Europe.
In 1616, the Dutch, attracted by the legend of El Dorado, founded a fort in Guayana and established three colonies: Demerara, Berbice, and Essequibo.
In 1624 France attempted to settle in the area of modern-day French Guiana, but was forced to abandon it in the face of hostility from the Portuguese, who viewed it as a violation of the Treaty of Tordesillas. However French settlers returned in 1630 and in 1643 managed to establish a settlement at Cayenne along with some small-scale plantations.
Since the sixteenth century there were some movements of discontent to Spanish and Portuguese colonial system. Among these movements, the most famous being that of the Maroons, slaves who escaped their masters and in the shelter of the forest communities organized free communities. Attempts to subject them by the royal army was unsuccessful, because the Maroons had learned to master the South American jungles. In a royal decree of 1713, the king gave legality to the first free population of the continent: Palenque de San Basilio in Colombia today, led by Benkos Bioho. Brazil saw the formation of a genuine African kingdom on their soil, with the Quilombo of Palmares.
Between 1721 and 1735, the Revolt of the Comuneros of Paraguay arose, because of clashes between the Paraguayan settlers and the Jesuits, who ran the large and prosperous Jesuit Reductions and controlled a large number of Christianized Indians.
Between 1742 and 1756, was the insurrection of Juan Santos Atahualpa in the central jungle of Peru. In 1780, the Viceroyalty of Peru was met with the insurrection of curaca Condorcanqui or Tupac Amaru II, which would be continued by Tupac Catari in Upper Peru.
In 1763, the African Cuffy led a revolt in Guyana which was bloodily suppressed by the Dutch. In 1781, the Revolt of the Comuneros (New Granada), an insurrection of the villagers in the Viceroyalty of New Granada, was a popular revolution that united indigenous people and mestizos. The villagers tried to be the colonial power and despite the capitulation were signed, the Viceroy Manuel Antonio Flores did not comply, and instead ran to the main leaders José Antonio Galán. In 1796, Essequibo (colony) of the Dutch was taken by the British, who had previously begun a massive introduction of slaves.
During the eighteenth century, the figure of the priest, mathematician and botanist José Celestino Mutis (1732–1808), was delegated by the Viceroy Antonio Caballero y Gongora to conduct an inventory of the nature of the Nueva Granada, which became known as the Botanical Expedition, which classified plants, wildlife and founded the first astronomical observatory in the city of Santa Fé de Bogotá.
On August 15, 1801, the Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt reached Fontibón where Mutis, and began his expedition to New Granada, Quito. The meeting between the two scholars are considered the brightest spot of the botanical expedition. Humboldt also visited Venezuela, Mexico, United States, Chile, and Peru. Through his observations of temperature differences between the Pacific Ocean between Chile and Peru in different periods of the year, he discovered cold currents moving from south to north up the coast of Peru, which was named the Humboldt Current in his honour.
Between 1806 and 1807, British military forces tried to invade the area of the Rio de la Plata, at the command of Home Riggs Popham and William Carr Beresford, and John Whitelocke. The invasions were repelled, but powerfully affected the Spanish authority.
1633 Mercator Antique Map of America & The Great Southern Land - Terra Australis
- Title : America sive India Nova. ad magna Gerardi Mercatoris aui Universalis imitationem in compendium redacta. Per Michaelem Mercatorem Duysburgensem
- Ref #: 61017
- Size: 21 1/2in x 17 3/4in (545mm x 450mm)
- Date : 1633
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique early map of America and the Great Southern Continent (Terra Australis) that was envisaged in the southern Hemisphere, prior to the discovery of Australia by Captain Cook in 1769 - the only map attributed to Gerard Mercator's Grandson Michael - was published in the 1633 French edition of Mercator's Atlas.
This map is magnificent with beautiful original hand colouring, wide margins and stable paper. Backed with transparent archival Japanese paper. Original colouring such as this is scarce and hard to find.
Condition Report:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red, green, orange, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/2in x 17 3/4in (545mm x 450mm)
Plate size: - 18 1/2in x 14 3/4in (470mm x 376mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - Uniform age toning, light creasing & uplift along center-fold
Verso: - Backed with transparent archival Japanese paper
Background: Largely based on Rumold Mercator's world map of 1587, this map aptly reflects 16th-century knowledge, theories and suppositions regarding the New World. Naturally, most of this new knowledge was coastal, and configurations of any large areas were greatly hampered by the lack of a sound means of determining longitude. Nevertheless, the collective accomplishment of explorers and mapmakers represented in this map is astounding, showing in a generally correct way the vast extent of the New World. "A few of the most famous theories are still present: a large inland lake in Canada, two of the four islands of the North Pole, a bulge to the west coast of South America and the large southern continent" (Burden).
The map appeared in 1595 and 1606 editions of the Atlantis Pars Altera , after which the plate was sold to Jodocus Hondius, who reissued the maps in varying editions through 1639. The present example includes French text on verso, confirming it to be a Hondius issue.
Several of the more fascinating theories are present, including the multiple islands of the North Polar Sea, bulging South America and vast unknown southern continent. The St. Lawrence crosses half the continent. No sign of the English in Virginia. The search for a water course across North America is interupted only by some mid-continental mountains. Evidence of the Spanish explorations in the Southwest is present and the Colorado and Gila Rivers already reflect a good knowledge of this area, as does the peninsular Baja California, based upon Uloa's work.
The depiction of the NW Passage and Western North America are also of great interest. Annotations reference the voyages of Columbus and Magellan.(Ref: Burden; Koeman; Tooley; M&B)
1638 Joan Blaeu Antique Map of America - Americae nova Tabula
- Title : Americae nova Tabula Auct: Guiljesino Blaeuw
- Date : 1638
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref # : 50685
- Size : 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 450mm)
Description:
This magnificent, classic hand coloured original antique map of America 2nd State - the quintessential image of 17th America - was published in the 1638 French edition of Joan Blaeus Atlas Novus. This map is in wonderful condition with a few minor repairs as mentioned below.
General Condition:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original color
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic & beautiful
Paper size: - 23in x 18 1/2in (585mm x 450mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 16 1/2in (555mm x 415mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Professional repair to centerfold, no loss.
Plate area: - Small professional repair to below Atlantic monster. Center-fold creases & re-joined at bottom, slight separation
Verso: - Creasing and restoration to center-fold, top & left margin, no loss
Background:
Originally issued by Joan Blaeus father, Willem, as early as 1617, this general map of the Americas was one of the longest lived plates in the atlas, having been used as an atlas map since 1630.
Here is the general seventeenth century European view of the Western Hemisphere: the delineation of the coasts and the nomenclature of the Pacific as well as the Atlantic coasts are basically Spanish in origin and follow the maps of the Fleming Abraham Ortelius and his countryman Cornelis Wytfliet. To these, Willem Blaeu inserted, on the east coast, the English names given by the Roanoke colonists in Virginia, and by Martin Frobisher, John Davis and Henry Hudson in the far north. In Florida and along the St Lawrence, Blaeu added the names given by the French settlers, almost the only memorials to their ill-fated venture in Florida during the latter part of the sixteenth century.
When Blaeu first made his map in the early years of the seventeenth century, Europeans still had no real knowledge of the nature of the Mississippi system. From the expedition journals of Hernando de Soto (1539 - 1543) they had inferred an extensive range of mountains trending eastwards to the north of the Gulf of Mexico in la Florida apparently precluding a great river system. The Great Lakes were as yet unknown although by the time Blaeu issued this map in its atlas form in the Huron region together with the hearsay accounts from Coral Indians were becoming well known through his 1632 map of the region. Evidently, this appears to have been unknown to Blaeu at the time, but surprisingly, he never incorporated the information on later printings of the map. The same applies to Manhattan and Long Island as well, despite the fact that only a short distance from Amsterdam, the Leiden academic Johannes D Late had published the first edition of his monumental work on the Americas which provided source material for any number of maps of the Americas throughout the remainder of the century and beyond.
In common with the other general continental maps in Blaeus atlas's, he has provided perspective plans or views of settlements in the Americas, including Havana, St Domingo, Cartagena, Mexico, Cusco, Potisi, I.la Moca in Chile, Rio Janeiro and Olianda in Pharnambucco, as well as the vignette illustrations of native figures taken from the accounts of John White (Virginia) or Hans Staden (Brazil) and others. (Ref: Burden; RGS; Koeman; Tooley)
1869 Shannon & Rogers Birds Eye View of New York City - New York Manual
- Title : Designed and Engraved For New York and Environs. The New York Manual 1869
- Size: 16in x 12in (405mm x 275mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1869
- Ref #: 93208
Description:
This original antique lithograph print of New York City by Joseph Shannon & WC Rogers in 1869 (dated) and was published in the 1869 edition of D T Valentines Manual of the Corporation of the City of New York or Valentines Manual.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 12in (405mm x 275mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12in (405mm x 275mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom right margin extended, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued.
Background:
Rare view of the island of Manhattan, New York City by W. C. Rogers. The view depicts the entire island of Manhattan with Hoboken as well as parts of Brooklyn and Queens. Important buildings, especially churches are depicted with considerable accuracy. The harbor itself is full of sailing ships.
William C. Rogers 1860 - 1873 (active) a New York based lithographer best known for his engravings issued in conjuction with Joseph Shannons (Valentines) Manual of the Corporation for the City of New York.
Valentine, David Thomas 1801 - 1869
As the Clerk of the Common Council of New York City, Valentine edited and published a series of books on the history and contemporary facts of New York City entitled Manual of the Corporation Of The City of New York. They became know as Valentines Manuals with updates published annually, between 1841 & 1870. Valentine used his manuals to produce some of the rarest and most important maps & views of the city of New York, some of which occasionally appear on the market. His contribution to the historical record of New York city cannot be over stated.
1768 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique 2nd edition Map of Colonial United States
- Title : Partie De L Amerique Septentrionale, qui Comprend Le Cours De L Ohio...Par le Sr Robert de Vaugondy
- Date : 1768
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93129
- Size: 30in x 22in (760mm x 560mm)
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured, scarce 2nd edition antique map of the east coast of the United States, illustrating the course of the Ohio River and stretching from New England to the Carolinas, north to the Great Lakes and south to the Mississippi - with an inset map of The Carolinas - was published in 1768 by Robert Du Vaugondy in his Atlas Universal.
This is one of the best examples of this map I have seen, beautiful hand colour on age toned heavy paper with original margins with a heavy dark ink denoting an early pressing.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 30in x 22in (760mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19 1/2in (635mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting in top margin
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Second state of the early de Vaugondy map of the British colonies, with changes after the 1763 Treaty of Paris, with Virginia & Carolina extended to the Mississippi and Pennsylvania extended to Lake Erie. The majority of geographical information is based upon John Mitchells great map of North America from the mid 1750s, also drawing from Lewis, Evans on the Middle British Colonies and Joshua Frys and Peter Jeffersons map of Virginia and Maryland. The Mitchell map was the culmination of many years of British surveying in the North American Colonies and was considered one of the best maps of the continent available to Europeans and Americans in the mid-eighteenth century.
De Vaugondys rendition does not copy the full scope of Mitchells map but instead focuses on the colonies stretching from southern Maine to the Carolinas. In the top left corner is an inset of South Carolina and Georgia. De Vaugondy also pays special attention to the river systems and settlements. This map shows some of the earliest accurate information of the trans-Allegheny regions (the Ohio River, Kentucky, Tennessee and Parts of Ohio) and inland areas to the southeast of the Great Lakes and interior of New England.
Maine is still part of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. During this era. The dispute between New Hampshire and New York over who controlled the area which is now Vermont has been resolved. The outbreak of the French & Indian War (Seven Years War) briefly suspended interest in the disputed area, and it was not until 1764 that the British crown upheld New Yorks claim to Vermont. Included is a beautiful title cartouche in the Rococo style. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1758 J N Bellin Large Antique Map of The Caribbean Island of Jamaica
- Title : Carte Particuliere De L Isle De La Jamaique Dressee au Depost des Cartes Plans et Journaux de la Marine . . . M. DCC LVIII
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 82084
- Size: 36in x 24in (915mm x 610mm)
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map, a sea chart, of the Caribbean Island of Jamaica by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 - dated in the title cartouche - was published by the Depot De La Marine, Paris.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36in x 24in (915mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 36in x 23 1/2in (915mm x 600mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - L&R margin cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - Professional restoration to top centerfold, 2 names penned in to top of map & bottom right corner
Verso: - Professional restoration along centerfold
Background:
At the time of publishing the Island of Jamaica was under the British, after 150 years of Spanish rule. The focus of the British was trade and specifically that of Sugar, which required a large labor force. This labor, as in all of the Americas, was supplied from the abhorrent African slave trade.
Jamaica is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Previously inhabited by the indigenous Arawak and Taíno peoples, the island came under Spanish rule following the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1494. Many of the indigenous people died of disease, and the Spanish transplanted African slaves to Jamaica as labourers. The island remained a possession of Spain until 1655, when England conquered it and renamed it Jamaica. Under British colonial rule Jamaica became a leading sugar exporter, with its plantation economy highly dependent on African slaves. The British fully emancipated all slaves in 1838, and many freedmen chose to have subsistence farms rather than to work on plantations. Beginning in the 1840s, the British utilized Chinese and Indian indentured labour to work on plantations.
Spanish Town has the oldest cathedral of the British colonies in the Caribbean. The Spanish were forcibly evicted by the English at Ocho Rios in St. Ann. In the 1655 Invasion of Jamaica, the English, led by Sir William Penn and General Robert Venables, took over the last Spanish fort on the island. The name of Montego Bay, the capital of the parish of St. James, was derived from the Spanish name manteca bahía (or Bay of Lard), alluding to the lard-making industry based on processing the numerous boars in the area.
In 1660, the population of Jamaica was about 4,500 white and 1,500 black. By the early 1670s, as the English developed sugar cane plantations and imported more slaves, black people formed a majority of the population. The colony was shaken and almost destroyed by the 1692 Jamaica earthquake.
The Irish in Jamaica also formed a large part of the islands early population, making up two-thirds of the white population on the island in the late 17th century, twice that of the English population. They were brought in as indentured labourers and soldiers after the conquest of Jamaica by Cromwells forces in 1655. The majority of Irish were transported by force as political prisoners of war from Ireland as a result of the ongoing Wars of the Three Kingdoms at the time. Migration of large numbers of Irish to the island continued into the 18th century.
Jews were expelled from Spain in 1492 and then forcibly converted to Christianity in Portugal, during a period of persecution by the Inquisition. Some Spanish and Portuguese Jewish refugees went to the Netherlands and England, and from there to Jamaica. Others were part of the Iberian colonisation of the New World, after overtly converting to Catholicism, as only Catholics were allowed in the Spanish colonies. By 1660, Jamaica had become a refuge for Jews in the New World, also attracting those who had been expelled from Spain and Portugal.
An early group of Jews arrived in 1510, soon after the son of Christopher Columbus settled on the island. Primarily working as merchants and traders, the Jewish community was forced to live a clandestine life, calling themselves Portugals. After the British took over rule of Jamaica, the Jews decided the best defense against Spains regaining control was to encourage making the colony a base for Caribbean pirates. With the pirates installed in Port Royal, which became the largest city in the Caribbean, the Spanish would be deterred from attacking. The British leaders agreed with the viability of this strategy to forestall outside aggression.
When the English captured Jamaica in 1655, the Spanish colonists fled after freeing their slaves. The slaves dispersed into the mountains, joining the maroons, those who had previously escaped to live with the Taíno native people. During the centuries of slavery, Maroons established free communities in the mountainous interior of Jamaica, where they maintained their freedom and independence for generations. The Jamaican Maroons fought the British during the 18th century. Under treaties of 1738 and 1739, the British agreed to stop trying to round them up in exchange for their leaving the colonial settlements alone, but serving if needed for military actions. Some of the communities were broken up and the British deported Maroons to Nova Scotia and, later, Sierra Leone. The name is still used today by modern Maroon descendants, who have certain rights and autonomy at the community of Accompong.
During its first 200 years of British rule, Jamaica became one of the worlds leading sugar-exporting, slave-dependent colonies, producing more than 77,000 tons of sugar annually between 1820 and 1824. After the abolition of the international slave trade in 1807, the British began to import indentured servants to supplement the labour pool, as many freedmen resisted working on the plantations. Workers recruited from India began arriving in 1845, Chinese workers in 1854.
1630-31 Hondius Antique World & Four Continental Maps America Africa Asia & Europe
- Title : Nova Totius Terrarum; America Noviter Delineata; Africae Nova Tabula; Asia recens summa; Europa Exactissime.
- Date : 1630-31
- Size: 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm) ea
- Condition: (A & A+) Very Good & Fine Condition
- Ref: 43164; 43157; 43158; 43160; 43159
Description:
These 5 original, hand coloured copper plate engraved world and 4 continental maps, engraved by Henricus Hondius between 1630 and 1631 were published in the same 1639 edition of the Hondius/Mercator Atlas.
Henricus Hondius' World and Four Continent Maps are a series of highly detailed and beautifully illustrated and hand coloured maps that represent some of the finest examples of 17th-century cartography & artistry. The world map features ornate illustrations of ships, sea monsters, and mythological creatures, as well as depictions of important cities and landmarks around the globe. The four continent maps - Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas - are similarly detailed and feature intricate illustrations of people, animals, and mythological figures from each region. These maps are notable for their use of the Mercator projection and their accuracy in depicting the size and shape of the continents. Henricus Hondius' maps were highly valued during his lifetime and continue to be prized by collectors and scholars today for their historical significance and artistic beauty.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - Please see background description below
Plate size: - Please see background description below
Margins: - Please see background description below
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see background description below
Plate area: - Please see background description below
Verso: - Please see background description below
Background:
Nova Totius Terrarum: Dated 1630. Beautiful original hand colour, strong clean paper, original margin size. General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 21 1/2in x 15in (545mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Old expert re-enforcement of margins front & verso. 4 small wormholes to margins
Plate area: - Creasing, slight separation of centerfold on bottom section of map
Verso: - Centerfold re-enforced
Overall condition: - VG
America Noviter Delineata: Dated 1631. Beautiful original hand colour, strong clean paper, original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Bottom margin of centerfold re-enforced
Overall condition: - Fine
Africae Nova Tabula: Dated 1631. Beautiful original hand colour, strong clean paper, original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Slight separation to bottom of centerfold
Verso: - Bottom margin of centerfold re-enforced
Overall condition: - Fine
Asia recens summa: Dated 1631. Beautiful original hand colour, strong clean paper, original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Bottom centerfold & left corner margin re-enforced
Overall condition: - Fine
Europa Exactissime: Dated 1631. Beautiful original hand colour, strong clean paper, original margins.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (520mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 19 3/4in x 15in (500mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - Bottom margin re-enforced
Overall condition: - Fine
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1742 Henry Popple & George Le Rouge Large Antique Map of Colonial America
- Title : Amerique Septentrionale Suivant la Carte de Pople....A Paris....Le Rouge...1742
- Date : 16742
- Size: 24 1/2in x 22 1/2in (625mm x 570mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 27093
Description:
This incredibly important, original hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of North America by George Le Rouge, after Henry Popples famous North America map, was published in 1742 - dated.
A handsome key sheet from a French edition of the first large-scale map of colonial North America. Among the 18 inset maps along the right border are ones of Bermuda, Boston, New York City, and Charleston. Popple's original, 1733 map ran to 20 sheets, hence the necessity of a key sheet. It was a semi-official undertaking intended to depict for British colonial administrators the respective North American territories of England, France and Spain. This French-published version, as expected, greatly exaggerates French territory at the expense of both England and Spain.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 22 1/2in (625mm x 570mm)
Plate size: - 20 3/4in x 19 3/4in (525mm x 500mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (30mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing along margins
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - Re-enforced along centerfold
Background:
In 1730, the English Board of Trade & Plantations issued a request for maps of the British, French, and Spanish territorial claims in the New World, as ongoing boundary conflicts hindered economic development in the colonies. A former employee, Henry Popple, created an incredible 20-sheet map first published in 1733 that covered a broad region between Hudson Bay and the northern coast of South America and inland as far as the Rio Grande. It would become tremendously influential diplomatically as disputes among European powers increased dramatically in subsequent decades.
Accompanying the monumental production was a keymap, seen here as a later French edition issued by Georges Louis Le Rouge in 1742. With the exception of the language, decorative elements, annotations, and a missing vignette in the upper left corner, the image is largely the same as the original. It’s surprisingly accurate, as Popple was studious in his use of the latest available sources, though several geographic features have been enlarged or distorted and a large mysterious lake filled with islands appears near the western edge of the sheet.
It’s likely this is a remnant of the great saline sea speculated by Baron Lahontan, a French military officer who traveled extensively throughout the Great Lakes region from 1684 -1689. He later wrote several popular travel volumes that included reports of a Long (or Longue) River that branched from the Missippi westward, eventually reaching a large salt lake at the foot of a mountain range. The geographic influences of his story would be reflected in subsequent cartographic efforts throughout the 18th and into the early 19th century, and speculation on Lahontan’s travels persists to this day.
Elsewhere in the image, the topography is depicted pictorially and shows a prominent Appalachian Mountain range as well as a curious plateau in Michigan that Lewis Karpinski describes as a “fanciful creation.” Native American and European settlements are identified throughout and geographic features are labeled according to the key in the upper right. Seventeen inset plans of prominent port cities and islands can be seen in the lower right; including Boston, Charleston, New York, St. Augustine, Havana, and Cartagena.
Popple, Henry 1680 - 1743
Henry Popple was a British cartographer active in the early part of the 18th century. Popple was a clerk with the Board of Trade and Plantations, the organization that governed Britain's colonies in America. With his father, grandfather, and brother all being employed the board of trade, the Popple family had a long history of association with the British colonial administration. Popple received his commission as a clerk at the board of trade in 1727, but resigned in the same year. Curiously this is the same year he began work on his signature production, the Popple of North America, he resigned from the board to take a position as the Cashier to Queen Anne. Nonetheless he continued to work on his great maps and a manuscript version of the Popple Map appeared in this very year. Subsequently, Popple continued to update and refine the map until 1733 when it was finally printed. The Board of trade intended the Popple map to be a British response to Delisle's French mapping of North America, which presented boundaries that conflicted with British colonial ambitions. However, since Popple in fact based much of his map on Delisle's superior cartography, he also managed to copy many of the French political boundaries - to the detriment of the Board of Trade and its expansionist intentions. Although Popple's map was never approved by the Board, examples were rushed to each colonial governor and the map played a significant role in the cartographic history of North America. Popple cartographic endeavor began and ended with this singular map however, it significance was such that he must be considered in any list of significant British mapmakers.
George Louis Le Rouge fl. 1740-80
A military engineer by profession, le Rouge took up cartography and over a long period from about 1740 to 1780 produced many attractive works covering a wide range of subjects including plans of fortifications, military campaigns, town plans as well as the more usual atlases and sea charts.
1756 J B D Anville Large Antique Bottom Map Texas, Mexico, Central America - 93518
- Title : (Amerique Septentrionale Publiee sous les Auspices de Monseigneur le Duc d Orleans.. Par Le Snr. D Anville MDCCXLVI)
- Date : 1756
- Size: 36in x 22in (915mm x 560mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93518
Description:
This large important original copper plate engraved antique map, bottom sheets of 4 sheets, of North America was engraved in 1746 and was published by Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anville in his Elephant Folio Atlas Generale. (I have included an image of the map of the map when it is complete)
This map was instrumental in instructing the European Colonial powers of the time, England France & Spain the importance of dominating the New World, that ultimately led to the French and Indian War of 1754–63. This conflict determined the political direction of North America leading to the American War of Independence in 1775 and ultimately the formation of The United States of America.
To illustrate the importance of cartography in the mid eighteenth century, especially that of North America, a J B D Anville map is essential. D Anville dominated 18th century European cartography with many of his cartographical achievements, especially in North America, copied by many of his contemporaries such as Kitchen, Sayer, Homann, Seutter, Mitchell and others .
He was one of the first to leave blank spaces in his maps, where knowledge was scant or insufficient. His representation of the great lakes is superior to that of his contemporary John Mitchell, responsible for publishing one of the most famous mid 18th century maps of North America, A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America on 8 sheets in 1755 and remained the standard map of North America up until the end of the 18th century. (Ref: Tooley, Printed maps of America, 104; The Mapping of America 316)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36in x 22in (915mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 17in (880mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small right side of margin & border restored
Plate area: - Folds as issued, small dis-colouration to bottom centerfold
Verso: - Folds as issued, several small repairs not affecting image
Background:
The French and Indian War (1754–63) comprised the North American theatre of the worldwide Seven Years War of 1756–63. It pitted the colonies of British America against those of New France. Both sides were supported by military units from their parent countries, as well as by American Indian allies. At the start of the war, the French North American colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British North American colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on the Indians. The European nations declared war on one another in 1756 following months of localized conflict, escalating the war from a regional affair into an intercontinental conflict.
The name French and Indian War is used mainly in the United States. It refers to the two enemies of the British colonists, the royal French forces and their various American Indian allies. The British colonists were supported at various times by the Iroquois, Catawba, and Cherokee, and the French colonists were supported by Wabanaki Confederacy members Abenaki and Mikmaq, and Algonquin, Lenape, Ojibwa, Ottawa, Shawnee, and Wyandot.
British and other European historians use the term the Seven Years War, as do English-speaking Canadians. French Canadians call it La guerre de la Conquête (the War of the Conquest) or (rarely) the Fourth Intercolonial War.
Fighting took place primarily along the frontiers between New France and the British colonies, from Virginia in the south to Newfoundland in the north. It began with a dispute over control of the confluence of the Allegheny River and Monongahela River called the Forks of the Ohio, and the site of the French Fort Duquesne in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The dispute erupted into violence in the Battle of Jumonville Glen in May 1754, during which Virginia militiamen under the command of 22-year-old George Washington ambushed a French patrol.
In 1755, six colonial governors in North America met with General Edward Braddock, the newly arrived British Army commander, and planned a four-way attack on the French. None succeeded, and the main effort by Braddock proved a disaster; he lost the Battle of the Monongahela on July 9, 1755 and died a few days later. British operations failed in the frontier areas of Pennsylvania and New York during 1755–57 due to a combination of poor management, internal divisions, effective Canadian scouts, French regular forces, and Indian warrior allies. In 1755, the British captured Fort Beauséjour on the border separating Nova Scotia from Acadia, and they ordered the expulsion of the Acadians (1755–64) soon afterwards. Orders for the deportation were given by William Shirley, Commander-in-Chief, North America, without direction from Great Britain. The Acadians were expelled, both those captured in arms and those who had sworn the loyalty oath to His Britannic Majesty. Indians likewise were driven off the land to make way for settlers from New England.
The British colonial government fell in the region of modern Nova Scotia after several disastrous campaigns in 1757, including a failed expedition against Louisbourg and the Siege of Fort William Henry; this last was followed by Indians torturing and massacring their British victims. William Pitt came to power and significantly increased British military resources in the colonies at a time when France was unwilling to risk large convoys to aid the limited forces that they had in New France, preferring to concentrate their forces against Prussia and its allies in the European theater of the war. Between 1758 and 1760, the British military launched a campaign to capture the Colony of Canada (part of New France). They succeeded in capturing territory in surrounding colonies and ultimately the city of Quebec (1759). The British later lost the Battle of Sainte-Foy west of Quebec (1760), but the French ceded Canada in accordance with the Treaty of Paris (1763).
The outcome was one of the most significant developments in a century of Anglo-French conflict. France ceded to Great Britain its territory east of the Mississippi. It ceded French Louisiana west of the Mississippi River (including New Orleans) to its ally Spain in compensation for Spains loss to Britain of Florida. (Spain had ceded Florida to Britain in exchange for the return of Havana, Cuba.) Frances colonial presence north of the Caribbean was reduced to the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, confirming Great Britains position as the dominant colonial power in eastern North America.
1756 J B D' Anville Large Antique Bottom Map Texas, Mexico, Central America, GOM
- Title : (Amerique Septentrionale Publiee sous les Auspices de Monseigneur le Duc d Orleans.. Par Le Snr. D Anville MDCCXLVI)
- Date : 1756
- Size: 35in x 19in (890mm x 485mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 61147
Description:
This large important original copper plate engraved antique map, bottom sheets of 4 sheets, of North America was engraved in 1746 and was published by Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anville in his Elephant Folio Atlas Generale. (I have included an image of the map of the map when it is complete)
This map was instrumental in instructing the European Colonial powers of the time, England France & Spain the importance of dominating the New World, that ultimately led to the French and Indian War of 1754–63. This conflict determined the political direction of North America leading to the American War of Independence in 1775 and ultimately the formation of The United States of America.
To illustrate the importance of cartography in the mid eighteenth century, especially that of North America, a J B D Anville map is essential. D Anville dominated 18th century European cartography with many of his cartographical achievements, especially in North America, copied by many of his contemporaries such as Kitchen, Sayer, Homann, Seutter, Mitchell and others .
He was one of the first to leave blank spaces in his maps, where knowledge was scant or insufficient. His representation of the great lakes is superior to that of his contemporary John Mitchell, responsible for publishing one of the most famous mid 18th century maps of North America, A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America on 8 sheets in 1755 and remained the standard map of North America up until the end of the 18th century. (Ref: Tooley, Printed maps of America, 104; The Mapping of America 316)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 35in x 19in (890mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 17in (880mm x 430mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small right side of margin & border restored
Plate area: - Folds as issued, small dis-colouration to bottom centerfold
Verso: - Folds as issued, several small repairs not affecting image
Background:
The French and Indian War (1754–63) comprised the North American theatre of the worldwide Seven Years War of 1756–63. It pitted the colonies of British America against those of New France. Both sides were supported by military units from their parent countries, as well as by American Indian allies. At the start of the war, the French North American colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British North American colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on the Indians. The European nations declared war on one another in 1756 following months of localized conflict, escalating the war from a regional affair into an intercontinental conflict.
The name French and Indian War is used mainly in the United States. It refers to the two enemies of the British colonists, the royal French forces and their various American Indian allies. The British colonists were supported at various times by the Iroquois, Catawba, and Cherokee, and the French colonists were supported by Wabanaki Confederacy members Abenaki and Mikmaq, and Algonquin, Lenape, Ojibwa, Ottawa, Shawnee, and Wyandot.
British and other European historians use the term the Seven Years War, as do English-speaking Canadians. French Canadians call it La guerre de la Conquête (the War of the Conquest) or (rarely) the Fourth Intercolonial War.
Fighting took place primarily along the frontiers between New France and the British colonies, from Virginia in the south to Newfoundland in the north. It began with a dispute over control of the confluence of the Allegheny River and Monongahela River called the Forks of the Ohio, and the site of the French Fort Duquesne in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The dispute erupted into violence in the Battle of Jumonville Glen in May 1754, during which Virginia militiamen under the command of 22-year-old George Washington ambushed a French patrol.
In 1755, six colonial governors in North America met with General Edward Braddock, the newly arrived British Army commander, and planned a four-way attack on the French. None succeeded, and the main effort by Braddock proved a disaster; he lost the Battle of the Monongahela on July 9, 1755 and died a few days later. British operations failed in the frontier areas of Pennsylvania and New York during 1755–57 due to a combination of poor management, internal divisions, effective Canadian scouts, French regular forces, and Indian warrior allies. In 1755, the British captured Fort Beauséjour on the border separating Nova Scotia from Acadia, and they ordered the expulsion of the Acadians (1755–64) soon afterwards. Orders for the deportation were given by William Shirley, Commander-in-Chief, North America, without direction from Great Britain. The Acadians were expelled, both those captured in arms and those who had sworn the loyalty oath to His Britannic Majesty. Indians likewise were driven off the land to make way for settlers from New England.
The British colonial government fell in the region of modern Nova Scotia after several disastrous campaigns in 1757, including a failed expedition against Louisbourg and the Siege of Fort William Henry; this last was followed by Indians torturing and massacring their British victims. William Pitt came to power and significantly increased British military resources in the colonies at a time when France was unwilling to risk large convoys to aid the limited forces that they had in New France, preferring to concentrate their forces against Prussia and its allies in the European theater of the war. Between 1758 and 1760, the British military launched a campaign to capture the Colony of Canada (part of New France). They succeeded in capturing territory in surrounding colonies and ultimately the city of Quebec (1759). The British later lost the Battle of Sainte-Foy west of Quebec (1760), but the French ceded Canada in accordance with the Treaty of Paris (1763).
The outcome was one of the most significant developments in a century of Anglo-French conflict. France ceded to Great Britain its territory east of the Mississippi. It ceded French Louisiana west of the Mississippi River (including New Orleans) to its ally Spain in compensation for Spains loss to Britain of Florida. (Spain had ceded Florida to Britain in exchange for the return of Havana, Cuba.) Frances colonial presence north of the Caribbean was reduced to the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, confirming Great Britains position as the dominant colonial power in eastern North America.
1939 Japanese Safety Agency Large Antique Map of Hawaii, Pacific - Pearl Harbor
- Title : North Pacific Ocean Southern Portion Eastern Sheet, Compiled from the United States and the British Charts to 1939
- Date : 1939
- Size: 43in x 30in (1.090m x 760mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27101
Description:
This original very large lithograph map, a sea chart, with depth soundings, of The Central Pacific, centering on the Hawaiian Islands was complied by the Maritime Safety Agency Japan (MSAJ) from American & British charts. The maps centers on the Hawaiian Islands east to California and south to the Christmas Islands.
The importance of this map cannot be overstated in the context of time and would have no doubt been used by the Japanese carrier group and their attack on Pearl Harbour in 1941.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 43in x 30in (1.090m x 760mm)
Plate size: - 43in x 30in (1.090m x 760mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Hawaii, just before 8:00 a.m. (local time) on Sunday, December 7, 1941. The United States was a neutral country at the time; the attack led to its formal entry into World War II on the side of the Allies the next day. The Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning.
The attack was preceded by months of negotiations between the U.S. and Japan over the future of the Pacific. Japanese demands included that the U.S. end its sanctions against Japan, cease aiding China in the Second Sino-Japanese war, and allow Japan to access the resources of the Dutch East Indies. Anticipating a negative response from the US, Japan sent out its naval attack groups in November 1941 just prior to receiving the Hull note—the U.S. demand that Japan withdraw from China and French Indochina.
Japan intended the attack as a preventive action. Its aim was to prevent the United States Pacific Fleet from interfering with its planned military actions in Southeast Asia against overseas territories of the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and those of the United States. Over the course of seven hours there were coordinated Japanese attacks on the U.S.-held Philippines, Guam, and Wake Island and on the British Empire in Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong.
The attack commenced at 7:48 a.m. Hawaiian Time (6:18 p.m. GMT). The base was attacked by 353 Imperial Japanese aircraft (including fighters, level and dive bombers, and torpedo bombers) in two waves, launched from six aircraft carriers. Of the eight U.S. Navy battleships present, all were damaged, with four sunk. All but USS Arizona were later raised, and six were returned to service and went on to fight in the war. The Japanese also sank or damaged three cruisers, three destroyers, an anti-aircraft training ship, and one minelayer. More than 180 US aircraft were destroyed. A total of 2,403 Americans were killed and 1,178 others were wounded, making it the deadliest event ever recorded in Hawaii. Important base installations such as the power station, dry dock, shipyard, maintenance, and fuel and torpedo storage facilities, as well as the submarine piers and headquarters building (also home of the intelligence section) were not attacked. Japanese losses were light: 29 aircraft and five midget submarines lost, and 64 servicemen killed. Kazuo Sakamaki, the commanding officer of one of the submarines, was captured.
Japan announced declarations of war on the United States and the British Empire later that day (December 8 in Tokyo), but the declarations were not delivered until the following day. The British government declared war on Japan immediately after learning that their territory had also been attacked, while the following day (December 8) the United States Congress declared war on Japan. On December 11, though they had no formal obligation to do so under the Tripartite Pact with Japan, Germany and Italy each declared war on the U.S., which responded with a declaration of war against Germany and Italy. There were numerous historical precedents for the unannounced military action by Japan, but the lack of any formal warning (required by part III of the Hague Convention of 1907), particularly while negotiations were still apparently ongoing, led President Franklin D. Roosevelt to proclaim December 7, 1941, a date which will live in infamy. Because the attack happened without a declaration of war and without explicit warning, the attack on Pearl Harbor was later judged in the Tokyo Trials to be a war crime.
1635 Joan Blaeu Antique Half Page Map of New England, Nova Belgica et Anglia
- Title : Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova
- Date : 1635
- Size: 18 1/2in x 12in (470mm x 305mm)
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
- Ref: 16385
Description:
This original copper-plate engraved antique half right hand page map of New England & NE America by Joan Blaeu was published in the 1635 German edition of Atlas Novus.
This is the right hand, cartouche title section of this important map.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 18 1/2in x 12in (470mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Soiling, small worm hole top right margin
Plate area: - Light soiling, 4 small worm holes
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
This important map was one of the most attractive of the Americas published at the time. It is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript figurative map of Adriaen Block from 1614. Indeed it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way. This helped to create an accurate picture of the longitudinal scale of the coastline. His manuscript map is the first document to delineate an insular Manhattan; it also provides the earliest appearance of Manhates and Niev Nederland.
It has been noted that the time difference between 1614, the date of the manuscript, and Blaeus map whose first appearance is in 1635, appears long for such an important advance. It would seem highly feasible that Blaeu, who published many separately issued maps, would have wanted to produce one like this sooner. However, evidence points to the fact that it could not have been made before 1630. The Stokes Collection in New York possesses an example of the map on thicker paper without text on the reverse which could well be a proof issue of some kind.
There are features on Blaeus map that differ from the Block chart. Some of these could be accounted for by the fact that the surviving figurative map is not the original, and that the copyist omitted some place names that are referred to in the text of de Laets work. Block drew on Champlains map of 1612 for the depiction of the lake named after him, but it is here called Lacus Irocoisiensis. … The lack of interrelation between the Dutch or English colonies and the French, led for some time to the eastward displacement of this lake when its true position would be north of the Hudson River.
Some nomenclature has its origins in Blaeus second Paskaert of c.1630, and others, such as Manatthans, in de Laet. The colony of Nieu Pleimonth is identified. This and other English names along that part of the coast are largely derived from Smith\\\'s New England, 1616. Cape Cod is here improved over the Block manuscript by being reconnected to the mainland, the narrow strait having been removed. The coastline between here and Narragansett Bay, which can be clearly recognized, is not so accurate. Adriaen Blocx Eylandt leads us to the Versche Rivier, or Connecticut River, which Block ascended as far as was possible. t Lange Eyland is named; however, it is incorrectly too far east, being applied to what is possibly Fishers Island. De Groote bay marks Long Island Sound. The Hudson River is still not named as such, but is littered with Dutch settlements, and the failed Fort Nassau is here depicted renamed as Fort Orange. He does, however, improve on the direction of its flow. Blaeu separates the sources of the Hudson and Delaware Rivers which had been causing some confusion. Nieu Amsterdam is correctly marked as a fort at the tip of an island separated on the east side by Hellegat, or the East River. The coastline south of Sandy Hook also shows signs of improvement.
The whole map is adorned by deer, foxes, bears, egrets, rabbits, cranes and turkeys. Beavers, polecats and otters appear on a printed map for the first time. The Mohawk Indian village top right is derived from the de Bry-White engravings.
1756 Homann Antique Map Colonial United States North America French Indian War
- Title : America Septentrionalis a domino d Anville in Galiis edita nunc in Anglia coloniis in interiorem Virginiam deductis nec non fluvii Ohio cursu aucta notisq geographicis et historicis illustrata.....1756
- Ref #: 27018
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique 1st edition map of the Colonial United States, at the beginning of the French-Indian war, was engraved in 1756 - dated in cartouche - by the Homann firm, Germany.
This map has original margins and colour on heavy clean sturdy paper.
First edition Homann map of the English Colonies in North America prior to the start of the French and Indian War. The map stretches just west of the Mississippi River to the east and from James Bay through the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Although most of the text is in German, there is also much in English, including numerous place named annotations associated the French and Indian War, such as the locations of Fort Duquesne and Fort Necessity, both taken by the French in 1754. Thus although the cartographer credits D Anville for the basic cartography, it is clear he is drawing from English, not French, sources. Bottom right and upper left are notes offering the history of North America.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 19in (535mm x 480mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light staining in lower margins, bottom margin centerfold rejoined with transparent archival tape
Plate area: - Light age toning along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
The French and Indian War (1754–63) comprised the North American theatre of the worldwide Seven Years War of 1756–63. It pitted the colonies of British America against those of New France. Both sides were supported by military units from their parent countries, as well as by American Indian allies. At the start of the war, the French North American colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British North American colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on the Indians. The European nations declared war on one another in 1756 following months of localized conflict, escalating the war from a regional affair into an intercontinental conflict.
The name French and Indian War is used mainly in the United States. It refers to the two enemies of the British colonists, the royal French forces and their various American Indian allies. The British colonists were supported at various times by the Iroquois, Catawba, and Cherokee, and the French colonists were supported by Wabanaki Confederacy members Abenaki and Mikmaq, and Algonquin, Lenape, Ojibwa, Ottawa, Shawnee, and Wyandot.
British and other European historians use the term the Seven Years War, as do English-speaking Canadians. French Canadians call it La guerre de la Conquête (the War of the Conquest) or (rarely) the Fourth Intercolonial War.
Fighting took place primarily along the frontiers between New France and the British colonies, from Virginia in the south to Newfoundland in the north. It began with a dispute over control of the confluence of the Allegheny River and Monongahela River called the Forks of the Ohio, and the site of the French Fort Duquesne in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The dispute erupted into violence in the Battle of Jumonville Glen in May 1754, during which Virginia militiamen under the command of 22-year-old George Washington ambushed a French patrol.
In 1755, six colonial governors in North America met with General Edward Braddock, the newly arrived British Army commander, and planned a four-way attack on the French. None succeeded, and the main effort by Braddock proved a disaster; he lost the Battle of the Monongahela on July 9, 1755 and died a few days later. British operations failed in the frontier areas of Pennsylvania and New York during 1755–57 due to a combination of poor management, internal divisions, effective Canadian scouts, French regular forces, and Indian warrior allies. In 1755, the British captured Fort Beauséjour on the border separating Nova Scotia from Acadia, and they ordered the expulsion of the Acadians (1755–64) soon afterwards. Orders for the deportation were given by William Shirley, Commander-in-Chief, North America, without direction from Great Britain. The Acadians were expelled, both those captured in arms and those who had sworn the loyalty oath to His Britannic Majesty. Indians likewise were driven off the land to make way for settlers from New England.
The British colonial government fell in the region of modern Nova Scotia after several disastrous campaigns in 1757, including a failed expedition against Louisbourg and the Siege of Fort William Henry; this last was followed by Indians torturing and massacring their British victims. William Pitt came to power and significantly increased British military resources in the colonies at a time when France was unwilling to risk large convoys to aid the limited forces that they had in New France, preferring to concentrate their forces against Prussia and its allies in the European theater of the war. Between 1758 and 1760, the British military launched a campaign to capture the Colony of Canada (part of New France). They succeeded in capturing territory in surrounding colonies and ultimately the city of Quebec (1759). The British later lost the Battle of Sainte-Foy west of Quebec (1760), but the French ceded Canada in accordance with the Treaty of Paris (1763).
The outcome was one of the most significant developments in a century of Anglo-French conflict. France ceded to Great Britain its territory east of the Mississippi. It ceded French Louisiana west of the Mississippi River (including New Orleans) to its ally Spain in compensation for Spains loss to Britain of Florida. (Spain had ceded Florida to Britain in exchange for the return of Havana, Cuba.) Frances colonial presence north of the Caribbean was reduced to the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, confirming Great Britains position as the dominant colonial power in eastern North America.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America Virginia to New York to New England
- Title : Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Good Condition
- Ref: 43134
- Size: 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured, important original antique map of the north east regions of the United States from Virginia, Chesapeake Bay, to New York & New England by Jan Jansson was published in the 1639 French edition of the Jansson, Hondius Atlas.
A beautiful map with sturdy, clean paper original wide margins and beautiful original hand colouring.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 19 1/2in (570mm x 495mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light toning on margin edges
Plate area: - Very light offsetting
Verso: - None
Background:
A beautiful original 17th map of Virginia, New York and New England which was derived from the less well circulated Johannes de Laet map of 1630. This version is enlarged and expanded to the north and slightly east, with de Laets narrative on the verso (De Laets map is one of extreme importance, being the first printed to use the namesManbattes (Manhattan) and N. Amsterdam)
The nomenclature on this map is virtually identical to the De Laet map, with the few minor differences most likely owing to the engravers error. C of Feare is still depicted over 2° too far south. This is not Cape Fear we know of today but actually Cape lookout.
During the fiercely competitive decade of the 1630's the families of Blaeu and Jansson produced maps drawn directly from one another. Here, however, Jansson produces one that was not followed by Blaeu, relying upon the more restricted map of Nova Belgica to represent the land north of Chesapeake Bay. A sign of the Dutch influence here is that both atlas producers largely declined to include the advanced cartography of Champlain, thereby relegating it altogether.
There are three know states of this map, the first one published in 1636 - entitled Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia.
The second edition in which the title of the map was changed to Nova Belgium et Anglia Nova (to give more weight to Dutch claims in North America) within a new square cartouche was first published in 1647.
State 3 was published in 1694 by Schenk & Valk which included new regional demarcation and a latitude and longitude grid. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley; Burden; AMPR)
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of North America Virginia to New York to New England
- Title : Nova Anglia Novvm Belgium et Virginia
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93508
- Size: 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Description:
This magnificent original copper plate engraved antique landmark 1st edition map of the NE region of North America, the original colonial states from Virginia to New England, was published in the 1639 French edition of Mercators Atlas
A magnificent early map of NE North America published only 19 years after the landing of the Pilgrims at Plymouth Rock, Massachusetts.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23in x 19in (585mm x 485mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/4in (505mm x 384mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - Age toning, old archival tape on verso
Background:
This influential map is derived from the less well circulated Johannes de Laet map of 1630. Enlarged and expanded to the north and slightly east, it carries de Laets narrative on the reverse. De Laets map is one of extreme importance, being the first printed to use the names Manbattes (Manhattan) and N. Amsterdam. The nomenclature is virtually identical, with the few minor differences most likely owing to the engravers error. C of Feare is still depicted over 2° too far south. This is not Cape Fear we know of today but actually Cape lookout.
During the fiercely competitive decade of the 1630s the families of Blaeu and Hondius - Jansson of ten produced maps drawn directly from one another. Here, however, Jansson produces one that was not followed by Blaeu, the latter relying upon the more restricted map of Nova Belgica to represent the land north of Chesapeake Bay. A sign of the Dutch influence here is that both atlas producers largely declined to include the advanced cartography of Champlain, thereby relegating it altogether.
There are three know states of this map, this one first published in 1636, the second edition was published in 1647 renamed Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova within a new square cartouche. State 3 was published in 1694 by Schenk & Valk which included new regional demarcation and a latitude and longitude grid. (Ref: Koeman; M&B; Tooley; Burden)
1851-1891 Original Antique Virginian American Civil War Documents F. Beckham, M D Ball, D Coffman
-
Title :
1. The Commonwealth of Virginia
2. Fairfax County Va April 15th 1861.
3. State of West Virginia Green brier co. June 11th 1866.
4. United States Stamp for Special Tax Internal Revenue. - Date : 1851-1891
- Size: Please view description below
- Condition: (A) Good Condition
- Ref: 27090
Description:
We have on offer a group of 4 original antique documents, three of which relate directly to Virginia and the American Civil War dated 1851,1861, 1866. The first two documents concern Fontaine Beckham & Mottrom Dulany Ball with the third relating to Daniel Coffman. These three are very interesting and scarce items.
The fourth document relates to the Internal Revenue Service in 1891. Details, descriptions and conditions below.
1. Printed court summons signed by Fontaine Beckham (1788-1859) as justice of the peace, Jefferson County, Virginia, 8 January 1851. Printed sheet completed in manuscript, signed 'F Beckham'.
Fontaine Beckham was mayor of Harpers Ferry during the raid by John Brown in 1859 with Beckham infamously shot and killed during the raid, making him possibly one of the first casualties of the American Civil War.
Condition: Mounted on red-velvet-covered thick card mount, sheet torn at lower right-hand corner not affecting text. Condition Good. - 7in x 53/4in (18 x 14.6 cm)
Fontaine Beckham (1788-1859) was mayor of Harpers Ferry, Virginia, and local agent for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. He was shot and killed in the famous raid on the small outpost by abolitionist John Brown, today seen as a major event in the build-up to the American Civil War.
...... Beckham was the most prominent man killed during John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry, being the town's mayor, a county magistrate (in which capacity he signs this document), and a station agent for the B & O Railroad. Despite being a slave owner himself, Beckham was quite well-liked and considered by most to be a friend and benefactor of black men. He maintained a close friendship with his former slave Heyward Shepard, who also died during the raid.. After Shepard's death, some accounts state the mayor exposed himself to fire due to his clouded judgment. After Beckham's death, the infuriated town's people seized one of John Brown's imprisoned men, riddling his body with bullets. Yet Beckham's death also resulted in the only lasting freeing of slaves accomplished by the raid, as his will stipulated the freeing of five of his slaves......)
2. Manuscript receipt for the purchase of 'negro slaves Dennis and Belinda', Fairfax County, Virginia, signed by a member of a prominent local family, Mrs. M C(sic) Ball, dated 15 April 1861. We believe this to a transaction by Mary Ball, the mother of the first Governor of Alaska, Mottrom Dulany Ball, who at the time was have been fighting for the confederacy. The verso of the receipt is marked for Dulany, (as he was sometimes known) who would have been considered the head of the family after the death of his farther in 1859. Single bifolium of heavy woven paper, 10 lines, written on one side only, conjugate leaf docketed 'Dulany'
Condition: Damp-stained, creased from folding, loss to upper inner corner. Although stained the parchment is stable and heavy. Condition Good.
- 7 1/2in x 53/4in (18.2 x 13.8 cm)
Mottrom Dulany Ball, of Fairfax County, Fairfax Court House, and Alexandria, Virginia, was a musician, poet, teacher, lawyer, soldier and a founding father of the State of Alaska. Mottrom Dulany Ball, who was known variously as Mott, M.Dulany, or M.D., was born at Oak Mount, the home of his grandfather, Daniel French Dulany, in Fairfax County, Virginia on June 23, 1835.
Mott was the son of Spencer Mottrom Ball and Mary L. Dulany. Both parents were from prominent Virginia families. President George Washington is included among their many distinguished relatives. Mott’s early years were spent at his grandfather, Mottrom Ball’s, plantation, Woodberry, near Lewinsville, Fairfax County, Virginia. The elder Mottrom Ball was a physician who was educated at the University of Glasgow, in Scotland. TheBall family estate, Woodberry, consisted of 1,200 acres of land, rectangular in shape, extending north from the Lewinsville Presbyterian Church all the way to the to the Potomac River. 2, 3 The extensive plantation included a grist mill, Ball’s Mill, which stood on Scott’s Run. The location is today known as Swink’s Mill.4 Modern day Ball’s Hill Road traces the path of a farm road which ran through the center of Woodberry ending at the family home, Elmwood, on Ball’s Hill, also known as Prospect Hill, just south of Georgetown Pike.5 Politically, Mott’s father, Spencer Mottrom Ball, was an Anti-Jacksonian. As the name implies, this party was opposed to the authoritarian policies of President Andrew Jackson and his Democratic party. Several anti-Jacksonian factions came together to form the Whig party in 1834. Whigs supported the supremacy of Congress over the presidency.....)
3. Contemporary manuscript copy of two affidavits, one the same sheet, confirming Daniel Coffman to have been a loyal man during the rebelion [sic]', Greenbrier County, West Virginia, 1866.
Single sheet of lined paper written recto only, small embossed stamp depicting the Capitol Building and with text 'Congress' various inconsistencies in spelling.
Condition: Old folds, central fold just splitting at head, nicked along inner edge. Condition Good.
- 9in x 7in (23.5 x 17.8 cm)
First affidavit.
State of West Virginia Greenbrier Co. June 1866.
Personelly (sic) apparent before me a justice of the Peace John Sydenrtrleker (sic) and made oath that he knew Daniel Coffman to have been a loyal man during the rebellion and consider him the same use (sic) to this time Signed and sworn to before me in my township of fort spring this june 11th 1866...D Coffman JPS.....
Second affidavit.
State of West Virginia Greenbrier Co. June 1866.
Personell (sic) apparent before me a justice of the Peace H H Brackman and made oath that he knew Daniel Coffman to have been a loyal man during the rebellion and he invest (sic) himself the same now and I believe what he said to me
Signed and sworn to befor (sic) me in my township of fort spring...D Coffman JPS.....
The Coffman family have lived in Greenbrier county since the Rev Isaac Coffman 1741 - 1824, buried in the Coffman Cemetery, Ronceverte, West Virginia.
4. Internal Revenue receipt 'for special tax on the business of retail liquor dealer', paid by R. D. Burns of Lynchburg, Virginia, 9 December 1891 Engraved receipt in red and black, completed in manuscript.
Condition: Aged, small hole to lower left, upper right corner chipped. Condition Good. - 9 3/4in x 7 1/4in (24.5 x 18 cm)
General Definitions:
Please view description above
Imperfections:
Please view description above
1778 John Mitchell & Antonio Zatta 12 Sheet Antique Map of North America - Rare
- Title : Le Colonie Unite dell' America Settentrle. di Nuova Projezione Ass. Ee. Li Signori Riformatori dello Studio di Padova. Venezia 1778, Presso Antonio Zatta, con Privilegio dell' Eccellentissimo Senato.
- Ref #: 93528
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 52 1/2in x 51in (1.33m x 1.30m)
- Date : 1778
Description:
This impressive very large twelve-sheet joined, original hand coloured important antique map is Antonio Zattas version of John Mitchells 1755 landmark map of North America, published first in 1778. This map is one of a few to be released during the late 18th century copying Mitchells map, in an effort to explain the rapidly changing political & economic situation in North America. Zatta has included many additional notes relating to both the Treaty of 1763 and events in the Revolutionary War. Most importantly, it is the first printed map devoted to the thirteen states, and to use the a name distinguishing them from their previous status as British Colonies. The name United Colonies was used in the Declaration of Independence and was not officially replaced until the Articles of Confederation adopted the name The United States of America.
This is an incredibly important and rare map, especially joined, in excellent condition with original colour. With John Mitchells map is now almost now impossible to find, with the last known sale in 2011 of $175,000US, this map is now one of the few, of that period, that is avaialble.
Zatta published these twelve separate sheets of Mitchells Map of North America, plus three other maps: Il Canada, Le Isole di Terra Nuova e Capo Breton, and La Baja D Hudson in the atlas Atlante Novissimo published from 1779-1785, with a second edition of the Zatta/Mitchell map published in 1791. Zattas version does not cover the far western portions of Mitchells map stretching to the Mississippi. An image of Mitchells map has been included as a point of reference.
Because Mitchells map was immediately recognized as seminal, it was exceedingly popular. Events leading up to the American Revolution only increased that demand. During the midst of the colonists on-going struggle for liberation from England, Zatta published this version which included some additional place names and information on early battles of the American Revolution.
The maps of Venetian publisher Antonio Zatta are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 52 1/2in x 51in (1.33m x 1.30m)
Plate size: - 49 1/2in x 49 1/4in (1.26m x 1.25m)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light creasing
Plate area: - Light creasing
Verso: - Light creasing
Background:
A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America by John Mitchell Map is a landmark map by John Mitchell (1711–1768), which was reprinted several times during the second half of the 18th century, in France, Italy & Germany. The Mitchell Map was used as a primary map source during the Treaty of Paris for defining the boundaries of the newly independent United Colonies. The Mitchell Map is the most comprehensive map of eastern North America made during the colonial era, measuring 6.5 feet (2.0 m) wide by 4.5 feet (1.4 m) high.
Mitchell started compiling a first draught map in 1750 from information acquired in London, both in official & private archives. This proved to be inadequate & George Montagu-Dunk, 2nd Earl of Halifax, accordingly ordered the governors of the 13 British colonies to survey and compile new maps, which most did. These became the basis, along with cartographical information of the French geographer Guillaume Delisle, of his landmark map. Late in 1754, Halifax was using one manuscript copy of Mitchells second map to successfully promote his political position (no compromise with the French) within the British cabinet in the build-up to the Seven Years War, also know as the French and Indian War. Halifax also permitted Mitchell to have the map published: it appeared in April 1755, engraved by Thomas Kitchin and published by Andrew Millar.
The published map bore the title A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America. It bore the copyright date of 13 February 1755, but the map was probably not sold to the public until April or even May. Minor corrections to the maps printing plates were made probably during the printing process (for example, the name and address of the publisher were corrected).
The geographer John Green criticized Mitchell and his map soon after it appeared, emphasizing two failings with respect to Nova Scotia (an area of particular dispute with the French). Mitchell, Green noted, had used neither the astronomical observations for latitude and longitude made by Marquis Joseph Bernard de Chabert in the 1740s nor a 1715 chart of the Nova Scotia coast. In response, Mitchell released a new version of his map, now with two large blocks of text that described all of his data sources; the new version of the map also adjusted the coastline in line with Chaberts work but rejected the 1715 chart as deeply flawed. This version of the map, which Mitchell referred to as the second edition, is commonly thought to have appeared sometime in 1757, but advertisements in the (London) Public Advertiser and Gazetteer and London Daily Advertiser on 23 April 1756 clearly indicate that this new map appeared at that time.
Mitchells map was printed in eight sheets; when assembled, it measures 136 cm by 195 cm (4 feet 6 inches by 6 feet 5 inches; height x width). The initial impressions printed in 1755 have a consistent coloring outlining British colonial claims. Mitchell extended the southern colonies across the entire continent, even over established Spanish territory west of the Mississippi. Mitchell divided up the Iroquois territories (as he understood them, reaching from Lake Champlain [Lac Irocoisia] to the Mississippi, and north of Lake Superior) between Virginia and New York, leaving only a much-reduced territory to the French.
Mitchells map was expensive but it spawned many cheaper variants that trumpeted Halifax and Mitchells powerful colonial vision to the British public. One of these, published in December 1755 by a Society of Anti-Gallicans, restricted the French even further just to Quebec.
The map is liberally sprinkled with text describing and explaining various features, especially in regions that were relatively unknown or which were subject to political dispute. Many notes describe the natural resources and potential for settlement of frontier regions. Others describe Indian tribes. Many Indian settlements are shown, along with important Indian trails.
Since Mitchells main objective was to show the French threat to the British colonies, there is a very strong pro-British bias in the map, especially with regard to the Iroquois. The map makes clear that the Iroquois were not just allies of Britain, but subjects, and that all Iroquois land was therefore British territory. Huge parts of the continent are noted as being British due to Iroquois conquest of one tribe or another. French activity within the Iroquois claimed lands is noted, explicitly or implicitly, as illegal.
In cases where the imperial claims of Britain and France were questionable, Mitchell always takes the British side. Thus many of his notes and boundaries seem like political propaganda today. Some of the claims seem to be outright falsehoods.
The Mitchell Map remained the most detailed map of North America available in the later eighteenth century. Various impressions (and also French copies) were used to establish the boundaries of the new United States of America by diplomats at the 1783 Treaty of Paris that ended the American Revolutionary War. The maps inaccuracies subsequently led to a number of border disputes, such as in Maine.[clarification needed] Its supposition that the Mississippi River extended north to the 50th parallel (into British territory) resulted in the treaty using it as a landmark for a geographically impossible definition of the border in that region. It was not until 1842, when the Webster-Ashburton Treaty resolved these inconsistencies with fixes such as the one that created Minnesotas Northwest Angle, that the U.S.–Canada border was clearly drawn from Maine to the Oregon Country.
Similarly, during the drafting of the Northwest Ordinance, the maps inaccuracy in depicting where an east–west line drawn through the southernmost point of Lake Michigan would intersect Lake Erie led to a long dispute over the Ohio–Michigan border that culminated in the Toledo War.
Zatta, Antonio fl. 1757-1797
Antonio Zatta was a prominent Italian editor, cartographer, and publisher. Little is known about his life beyond his many surviving published works. It is possible that he was born as early as 1722 and lived as late as 1804. He lived in Venice and his work flourished between 1757 and 1797. He is best known for his atlas, Atlante Novissimo (1779-1785), and for his prolific output of prints and books that were both precisely made and aesthetically pleasing. Zatta clearly had a large network from which to draw information; this is how he was able to publish the first glimpse of the islands visited by Captain Cook in the Atlante Novissimo.
Zattas maps are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. His re-engraving and publication of John Mitchells famous map of North America A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America in 1778, is considered one of the best re-issues of this seminal, landmark map .
......He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.... (Portinaro & Knirsch, The Cartography of North America, 1500-1800, p. 319).
Zatta was among the leaders in the eighteenth-century revival of fine printing in Italy and his choice of the text of Raynal to support his re-issue of Mitchells Map, is not surprising. Anne Palms Chalmers describes Zatta as a sardonic writer with the focus of a certain amount of political controversy (Venetian Book Design in the Eighteenth Century, The Metropolitan Museum of Art Bulletin, New Series, Vol. 29, No. 5, January 1971, pp. 226-235). Chalmers describes Zattas printing and design as harmonious in composition with ornament unified by style, quality of line, and tone of printing.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1662 Joan Blaeu Complete Set of 9 Antique Maps of North America from Atlas Major, 1st Edition
- Titles:
1. Extrema Americae....Terra Nova Francia;
2. Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova;
3. Nova Virginiae Tabula;
4. Virginiae partis australis, et Floridae;
5. Nova Hispania;
6. Yucatan...Guatimala;
7. Insulae Americanae;
8. Canibales Insulae;
9. Mappa Aestivarum Insularum Alias Barmudas - Sizes: 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)ea
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date: 1662
- Ref #: BlaeuNA 1662
Description:
This is a unique opportunity to acquire a complete set of 9 maps of North America published by Joan Blaeus in the monumental & rare 1st 1662 Latin edition of Atlas Major. The maps cover the geographical detail of Canada, North America, Mexico, The Caribbean & Central America. Please see the background section below for details of each map. All maps have wide original margins & colour on strong sturdy paper.
Joan Blaeus 11 volumes of Atlas Major, is considered by many to be the greatest atlas set ever published. It excels in comprehensiveness, engraving, color, and overall production. The first edition was published in Latin in 1662 and was subsequently published in French, Dutch, German, and Spanish over the next 10 years.
On the 23rd of February 1672, a fire broke out in central Amsterdam, that ended the reign of one of the greatest & most prolific publishers of printed maps and atlases in publishing history. The Blaeu family had reached its zenith 10 years previously, with the publication of its greatest achievement, the Atlas Major or Great Atlas, consisting of 11 volumes, with geographical detail reflecting many of the achievements of the Golden Age of the United Netherlands. Blaeus Atlas Major were the most expensive books printed in the 17th century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20 1/2in (610mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - Various, pls see below
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm) min
Imperfections:
Margins: - Pls see below
Plate area: - Pls see below
Verso: - Pls see below
Background:
1. Extrema Americae ( Eastern Canada) - Rare only published in Atlas Major. Derived mainly from the Samuel de Champlain Nouvelle France map of 1632, this map reflects the growing financial importance of the waters of New France to Europe.
Plate: 22 1/2in x 17 3/4in.
Condition: Age toning, text show-through & browning to image.
2. Nova Belgica Et Anglia Nova (New England) - NE America, centering on New York and Manhattan from Virginia to the St Lawrence River. This map is noted for the fact that its primary source is the first manuscript figurative map of Adriaen Block from 1614. Indeed it is the first full representation of it in print. It is one of the earliest to name Nieu Amsterdam. Block, a Dutch fur trader, explored the area between Cape Cod and Manhattan, examining the bays and rivers along the way.
Plate: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in
Condition: Age toning, text show-through & browning to image.
3. Nova Virginiae Tabula (John Smiths Virginia & Chesapeake Bay) This map was printed from a plate engraved by Dirk Grijp from a previous plates by Henricus Hondius.
Plate: 19in x 15in
Condition: Light age toning
4. Virginiae partis australis, et Floridae Virginia, the Carolinas & Georgia.
Plate: 20in x 15in
Condition: Light age toning
5. Nova Hispania et Nova Galicia Western Mexico
Plate: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
6. Yucatan...Guatimala (Yucatan, Central America) Rare only published in Atlas Major.
Plate: 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in
Condition: Light age toning
7. Insulae Americana (GOM, Caribbean)
Plate: 20 1/2in x 15in
Condition: Light age toning
8. Canibales Insulae (Lesser Antilles Islands) Rare, printed only in Atlas Major
Plate: 21in x 16 1/2in
Condition: Age toning
9. Mappa Aestivarum Insularum Alias Barmudas Dictarum Bermuda. Like all 17th century maps of Bermuda this map is based ultimately on the survey made by John Norwood, of the Bermuda Company, in 1618 in the form as published by the English map-maker John Speed in 1627.
Plate: 21in x 16in
Condition: Light age toning
1755 JB D Anville Large Original Antique Map of North America, Great Lakes, Indian Wars
- Title : Canada Louisiane et Terres Anglois Par Le Sr. D Anville...MDCCLV
- Ref #: 61140
- Size: 52in x 38in (1.32m x 960mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This magnificent, scarce, very large (52in x 38in) & highly detail map of North America was engraved in 1755 - dated in the title cartouche - by George De La Haye and was published by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon D Anville in his large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
Geopolitically this map is extremely significant drawn as war between the Global Powers of the day, France, England & Spain, was breaking, known in Europe as the Seven Year War known in North America as the French & Indian war. (Please see below for more detail)
This map rivals John Mitchells "A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America published in 1755" - considered to be one of the most significant maps of North America published in the 18th & 19th centuries (a 1st edition of Mitchells map is currently for sale for $165,000).
I have included an image of the Mitchell map for comparison. The D Anville map is considered by many to be cartographically superior to the Mitchell map, at a fraction of the price.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 52in x 38in (1.32m x 960mm)
Plate size: - 45in x 35in (1.12m x 890mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Light ceasing along folds
Verso: - Very small worm holes
Background: This extraordinary map of the eastern half of North America extends from Newfoundland, Canada to St. Augustine, Florida, stretching westward beyond the Mississippi as far as modern day Texas. The map includes both the original colonial colonies along the Atlantic seaboard from Maine to Georgia and the French claims in Louisiana (the Mississippi Valley) and modern day Canada. Florida is acknowledged as a Spanish enclave. Elevation is rendered in profile with fortifications, towns, and American Indian villages identified. A large inset map centres on the course of the St. Lawrence River from the Isle Aux Coudres to Lake Ontario.
The is a very significant map, drawn from a definitive French perspective, defining the territorial alignments and claims within North America shortly following the outbreak of the French and Indian War, considered to be a New World reflection of the European Seven Years War. It is however notable that it began before the larger hostilities in Europe and most of the major battles involved primarily parties only loosely aligned with the French or English - most specifically American Indians and lawless frontiersman, who had their own political agenda.
The war began with French incursions into western Pennsylvania and other territories claimed simultaneously by the French, English and American Indian forces. Just prior to the war, the French, in the interest of broadening their hold on the lucrative fur trade, established a series of forts, all of which are here noted, along the length of the Mississippi and further east, including Fort Duquesne (here Fort de Quene, Pittsburgh), Fort de la Presquisle, and for Le Beouf (here, Fort de la Riv Jaus Beufs).
The map also recognizes British claims, only inland as far as the Appalachian Mountains, beyond which place names take on a noticeably French character. These last three forts occupied particularly contested territory under the control of the powerful British allied Iroquois League. The most contested of these was Fort Duquesne (modern day Pittsburgh) in direct opposition to another fort then being constructed by the Ohio Company, a trading and land speculation firm established by prominent Virginia colonials, including George Washington. The Virginian colonial governor responded to Duquesne by sending then Lieutenant George Washington and a band of Virginia militiamen to harass the French. The resulting Jumonville Affair, in which Washington oversaw an attack on a French Canadian diplomatic forces led by Joseph Coulon de Villiers de Jumonville, to warn the Ohio Company fort builders away from French claimed territory. The slaying of Jumonville and several other French diplomats prompted a response from French forces at Fort Duquesne, leading to Washingtons retreat and construction of Fort Necessity, really little more than a palisaded shack, marked here just south of Fort Duquesne. These events, all of which occurred in May of 1754, were said to have increased hostilities in Europe and led to the start of the Seven Year War in 1755.
Beyond the political agenda of this map, is the map itself, being one of the finest and most heavily detailed maps of North America published in the mid 18th century. Ranking alongside the large 1755 Mitchell map in detail but judged by many as cartographically superior. Drawing on both French and British cartographical detail, D Anville identifies countless American Indian tribes, many of which, like the Sioux and Missouri, the British had only vague knowledge. Moreover, he also includes detail such as swamps, rapids, fords, abandoned villages, and even the ancient remnants of mound builder culture in the Ohio Valley. D Anville notably does not include Mitchells fictional Lake Superior islands.
This map was originally published to accompany the pamphlet entitledMemoire sur la carte intitulee: Canada, Louisiane, & Terres angloises and was also published in four parts for D Anvilles Atlas General.
These large maps are hard to find in such good condition and make fantastic historical reference tools due to the size and high level of detail as with all D Anvilles work. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
1720 Guillaume Delisle Large Antique Map of America, New Zealand, Pacific Ocean
- Title : Hemisphere Occidental Dresse en 1720 pour l usage
- Date : 1720
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93081
- Size: 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Description:
This very large 1st edition beautifully hand coloured original antique Map of America by Guillaume Delisle, was engraved by J De la Haye in 1720, dated, and was was published in the Atlas Nouveau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 19in (490mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Uniform age toning
Plate area: - Uniform age toning
Verso: - Uniform age toning
Background:
Guillaume de L isle was responsible for some of the most accurate maps of America avaialble in the early 18th century. Delisle did away with most of the speculative cartography especially of North America and researched his information in finite detail. This can be seen in many ways. The most oblivious is showing California as a Peninsular - which some cartographers did not believe until the 1740\'s - and the NW region has been left blank, free of speculation. Another noticeable difference is the accurate depiction of the Great Lakes.
As with all Delisle\'s map this is finely engraved with amazing detail and hand colour. The map includes the tracks of many explorers up until 1710. These include Magellan 1520, Halley 1700, de Quiros 1605, de Mendana 1595, de la Maire 1616, Tasman, Halley and others. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1708 Guillaume Delisle Large Antique Map of North America - 4th State, rare
- Title : Carte Du Mexique et de la Floride des Terres Angloises et des Isles Antilles du Cours et des Environs de la Riviere Mississipi . . .Chez L Auteur sue le Quaide de l Horlage Privilege du Roy po. 20 ana 1703
- Date : 1708
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93525
- Size: 29 1/4in x 20 1/2in (750mm x 520mm)
Description:
In the world of early 18th century American cartography, no one published as many landmark maps of North America as the French family firm of Delisle. This large original copper-plate engraved scarce map of North America became one of the most copied map of the next 100 years by the likes of Homann, Seutter, Lotter, Sanson and many others. Engraved by Charles Simoneau, this map is the 4th state of seven (identified with the date 1703 in the cartouche with Delisles address in Paris erased) was published by Guillaume Delisle in the <i>Atlas Nouveau.</i>
The 7 states outlined by Tooley are:
- State 1 (1703): De LIsles first address on Rue Des Canettes.
- State 2 (1703): address changed to Quai de lHorloge Couronne de Diamans and the imprint of Renard.
- State 3 (1708): Couronne de Diamans is erased and <i>se trouve a Amsterdam chez L. Renard Libraire prez de la Bourse</i> is added
- State 4 (1708): <i>A Paris Chez L Auteur sur le Quai de l Horloge</i> is added and <i>Couronne de Diamans and Renards</i> imprint are removed and the engravers name (Simoneau) appears below the cartouche.
- State 5 (1722): <i>A Amsterdam Chez Jean Covens & Corneille Mortier avec Privilege 1722</i> Re-engraved and published by Covens & Mortier in Atlas Nouveau
- State 6 (1745): Philippe Buache imprint added below neatline at right.
- State 7 (1783): Title altered to Carte du Mexique et des Etas Unis dAmerique, Partie Meridionale, issued by Dezauche, showing US States and boundaries.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29 1/4in x 20 1/2in (750mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 26in x 19 1/2in (660mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This map, which is one of the three great maps of regional North America conceived by Delisle during the first quarter of the eighteenth century, identifies the colonial affiliations that defined the destiny of North America by the end of the century. As is often the case, the British North American Colonies are shown hemmed in by the Appalachians and crowding the Atlantic coast. The status of present-day South Carolina is dubious, the coloring implying that it may belong to Spain. To the north and west of New England, Canada confines the British colonies even further. In the Southwest, French Floride extends to the Rio Grande and south to present-day Brownsville. The northern boundary of Floride is indicated, except that it abuts Canada, thereby giving France possession of the entire middle part of the continent. Various remarks and locations for Native American tribes are shown, indicating, for example, the locations of the Apache Vaqueros, the Apache Navaio, and the Tiguas. In the French possessions many tribes and their villages are indicated, for example, the famous Cenis in Texas, the Apalache in Georgia and Florida, and the Kicapou near the Great Lakes (their original location before they were pushed all the way to Mexico). Delisles debts to Ibervilles explorations are frequently shown on this map.
The map was compiled from the reports brought back to France from the survivors of the La Salle expedition into the interior of North America and from the information derived from the explorations of Bienville and dIberville. In the year preceding the publication of the map, De LIsle utilized his position with the King of France to gain access to the best available information from the new world. During this time period he assiduously compiled the geographical data from the reports of the French Jesuit Missionaries and Explorers in North America, along with Spanish manuscript maps (often copied by the Missionaries while they were acting in the service of the Spanish as spiritual guides and gaining their confidence).
The result of this work were a series of landmark maps of the North America, including his map of North America ( LAmerique Septentrionale, 1700), Canada and the Great Lakes ( Carte du Canada ou de la Nouvelle France 1703), and the Mississippi Valley & Gulf Coast ( Carte de la Louisiane et du Cours du Mississipi 1708).
The map has been a towering landmark along the path of Western cartographic development. De LIsles map also includes greater accuracy in the Great Lakes region and in its depiction of English settlements along the East Coast. Excellent detail of the Indian villages in East Texas, based upon the reports of dIberville and the Spanish missionaries. The best depiction of the Southwest to date, with early trails & Indian tribes. Cumming described the map as profoundly influential.
Many have suggested that Claude Delisle, father of Guillaume, was the one who conducted the research on the maps, whereas Guillaume was the one who actually drew the maps and engraved the plates. Obviously the maps were a collaborative effort of the Delisle firm.
1722 Guillaume Delisle Large Antique Map of America, True Rare 1st Edition
- Title : Carte D Amerique...1722
- Size: 26 1/2in x 20 1/2in (675mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1722
- Ref #: 93338
Description:
This large original copper plate engraved hand coloured antique, true first edition, map of America was published by Guillaume Delisle in 1722.
Even though this map was published for the better part of the 18th century, the date 1722 in the cartouche, was not updated or removed in most instances. This makes identification of the true 1st editions complicated, but not impossible. The design of the cartouche itself is the defining evidence. I have included an image of the 4 different cartouche designs, from Tooleys The Mapping of America that define the different editions. This map is the first edition, state 2, illustrated in the image as No.2.
This 1st edition is a landmark map and one of the most important maps of America published in the early 18th century. So detailed was it, for its day, that it was copied many times over the next 100 years.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 20 1/2in (675mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 19 1/2in (620mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Detailed map of America, showing a blank coastline above Cap Blanc and the mythical entry of D\'Aguilar. The map shows tremendous detail throughout. Nice detail in California and the Southwest. The course of the Mississippi si pushed considerably west of its true location, but the Missouri River is shown in a remarkably accurate fashion, with headwaters in the Northern Rocky Mountains. The map is rich with Indian and other early American details. Decorative cartouche, compass rose and extensive notes throughout the map. First edition, 2nd State of the map. A bit of minor soiling, some lifting at the centerfold near the bottom of the map and a bit of wear at the lower centerfold, but generally a fine dark impression of this important early map.
1715 J B Homann Large Antique Map of North America Virginia Chesapeake Bay NJ, NY
- Title : Virginia Marylandia et Carolina in America Septentrionali Britannorum industria excultae"...Homann
- Date : 1715
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 82002
- Size: 24 1/2in x 21 1/4in (625mm x 540mm)
Description:
This large finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Virginia, Chesapeake Bay, Maryland, the Carolina's, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Maryland, New York and parts west of the Apalchians, was published by J.B Homann in 1715.
An exceptionally beautiful example of J. B. Homann's 1715 map of Virginia, Carolina, Maryland, and New Jersey; considered one of the most important and decorative maps of is region to appear in the 18th century. This fine decorative map covers from New York City and Long Island south along the Atlantic Cost as far as modern day Georgia, and as far west as Lake Erie.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24 1/2in x 21 1/4in (625mm x 540mm)
Plate size: - 23in x 19 1/2in (580mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Homann drew this map in response to Virginia Lieutenant-Governor Alexander Spotswood's plan to settled the little known interior of Virginia with German immigrants. Shown here is the first mapping of Germantown Teutsche Statt on the Rappahanock River and Fort Christanna (Christ Anna Fort) on the Makharing River. Fort Christanna was built with the intention of defending the region against incursions from hostile American Indian groups such as the Tuscarora to the west. Christanna also acted as the headquarters of the Virginia Indian Company, a stock venture founded in 1714 with the intention of trading with indigenous groups in the interior.Though Homann's remarkable representation of Spottswood's plan is extraordinarily up-to-date considering that Fort Christana was founded in the same year that this map was initially published, the remainder of the map embraces a number of common misconceptions and cartographic inaccuracies common to the region. Probably the most notable of these is his inclusion of Apalache Lacus. This fictional lake, the source of the May River, appeared on maps of this region since the mid 16th century Le Moyne-De Bry map and was popularized by Mercator and Hondius in 1606.
It would remain on maps well into the mid 18th century before exploration and settlement finally disproved the theory. Further north Lake Erie and been expanded dramatically and shifted somewhat to the south where it takes on the appearance of a vast inland sea occupying the entire northwestern quadrant of the map. This region, west of the English colonies and north as far as Pennsylvana, Homann attaches to the Spanish claims in Florida.
Homann's also offers a wealth of detail along the Atlantic coast, where most of the European colonization efforts were focused. From Long Island, about two-thirds of which is shown, south to Craven County, Carolina, countless towns and cities are identified. New York City is mapped on the southern tip of Manhattan Island, but is not specifically labeled. New Jersey is divided into the colonial provinces of East New Jersey and West New Jersey. Curiously Homann maps a large inland lake "Zuyd Lac" straddling the New Jersey - Pennsylvania border. This is no doubt a early misinterpretation of the natural widening of the Delaware River at the Delaware Water Gap. Heading south along the Delaware River Philadelphia is identified and beautifully rendered as a grid embraced in four quadrants. Both the Delaware Bay and the Chesapeake Bay are rendered in full and even include a number of undersea notations and depth soundings. In Virginia and Carolina the river systems are surprisingly well mapped and a primitive county structure is beginning to emerge.
The early Virginia counties of Rappahannock, Henrico, City, Isle of Wright, Nansemond, Northumberland, Middlesex, Gloster and Corotvk are noted. Similarly in Carolina a number of counties are named, most of which refer to the Lords Proprietors, including Albemarle, Clarenden, and Craven. Cape Fear, Cape Lookout, and Cape Hattaras are noted and a number of anchorages, reefs, and depth sounding are noted along the entire coastline. The lower right quadrant of this map is occupied by a fabulous decorative title cartouche. Centered on an enormous scallop shell bearing the map's title and Homann's Privilege, the cartouche features a number of stylized American Indians trading with European merchants.
The wealth of the region is expressed by an abundance of fish, game, and other trade products. Curling behind the scallop shell is a gigantic stylized alligator looking like nothing so much as a mediaeval dragon. The inclusion of Homann's Provildge in the title cartouche helps us to date this map to about 1715, when Homann was granted the right to add this royal distinction to his maps. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1776 Tobias Lotter Large Antique Post Revolutionary North America Map 13 Colonies
- Title : Carte Nouvelle de l Amerique Angloise Contenant Tout ce que les Anglois Possedent sur le Continent de l'Amerique Septentrionale Savior le Canada, la Nouvelle Ecosse ou Acadie, les Treize Provinces Unies ... avec la Floride
- Ref #: 27009
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
- Date : 1776
Description:
This is possibly one of the last significant maps, of the original 13 American colonies, published prior to the American Revolution for Independence from Britain, beginning in 1763 and ending with the signing of the Declaration of Independence in 1776.
Published in Augsberg, Germany in 1776 by Conrad Tobias Lotter, this large original antique map reflects both the French & German interests in North America just prior to the outbreak of hostilities.
The map covers the area from the James Bay to the Gulf of Mexico and west to Lake Michigan. It shows provinces, towns and cities, some forts and trails, as well as Indian villages and tribal territory. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 19 1/2in (610mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Each of the thirteen Colonies is identified by name both on the map, and in the title. The title is placed within an attractive decorative border surmounted by the British Royal arms. The French title and nomenclature indicates that Lotter, a leading German mapmaker, intended this for the French market, as does the fact that he limits the claims of the British to the regions east of the Appalachian Mountains. The delineation of the thirteen Provinces unies is generally well done (although Maryland and Georgia are both strangely shaped): a number of locations are named in the Ohio Valley, including Logs Town, Twictwees, Ft. Du Quesne, Allegheny, Vinango, Buffaloons, Sandoski and Mingos. Some interesting details are also shown in the region of the Great Lakes.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1784 Cook & Webber Large Antique Print of a Village on Kauai Island, Hawaii - Ist Edition
- Title : An Island View, in Atooi
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1784
- Ref #: 82065
Description:
This large original 1st edition copper-plate engraved antique print of a village the Hawaiian Island of Kauai (Atooi) visited by Captain Cook in 1778 was drawn by the official artist on Cooks crew, John Webber, and later published for the 1784 1st edition and official British Admiralty sanctioned account of Captain Cook’s third and final voyage along with that of Cooks successor Capt. James King......
A Voyage to the Pacific Ocean. Undertaken, by the Command of his Majesty, for making Discoveries in the Northern Hemisphere. To determine The Position and Extent of the West Side of North America; its Distance from Asia; and the Practicability of a Northern Passage to Europe. Performed under the direction of Captains Cook, Clerke, and Gore, In His Majesty\'s Ships the Resolution and Discovery. In the Years 1776, 1777, 1778, 1779, and 1780. In Three Volumes. Vol. I and II written by James Cook, F.R.S. Vol. III by Captain James King, LL.D. and F.R.S
Captain Cook arrived at the island of Atooi (Kauai) Hawaii on the 19th of January, 1778 and stayed until 23rd January. On the 21st January, Cook accompanied by John Webber, proceeded inland from their beach side anchorage to Waimea, on the south coast of Kauai. Their intention was to examine elevated objects visible from the ship. It proved to be a morai, or temple similar to ones they had seen in Tahiti and other South Pacific islands. This structure was nearly 20-feet high and covered in a thin, light-grey cloth, which likely had ceremonial significance. The temple rested on a platform and consisted of thousands of rough-edged lava rock piled in a tight, mortarless fashion. In the center is the spindly-legged oracle tower, where the priest (kahuna) might seek counsel or pray. Carved figures with tapa and leaf offerings are seen outside thatched huts topped with pili, the tall grass that grew throughout the lowlands. In his journal, Cook took particular note of several stone objects he had observed:
Cooks Journals - January 21, 1778
...........about the middle of the Morai, there were three of these places in line. We were told three chiefs had been buried there, and before them was another that was oblong. This they called Tanga (taboo or kapu in Hawaiian) and gave us clearly to understand that three human sacrifices had been buried there, that is, one at the burial of each chief.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
Plate size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Kauai is geologically the oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands. In 1778, Captain James Cook arrived at Waimea Bay, the first European known to have reached the Hawaiian islands. He named the archipelago after his patron the 6th Earl of Sandwich, George Montagu
Hawaii is the 50th and most recent state to have joined the United States of America, having received statehood on August 21, 1959. Hawaii is the only U.S. state located in Oceania and the only one composed entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean. Hawaii is the only U.S. state located outside North America.
It is possible that Spanish explorers arrived in the Hawaiian Islands in the 16th century—200 years before Captain James Cook\\\\\\\'s first documented visit in 1778. Ruy López de Villalobos commanded a fleet of six ships that left Acapulco in 1542 bound for the Philippines with a Spanish sailor named Juan Gaetano aboard as pilot. Depending on the interpretation, Gaetanos reports describe an encounter with either Hawaii or the Marshall Islands. If de Villalobos crew spotted Hawaii, Gaetano would be considered the first European to see the islands. Some scholars have dismissed these claims due to a lack of credibility.
Spanish archives contain a chart that depicts islands at the same latitude as Hawaii but with a longitude ten degrees east of the islands. In this manuscript, the island of Maui is named La Desgraciada (The Unfortunate Island), and what appears to be Hawaii Island is named La Mesa (The Table). Islands resembling Kahoolawe, Lanai, and Molokai are named Los Monjes (The Monks). For two-and-a-half centuries, Spanish galleons crossed the Pacific from Mexico along a route that passed south of Hawaii on their way to Manila. The exact route was kept secret to protect the Spanish trade monopoly against competing powers.
The 1778 arrival of British explorer James Cook was the first documented contact by a European explorer with Hawaii. Cook named the archipelago as the Sandwich Islands in honor of his sponsor John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich. Cook published the islands location and rendered the native name as Owyhee. This spelling lives on in Owyhee County, Idaho. It was named after three native Hawaiian members of a trapping party who went missing in that area. The Owyhee Mountains were also named for them
Cook visited the Hawaiian Islands twice. As he prepared for departure after his second visit in 1779, a quarrel ensued as Cook took temple idols and fencing as firewood and a minor chief and his men took a ship\\\\\\\'s boat. Cook abducted the King of Hawaii Island, Kalani ōpu u, and held him for ransom aboard his ship in order to gain return of Cook\\\\\\\'s boat. This tactic had worked in Tahiti and other islands. Instead, Kalani ōpu u s supporters fought back, killing Cook and four marines as Cooks party retreated along the beach to their ship. They departed without the ships boat.
Captain James King FRS 1750 – 1784 was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served under James Cook on his last voyage around the world, specialising in taking important astronomical readings using a sextant. After Cook died he helped lead the ships on the remainder of their course, also completing Cooks account of the voyage. He continued his career in the Navy, reaching the rank of post-captain, commanding several ships and serving in the American War of Independence.
King joined HMS Resolution as second lieutenant, sharing the duties of astronomer with Cook, taking astronomical observations on board by sextant and with Larcum Kendals timekeeper K1, to establish the Resolutions position at sea and on shore by sextant or by astronomical quadrant to establish the geographical position of salient points during the course of Cooks surveys. Thus Kings geographical positions were an important contribution to the accuracy of the various surveys carried out during the voyage and his use of the early chronometers helped prove their use at sea for calculation of Longitude. .
Following the death of Cook, King remained in the Resolution but on the death of Charles Clerke, Cooks successor, King was appointed to command HMS Discovery, the Resolutions consort, remaining in her for the rest of the voyage. After his return to England King was very much involved in the publication of the official account of Cooks third voyage, writing the third volume at Woodstock, near Oxford, where his brother Thomas was rector of St Mary Magdalene. But shortly after his return King was promoted Post-captain and appointed commander of HMS Crocodile in the English Channel.
John Webber RA 1751 – 1793 was an English artist who accompanied Captain Cook on his third Pacific expedition. He is best known for his images of Australasia, Hawaii and Alaska.
Webber was born in London, educated in Bern and studied painting at Paris.His father was Abraham Wäber, a Swiss sculptor who had moved to London, and changed his name to Webber before marrying a Mrs Mary Quant in 1744.
Webber served as official artist on James Cooks third voyage of discovery around the Pacific (1776–80) aboard HMS Resolution. At Adventure Bay in January 1777 he did drawings of A Man of Van Diemens Land and A Woman of Van Diemens Land. He also did many drawings of scenes in New Zealand and the South Sea islands. On this voyage, during which Cook lost his life in a fight in Hawaii, Webber became the first European artist to make contact with Hawaii, then called the Sandwich Islands. He made numerous watercolor landscapes of the islands of Kauai and Hawaii, and also portrayed many of the Hawaiian people.
In April 1778, Captain Cooks ships Resolution and Discovery anchored at Ship Cove, now known as Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada to refit. The crew took observations and recorded encounters with the local people. Webber made watercolour landscapes including Resolution and Discovery in Ship Cove, 1778. His drawings and paintings were engraved for British Admiraltys account of the expedition, which was published in 1784.
Back in England in 1780 Webber exhibited around 50 works at Royal Academy exhibitions between 1784 and 1792, and was elected an associate of the Royal Academy in 1785 and R.A. in 1791. Most of his work were landscapes. Sometimes figures were included as in A Party from H.M.S. Resolution shooting sea horses, which was shown at the academy in 1784, and his The Death of Captain Cook became well known through an engraving of it. Another version of this picture is in the William Dixson gallery at Sydney
1785 Antonio Zatta Large Antique Map of Southern United States, Texas, Mexico
- Title : Messico ouvero Nuova Spagna che contiene Il Nuovo Messico La Californoa Con Una Partie de Paesi Adjacenti Venezi 1785
- Ref #: 93526
- Size: 21in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
- Date : 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Mexico including Texas, California, and the Southern United States was engraved in 1785 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published by Antonio Zatta in his Atlas Atlante Novissimo. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21in x 15in (535mm x 385mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12 1/2in (405mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The capture of Tenochtitlan and refounding of Mexico City in 1521 was the beginning of a 286-year-long colonial era during which Mexico was known as Nueva España (New Spain). The Kingdom of New Spain was created from the remnants of the Aztec hegemonic empire. Subsequent enlargements, such as the conquest of the Tarascan state, resulted in the creation of the Viceroyalty of New Spain in 1535. The Viceroyalty at its greatest extent included the territories of modern Mexico, Central America as far south as Costa Rica, and the western United States. The Viceregal capital Mexico City also administrated the Spanish West Indies (the Caribbean), the Spanish East Indies (the Philippines), and Spanish Florida.
The indigenous population stabilized around one to one and a half million individuals in the 17th century from the most commonly accepted five to ten million pre-contact population. The population decline was primarily the result of communicable diseases, particularly smallpox, introduced during the Columbian Exchange. During the three hundred years of the colonial era, Mexico received between 400,000 and 500,000 Europeans, between 200,000 and 250,000 Africans and between 40,000 and 120,000 Asians. The 18th century saw a great increase in the percentage of mestizos.
Colonial law with Spanish roots was introduced and attached to native customs creating a hierarchy between local jurisdiction (the Cabildos) and the Spanish Crown. Upper administrative offices were closed to native-born people, even those of pure Spanish blood (criollos). Administration was based on the racial separation, among Republics of Spaniards, Amerindians and castas, autonomous and directly dependent on the king himself.
The Council of Indies and the mendicant religious orders, which arrived in Mesoamerica as early as 1524, labored to generate capital for the crown of Spain and convert the Amerindian populations to Catholicism. The 1531 Marian apparitions to Saint Juan Diego gave impetus to the evangelization of central Mexico. The Virgin of Guadalupe became a symbol of criollo patriotism and was used by the insurgents that followed Miguel Hidalgo during the War of Independence. Some Crypto-Jewish families emigrated to Mexico to escape the Spanish Inquisition.
The rich deposits of silver, particularly in Zacatecas and Guanajuato, resulted in silver extraction dominating the economy of New Spain. Taxes on silver production became a major source of income for Spain. Other important industries were the haciendas (functioning under the encomienda and repartimiento systems) and mercantile activities in the main cities and ports. Wealth created during the colonial era spurred the development of New Spanish Baroque.
As a result of its trade links with Asia, the rest of the Americas, Africa and Europe and the profound effect of New World silver, central Mexico was one of the first regions to be incorporated into a globalized economy. Being at the crossroads of trade, people and cultures, Mexico City has been called the first world city. The Nao de China (Manila Galleons) operated for two and a half centuries and connected New Spain with Asia. Goods were taken from Veracruz to Atlantic ports in the Americas and Spain. Veracruz was also the main port of entry in mainland New Spain for European goods, immigrants, and African slaves. The Camino Real de Tierra Adentro connected Mexico City with the interior of New Spain. Mexican silver pesos became the first globally used currency and the silver mined in Mexico were used to run commerce and wage crusades in two sides of globe, at the Mediterranean were Spain fought against the Ottoman Caliphate and at Southeast Asia where the Philippines fought against the Brunei Sultanate.
Due to the importance of New Spain administrative base, Mexico was the location of the first printing shop (1539), first university (1551), first public park (1592), and first public library (1646) in the Americas, amongst other institutions. Important artists of the colonial period, include the writers Juan Ruiz de Alarcón and Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, painters Cristóbal de Villalpando and Miguel Cabrera, and architect Manuel Tolsá. The Academy of San Carlos was the first major school and museum of art in the Americas. Scientist Andrés Manuel del Río Fernández discovered the element vanadium.
Spanish forces, sometimes accompanied by native allies, led expeditions to conquer territory or quell rebellions through the colonial era. Notable Amerindian revolts in sporadically populated northern New Spain include the Chichimeca War (1576–1606), Tepehuán Revolt (1616–1620) and the Pueblo Revolt (1680). To protect Mexico from the attacks of English, French and Dutch pirates and protect the Crowns monopoly of revenue, only two ports were open to foreign trade—Veracruz on the Atlantic and Acapulco on the Pacific. Among the best-known pirate attacks are the 1663 Sack of Campeche and 1683 Attack on Veracruz.
Many Mexican cultural features including tequila, first distilled in the 16th century, charreria (17th), mariachi (18th) and Mexican cuisine, a fusion of American and European (particularly Spanish) cuisine, arose during the colonial era.
On September 16, 1810, a loyalist revolt against the ruling junta was declared by priest Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla, in the small town of Dolores, Guanajuato. This event, known as the Cry of Dolores (Spanish: Grito de Dolores) is commemorated each year, on September 16, as Mexicos independence day. The first insurgent group was formed by Hidalgo, the Spanish viceregal army captain Ignacio Allende, the militia captain Juan Aldama and La Corregidora Josefa Ortiz de Domínguez. Hidalgo and some of his soldiers were captured and executed by firing squad in Chihuahua, on July 31, 1811. Following his death, the leadership was assumed by priest José María Morelos, who occupied key southern cities.
In 1813 the Congress of Chilpancingo was convened and, on November 6, signed the Solemn Act of the Declaration of Independence of Northern America. Morelos was captured and executed on December 22, 1815.
In subsequent years, the insurgency was near collapse, but in 1820 Viceroy Juan Ruiz de Apodaca sent an army under the criollo general Agustín de Iturbide against the troops of Vicente Guerrero. Instead, Iturbide approached Guerrero to join forces, and on August 24, 1821 representatives of the Spanish Crown and Iturbide signed the Treaty of Córdoba and the Declaration of Independence of the Mexican Empire, which recognized the independence of Mexico under the terms of the Plan of Iguala.
Mexicos short recovery after the War of Independence was soon cut short again by the civil wars and institutional instability of the 1850s, which lasted until the government of Porfirio Díaz reestablished conditions that paved the way for economic growth. The conflicts that arose from the mid-1850s had a profound effect because they were widespread and made themselves perceptible in the vast rural areas of the countries, involved clashes between castes, different ethnic groups and haciendas, and entailed a deepening of the political and ideological divisions between republicans and monarchists.
Agustín de Iturbide became constitutional emperor of the First Mexican Empire in 1822. A revolt against him in 1823 established the United Mexican States. In 1824, a Republican Constitution was drafted and Guadalupe Victoria became the first president of the newly born country. Central America, including Chiapas, left the union. In 1829 president Guerrero abolished slavery. The first decades of the post-independence period were marked by economic instability, which led to the Pastry War in 1836. There was constant strife between Liberals, supporters of a federal form of government, and Conservatives, who proposed a hierarchical form of government.
During this period, the frontier borderlands to the north became quite isolated from the government in Mexico City, and its monopolistic economic policies caused suffering. With limited trade, the people had difficulty meeting tax payments and resented the central governments actions in collecting customs. Resentment built up from California to Texas. Both the mission system and the presidios had collapsed after the Spanish withdrew from the colony, causing great disruption especially in Alta California and New Mexico. The people in the borderlands had to raise local militias to protect themselves from hostile Native Americans. These areas developed in different directions from the center of the country.
Wanting to stabilize and develop the frontier, Mexico encouraged immigration into present-day Texas, as they were unable to persuade people from central Mexico to move into those areas. They allowed for religious freedom for the new settlers, who were primarily Protestant English speakers from the United States. Within several years, the Anglos far outnumbered the Tejano in the area. Itinerant traders traveled through the area, working by free market principles. The Tejano grew more separate from the government and due to its neglect, many supported the idea of independence and joined movements to that end, collaborating with the English-speaking Americans.
General Antonio López de Santa Anna, a centralist and two-time dictator, approved the Siete Leyes in 1836, a radical amendment that institutionalized the centralized form of government. When he suspended the 1824 Constitution, civil war spread across the country. Three new governments declared independence: the Republic of Texas, the Republic of the Rio Grande and the Republic of Yucatán.
The 1846 United States annexation of the Republic of Texas and subsequent American military incursion into territory that was part of Coahuila (also claimed by Texas) instigated the Mexican–American War. The war was settled in 1848 via the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. Mexico was forced to give up more than one-third of its land to the U.S., including Alta California, Santa Fe de Nuevo México and the territory claimed by Texas. A much smaller transfer of territory in what is today southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico—known as the Gadsden Purchase—occurred in 1854.
The Caste War of Yucatán, the Maya uprising that began in 1847, was one of the most successful modern Native American revolts. Maya rebels, or Cruzob, maintained relatively independent enclaves in the peninsula until the 1930s.
Dissatisfaction with Santa Annas return to power led to the liberal Plan of Ayutla, initiating an era known as La Reforma. The new Constitution drafted in 1857 established a secular state, federalism as the form of government, and several freedoms. As the Conservatives refused to recognize it, the Reform War began in 1858, during which both groups had their own governments. The war ended in 1861 with victory by the Liberals, led by president Benito Juárez, who was an ethnic Zapotec.
In the 1860s Mexico was occupied by France, which established the Second Mexican Empire under the rule of the Habsburg Archduke Ferdinand Maximilian of Austria with support from the Roman Catholic clergy and the Conservatives. The latter switched sides and joined the Liberals. Maximilian surrendered, was tried on June 14, 1867, and was executed a few days later on June 19 in Querétaro.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1770 De Vaugondy & Diderot Antique Maps of Cartographical Views of California
- Title : Carte de la Californie suivant / I. La carte manuscrite de l'Amérique de Mathieu Néron Pecci olen dresse à Florence en 1604 / II. Sanson 1656 / III. De L'Isle Amérique Sept. 1700 / IV. le Pere Kino Jesuite en 1705 / V. La Societe des Jésuites en 1767.
- Ref: 93434
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
- Date : 1770
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine large historically important original hand coloured, copper-plate engraved antique map, illustrating 5 of the most influential depictions of California and its cartographical evolution between 1604 and 1767.
The map was engraved by the important French cartographer Robert De Vaugondy, for the 1770 edition of the Denis Diderot Encyclopaedie Raisonee des Sciences des Artes.
- The earliest map (upper right corner) is based upon a manuscript map by Mathieu Neron Pecci, drawn in Florence in 1604. This map also forms the basis of a map popularized in 1770 by Rigobert Bonne.
- The second map is Nicholas Sanson's map of California as an Island, based upon his larger map of 1656. This map was probably the single most influential projection of California as an Island.
- The third map map (lower right) is a portion of Guillaume De L'Isles map of America, published in 1700. While not truly peninsular in nature, it was influential in the shift back toward depicting California as a Peninsula.
- The fourth map (upper center) is a portion of Fra. Eusebio Kino's map, generally credited with being the map which dispelled the California as and Island myth. Issued in 1705, the map is based upon Father Kino's overland expedition from the mainland to the top of the Gulf of Cortez.
- The fifth map is one of the most interesting and enduring maps of California and the Baja (left side). Initially issued by the Society of Jesuits in 1767, it was popularized by Isaak Tirion and was perhaps the most interesting of all maps of Baja California in the 2nd half of the 18th Century.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12in (405mm x 315mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin expended from plate mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
This map was 1 of 10 maps to appear in the Supplement to Diderot\'s monumental encyclopedia, one of the most influential and widely distirbuted works of the second half of the 18th Century. Diderot\'s goal was to examine and display the popular geographical conceptions of several different parts of the world where the knowledge of the region\'s geogaphy was still largely unknown and evolving. Other maps treat the Northwest Passage, Northeast Passage and the NW Coast of America, among other topics.
A marvelous amalgam and an essential map for collectors of North American & California maps.
Encyclopaedie Raisonee des Sciences des Artes: At the time of publication these maps of Encyclopedie were some of the most in-depth and accurate maps published of Asia, Canada, California and the NW region of America.
Diderot\'s maps were intended to further an understanding of the Western Coast of America, and NE Asia, during a time period immediately prior to Cook\'s voyage to the region - less than a decade later- where numerous theories abounded on the NW Coast of America.(Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1639 Jan Jansson Antique Map of Peru, South America
- Title : Peru
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 43147
- Size: 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 500mm)
Description:
This finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the ancient South American country of Peru was published in the 1639 French edition of Jan Jansson's Atlas Nouvs.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, pink, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 22 1/2in x 20in (570mm x 500mm)
Plate size: - 20in x 15 1/2in (535mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light toning on margin edges
Plate area: - Light creasing along centerfold
Verso: - None
Background:
Jansson in this map shows the Pacific coast of South America from Ecuador - at the left hand side - as far south as the Atacama desert in the northern reaches of Chile.
Although the interior terrain is not mapped with any particular degree of accuracy, this map nevertheless conveys a vivid impression of the difficult terrain of the Andes in Peru.
As early as 1520, Spanish settlers in Panama had heard tales of a powerful civilisation rich in gold that lay to the south, and in 1522 an expedition was organised to find this land and the people called Biru or Piru in the south. In 1524 Francisco Pizarro led the first of his expeditions that led ultimately to the discovery & conquest of the Inca Empire which extended over wide areas of modern Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia and part of Chile. Pizarro obtained from Atahuallpa, the head of the Inca Empire, a huge ransom of silver and gold that made Spain rich almost beyond the most inventive dreams of the Spanish conquerors, and once the mountain city of Cuzco was captured in 1533, the Spanish hold over much of South America was virtually complete.
A beautiful map with a fine impression on clean heavy paper with beautiful hand colouring. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
1639 Jan Jansson Original Antique Map of Peru, South America
- Title : Peru
- Date : 1639
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 70709
- Size: 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique and very important map of Peru, South America by Jan Jansson was published in the 1639 French edition of Gerard Mercators Atlantis Novi Atlas.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 20in (610mm x 510mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15in (495mm x 390mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
Jansson in this map shows the Pacific coast of South America from Ecuador - at the left hand side - as far south as the Atacama desert in the northern reaches of Chile.
Although the interior terrain is not mapped with any particular degree of accuracy, this map nevertheless conveys a vivid impression of the difficult terrain of the Andes in Peru.
As early as 1520, Spanish settlers in Panama had heard tales of a powerful civilisation rich in gold that lay to the south, and in 1522 an expedition was organised to find this land and the people called Biru or Piru in the south. In 1524 Francisco Pizarro led the first of his expeditions that led ultimately to the discovery & conquest of the Inca Empire which extended over wide areas of modern Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia and part of Chile. Pizarro obtained from Atahuallpa, the head of the Inca Empire, a huge ransom of silver and gold that made Spain rich almost beyond the most inventive dreams of the Spanish conquerors, and once the mountain city of Cuzco was captured in 1533, the Spanish hold over much of South America was virtually complete.
A beautiful map with a fine impression on clean heavy paper with beautiful hand colouring. (Ref: Tooley, Koeman)
1772 De Vaugondy Visscher Large Antique Map of California & SW America
- Title : Carte De La Californie Et Des Pays Nord Ouest separes de L'Asie par le Detroit d'Anian…1772
- Date : 1772
- Ref # : 50674
- Size : 20in x 15 3/4in (510mm x 400mm)
Description:
Fascinating study in the comparative cartography of the West Coast of North America, from the Straits of Anian to Cabo San Lucas and the southern tip of Baja California. The work consists of extracts from two maps, both reportedly done by Visscher in the 1612 and 1641 respectively and with information derived from Mercator and Plancius. The larger map prominently shows the Strait of Anian, Anian Regnum, Quivira Regnum, the Sierra Nevada, Nova Albion, Tontonteac Regnum, Tolm Regnum and a coastal detail which includes over 30 coastal place names, including Mendocino, San Miguel (San Diego), Cape Fortuna, I. De Paxaros (Catalina?), and many mythical/ephemeral place names. The smaller map also shows the Straits of Anian, but depicts an open sea above, clearly portending a NW Passage in the Arctic Circle. The NW Coastline differs radically, and only Anian Regnum and Quivira Regnum are located, that later considerably south of the location on the larger map. The smaller map includes a similar number of coastal placenames, but includes several important ones not listed on the larger map, including C. Blanco (3 times), C. de San Francisco and los Farilones, but ommits any significant effort to depict bays.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 20in x 15 3/4in (510mm x 400mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 12 1/2in (410mm x 320mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Encyclopaedie Raisonee des Sciences des Artes:
At the time of publication these maps of Encyclopedie were some of the most in-depth and accurate maps published of Asia, Canada, California and the NW region of America.
Diderot's maps were intended to further an understanding of the Western Coast of America, and NE Asia, during a time period immediately prior to Cook's voyage to the region - less than a decade later- where numerous theories abounded on the NW Coast of America. A nice dark impression of this essential map for American map collectors. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1839 James Wyld Large Antique Map Provinces of Lower Canada, St Lawrence River
- Title : A New Map of the Province of Lower Canada, Describing all the Seigneuries, Townships, Grants of Land, &c. Compiled from Plans deposited in the Patent Office Quebec: by Samuel Holland, Esq. Surveyor General
- Ref #: 50391
- Size: 35 1/4in x 23 1/4in (895mm x 590mm)
- Date : 1839
- Condition: (B) Good Condition
Description:
This large, rare hand coloured original antique map of the provinces of Lower Canada and The St Lawrence River was engraved in 1839 - dated in title - and was published by James Wyld, Charing Cross, London.
This map has undergone some repairs and is priced accordingly. Currently this map is priced as high as $1500.
Background:
This boldly engraved map extends westward to include Lake St. Francis and the extreme tip of Upper Canada, eastward to part of New Brunswick showing the River St. John and beyond, and south to just below the Canadian border with New York and Vermont. It is filled with towns and settlements and individual named townships, roads and trails. It includes several interesting notations and delineates the "Boundary awarded to the King of Holland." Samuel Holland was originally a Dutch surveyor who fought on the side of the British during the French and Indian Wars and served as Surveyor General for the Province of Quebec and the Northern District of America. An infrequently seen issue.
This updated example of this important map of the Lower Province of Canada, first issued by Faden in 1813, which identifies in manuscript the location of the disputed lands southeast of the St. Lawrence River, the so-called "English Line" and "American Line," which would be the subject of an early boundary dispute between the two countries.
The original Faden map included information concerning over 100 land grants on either side of the St. Lawrence River, including the names of Land Owners. Faden's orginal map showed the surveys conducted in 1796-98 along the Scoudiac and Magaguadavic Rivers, in order to ascertain the true location of the St. Croix River. In the present map, there is significant new information and topographcal details, showing the remarkable advancement in the surveying of the region in the 12 years after the publication of Faden's map of 1813.
This new addition includes the District of Maine, Moosehad Lake, Penobscot River and the Bowding County Township and Bingham's Purchase. Whereas the original Faden map had no topographical detail, the present map is a dramatic improvement.
In addition to the topographical improvements, there is now an annotation in the centre of the map identifying the boundary dispute in the region, relating to the existence of two St. Croix Rivers in the region.
The second article of the Treaty of Peace between the US and Britain included the setting of the boundary between the two nations, "From the northwest angle of Nova Scotia, viz., that angle which is formed by a line drawn due north from the source of St. Croix River to the highlands . . ." It later became apparent that there was more than one St. Croix River. A further treaty provision in 1794 appointed a boundary commission, which determined in 1798 that the intended St. Croix was the Schoodiac River and its northern branch Cheputnaticook. The Treaty of Ghent, concluded on December 24, 1814, agreed to provide for a final adjustment of the boundaries described in the Treaty of 1783 that had not yet been determined, which included the boundary line from the source of the River St. Croix to the most north-western point of the Lake of the Woods.
A further commission was appointed to settle the boundary from the St. Croix to the St. Lawrence. Joseph Bouchette and John Lawrence were hired to conduct the surveys and the reports submitted for resolution to a third nation and ultimately resolved by the Webster-Ashburton Treaty of 1842.
The present map shows the two boundary claims at a time when they were not yet fully resolved. (Ref: M&B; Tooley; Clancy)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 35 1/4in x 23 1/4in (895mm x 590mm)
Plate size: - 35 1/4in x 23 1/4in (895mm x 590mm)
Margins: - min. 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling, repair to bottom right margin , border into image
Plate area: Light soiling, creasing along left fold
Verso: - Light soiling, repairs as noted
1774 Malachy Postlethwayt Antique 2 Volume Atlas 7 Large Cont Maps North America
- Title : The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commercewith large Improvements Adapting the Same to the Present State of British Affairs in America since the last Treaty of Peace made in the year 1763....MDCCLXXIV
- Ref #: 93529
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: Large Folio
- Date : 1774
Description:
These very large, heavy leather backed original antique dictionary & atlas volumes of early Global Economic Commerce by Malachy Postlethwayt was published in 1774.
The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce in 2 volumes is the 4th edition published in London by W. Strahan, J and F. Rivington, et al., in 1774. The first edition was published between 1751 & 1755. Titles in red and black with engraved vignettes, engraved allegorical frontispiece to volume 1 (offset onto title) and contain 24 engraved folding maps sheets that when assembled make 7 complete very large maps. Occasional minor spotting, contemporary diced calf, re-backed preserving original contrasting morocco labels, extremities repaired.
The seven maps once assembled, to the left, are as follows with titles, cartographers dates and dimensions;:
1. A Correct Map of Europe by Thomas Kitchin after D Anville, 80cm x 70cm, 1774
2. Africa Performed by the Sr D Anville Samuel Bolton after D Anville, 103cm x 94cm, 1774
3. A New and Correct Map of the Coast of Africa, so called Slave Coast Map, Richard Seale 48cm x 38cm, 1774
4. North America Performed under the Patronage of Louis Duke of Orleans Richard Seale after D Anville, 88cm x 86cm, 1774
5. South America Thomas Kitchin after D Anville, 124cm x 75cm, 1774
6. First Part of Asia RW Seale, after D Anville, 83cm x 77cm, 1755
7. Second Part of Asia R W Seale, after D Anville, 96cm x 70cm, 1755
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - Please see above
Plate size: - Please see above
Margins: - Please see above
Imperfections:
Margins: - Please see above
Plate area: - Please see above
Verso: - Please see above
Background:
Postlethwayts most noted work, The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce, appeared after he had devoted twenty years to its preparation. The first edition was published in London in instalments between 1751 and 1755, and then in subsequent editions as a two-volume set in 1757, 1766, and 1774. This dictionary was a translation, with large additions and improvements, from Jacques Savary des Bruslons Dictionnaire universal de commerce (1723–1730). Postlethwayts dictionary was a huge storehouse of economic facts, laws and theory and his departures from the French version reflected his greater interest in political problems; his more intense economic nationalism; and his exuberant belief in the economic usefulness of experimental philosophy
In the 1757 edition of the Universal Dictionary, Postlethwayt outlined his vision for the establishment of a British mercantile college to benefit those who intended to work as merchants, or in gathering public revenue, or in merchandizing. He proposed that theoretical training for business should occur in formal academies and involve the study of mercantile computations, foreign exchanges and the intrinsic value of foreign coins, double-entry accounting, languages, geography, and public revenues and related laws. Postlethwayts ideas appear to have been influential in developing the statutes and procedures of the Portuguese School of Commerce, established in Lisbon in 1759.
It is documented that Thomas Jefferson gave a copy of this dictonary to his son in law, Thomas Mann Randolph, and as a prolific reader we must assumed also read by Jefferson.
Postlethwayt, Malachy 1707-1767
Malachy Postlethwayt was a prolific English writer and publicist on matters of mercantilist economics in the 1740s and 1750s. Little is known about his upbringing or formal education, although he is believed to be the brother of James Postlethwayt (d. 1761), a writer on finance and demography. Malachy Postlethwayt was elected a fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London in 1734. His writings are claimed by Edgar Johnson to have exerted a good deal of influence on the trend of British economic thought.
Postlethwayt was alleged to be propagandist for the mercantilist endeavours of the Royal Africa Company, whose interests were well served by his publications The African Trade, the Great Pillar and Supporter of the British Plantation Trade in North America (1745) and The National and Private Advantages of the African Trade Considered (1746). These works supported a strategy of British commercial and manufacturing expansion through trade with Africa and the colonies, and promoted the importance of slavery for British commerce and industry.
Postlethwayts most noted work, The Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce, appeared after he had devoted twenty years to its preparation. The first edition was published in London in instalments between 1751 and 1755, and then in subsequent editions as a two-volume set in 1757, 1766, and 1774. This dictionary was a translation, with large additions and improvements, from Jacques Savary des Bruslons Dictionnaire universal de commerce (1723–1730). Postlethwayts dictionary was a huge storehouse of economic facts, laws and theory and his departures from the French version reflected his greater interest in political problems; his more intense economic nationalism; and his exuberant belief in the economic usefulness of experimental philosophy
In the 1757 edition of the Universal Dictionary, Postlethwayt outlined his vision for the establishment of a British mercantile college to benefit those who intended to work as merchants, or in gathering public revenue, or in merchandizing. He proposed that theoretical training for business should occur in formal academies and involve the study of mercantile computations, foreign exchanges and the intrinsic value of foreign coins, double-entry accounting, languages, geography, and public revenues and related laws. Postlethwayts ideas appear to have been influential in developing the statutes and procedures of the Portuguese School of Commerce, established in Lisbon in 1759.
Postlethwayts most important contribution to economic literature is regarded by many to be Britains Commercial Interest Explained and Improved (1757), in which he outlines his concept of physical commerce and the policies England should follow to attain commercial parity with foreign rivals.
Whether Postlethwayts writings were his original thoughts and words is a matter for conjecture. His Universal Dictionary included ideas taken from fifty other past or contemporary writers and that it had scattered throughout it practically all of Richard Cantillons Essai sur la nature du commerce en général (Essay on the Nature of Commerce in General, 1755). Although Postlethwayt was alleged widely to be a plagiarist, this accusation is believed to be exaggerated.
Postlethwayt died suddenly on September 13, 1767, and was buried in the Old Street Churchyard, Clerkenwell, in London.
Postlethwayt also published:
- The African Trade the great Pillar and Support of the British Plantation Trade in America, &c., 1745.
- The Natural and Private Advantages of the African Trade considered, &c., 1746.
- Britains Commercial Interest Explained, Vol. I of his Universal Dictionary of Trade and Commerce, 1747.[5]
- Considerations on the making of Bar Iron with Pitt or Sea Coal Fire, &c. In a Letter to a Member of the House of Commons, London, 1747.
- Considerations on the Revival of the Royal-British Assiento, between his Catholic Majesty and the … South-Sea Company. With an … attempt to unite the African-Trade to that of the South-Sea Company, by Act of Parliament, London, 1749.
- The Merchants Public Counting House, or New Mercantile Institution, &c., London, 1750.
- A Short State of the Progress of the French Trade and Navigation, &c., London, 1756.
- Great Britains True System. … To which is prefixed an Introduction relative to the Forming a New Plan of British Politicks with respect to our Foreign Affairs, &c., London, 1757.
- Britains Commercial Interest explained and improved, in a Series of Dissertations on several important Branches of her Trade and Police. … Also … the Advantages which would accrue … from an Union with Ireland, 2 vols., London, 1757; 2nd edit., With … a clear View of the State of our Plantations in America, &c., London, 1759.
- In Honour to the Administration. The importance of the African Expedition considered, &c., London, 1758
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1856 Mitchell Large Antique Pre Civil War Map United States of America California Gold Rush
- Title : Mitchells New Travellers Guide through the United States Showing the Rail Roads, Canals, Stage Roads and c. with Distances from Place to Place. Drawn and engraved by Ira S Drake Philadelphia 1856. Published by Charles Desilver
- Size: 28 3/4in x 22in (730mm x 560mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1856
- Ref #: 82034
Description:
This is a large uncommon, beautifully hand coloured and separately issued pre-Civil War original antique map of the United States issued by Charles Desilver in 1856 and is based on the earlier maps by the famous American cartographer, Samuel Augustus Mitchell.
The map covers the United States from the Atlantic seaboard to the western states beyond the Mississippi, with insets maps offering additional detail of the New England states, Lake Superior Copper Mines Region and in the California Gold Mining regions. As to be expected of a map designed for the traveler & explorer, Desilver offers in-depth detail of contemporary railways, canals, and roads with inset maps showing routes to California, illustrating the huge interest in the gold mining of California.
This map was drawn & engraved by Ira Drake and issued first by Desilver in 1856.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28 3/4in x 22in (730mm x 560mm)
Plate size: - 28 3/4in x 22in (730mm x 560mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (8mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Charles Desilver (fl. c. 1850 - 1862) is a little known American map published active in the middle part of the 19th century. Desilver began is cartographic career as a partner in the firm Thomas, Cowperthwait and Company, the publisher of S. A. Mitchell popular New Universal Atlas. In 1856 Desilver acquired Mitchell\'s copyrights and print plates and began to issue his own vaJacques Nicholas Bellinmitriant of the New Universal Atlas. Desilver altered Mitchell\'s maps only slightly; adding a new grillwork border, his own color scheme, new titles, and some updated political data. Despite a noble pedigree, Desilver\'s maps did not sell well - possibly because they followed the long and very popular run of Mitchell\'s own atlases. Desliver continued to publish his atlas until 1859 (though we have heard that he also published an 1862 edition). In 1859 he resold the Mitchell copyrights and printing plates to S. A. Mitchell\'s son S. A. Mitchell Jr. The younger Mitchell again updated the plates with own border and color scheme and began publishing his own successful atlas in 1860.
1718 Henri Chatelain & Claude Delisle Large Antique Map of North America
- Title : Nouvelle carte de l'Amerique Septentrionale dressée sur les plus nouvelles observations de messieurs de l'Academie des Sciences et des meilleurs geographes
- Ref #: 27008
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 27in x 20 1/2in (685mm x 520mm)
- Date : 1720
- Price: $1499.00US
Description:
This original large hand coloured copper plate engraved antique map of North America, with a index to the territorial claims of the three Europeans powers, England, France & Spain and the indigenous peoples of those regions was published by Henri Chatelain in the 1718 edition of Atlas Historique, Ou Nouvelle Introduction A l'Histoire, aÌ la Chronologie & aÌ la Geìographie Ancienne & Moderne
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Blue, yellow, red, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 27in x 20 1/2in (685mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 19in (610mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Top margin cropped close to plate mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
An attractive map of North America, based upon Claude De L Isle's highly influential map of North America published in 1700, from Chatelain's monumental 7 volume Atlas Historique, published in Amsterdam.
California is a peninsula with a number of villages, mountains, and the Channel Islands shown. Mississippi extends far north of its true source. Large Florida and downplayed English colonies.
This fine map is a wonderful example from Chatelain's important text. By combining a wealth of information and geographical observation, with delicate engraving and an uncomplicated composition, this elegant map is a superb example from the golden age of French mapmaking.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1687 Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi Large Antique Map of North America
- Title : L America Settentrionale....Guglielmo Sansone...Gio Giacomo De Rossi in Roma l Anno 1687
- Size: 23 1/2in x 18in (595mm x 455mm)
- Condition: (AVery Good Condition
- Date : 1687
- Ref #: 17061
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of North America was engraved in 1687 by Giorgio Widman and was published by Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi in the 1688 edition of Atlas Mercurio Geografico
Giorgio Widman (active 1672 to 1682) was a celebrated map and lettering engraver, who worked primiparity with the De Rossi publishing house. He is perhaps best known for having executed the lettering of Giovanni Battista Faldas superb 1675 map of Rome.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 23 1/2in x 18in (595mm x 455mm)
Plate size: - 22in x 16in (560mm x 405mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small nick to left bottom margin
Plate area: - Light creasing, top centerfold rejoined
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Attractive map of North America, with California depicted as an island. This is the Italian edition of the 1669 revised edition of Nicolas Sansons 1650 map. This is the third state of De Rossi s map, dated 1687 (after the first in 1677), with the addition of place names and other features, i.e. a coastline added from Agubela de Cato northward, Stretto d ANIAN named at 60 deg. N., MARE DI CALIFORNIA named to the west of California, and with many internal features added above 45 deg. N. Describing the first state, McLaughlin notes California with indented northern coast, with nothing to west and Agubela de Cato to north. Among the place names are C. de Mendocino, Pta. de los Reyes, Pta. de Monte Rey, Pta. de Francisco Draco (south of Pta de Monte Rey), Canal de S. Barbara, I. de S. Catalina, P. de S. Diego, etc. In the southwest, there is a large lake near Taosii, with R. de Norte flowing southwest from it to the Mar Rosso.
de Rossi, Giovanni Giacomo (1627 – 1691)
De Rossi was an Italian engraver and printer, active in Rome in the second half of the 17th century.
His father, Giuseppe de Rossi (1570-1639), was the founder of the most important and active printing press of the 17th century in Rome. The printing press begun in 1633, by Giuseppe de Rossi, and it passed firstly to Giovanni Giacomo and to his brother Giandomenico (1619-1653), and then later to Lorenzo Filippo (1682-?); in 1738 it became the Calcografia Camerale, from 1870 until 1945 the Regia Calcografica, and today it is known as the Calcografia Nazionale. Here are conserved, amongst many others, the plates of Giambattista Piranesi (1720-1778).
Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi was the most involved of all the various family members who ran the press, and he worked between 1638 and 1691, and was to take the company to the height of its success. The artists that he printed the etchings for included Giovanni Benedetto Castiglione (1609-1665), Pietro Testa (1612-1650) and Giovan Francesco Grimaldi (1606–1680).
1755 (1778) De Vaugondy Large Antique Map of The Great Lakes America East Canada
- Title : Partie De L Amerique Septent. qui comprend La Nouvelle France ou le Canada...Par le Sr Robert de Vaugondy; Supplement pour Les Lacs du Canada
- Ref #: 17017
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 31 1/2in x 22 1/2in (800m x 570mm)
- Date : 1775 (1778)
Description:
This large original beautifully hand coloured, scarce 4th edition, antique map of The Great Lakes of North America, Eastern Canada & part of New England, with border changes from the 1763 Treaty of Paris, was published in 1768 by Robert Du Vaugondy in his Atlas Universal.
One of the nicest examples I have seen, of this scarce and beautiful hand coloured map, on heavy paper with original margins and heavy dark ink denoting an early pressing.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 31 1/2in x 22 1/2in (800m x 570mm)
Plate size: - 24in x 19 1/2in (610mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 2in (50mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The mapping of the Great Lakes region began in the early seventeenth century, when the first indications of the lakes appeared on maps made by European cartographers. By the mid-1600s, the maps of French Royal Geographer Nicolas Sanson had recognizable depictions of all five Great Lakes. His map is imprecise—Lake Superior lacks its distinctive shape and is unbounded on the west—but Lakes Ontario, Erie, Huron and Michigan can be discerned without difficulty. The lack of any reference to the Mississippi River in Sansons map reflects how little cartographers really knew about the region at the time.
Until the late eighteenth century, maps were made with information acquired in an irregular and imprecise manner. They were not based on formal surveys, but on written records supplemented with sketches by explorers, missionaries and trappers traveling the Upper Midwest. European cartographers had the task of fitting together this often contradictory information and putting the results into the framework of a geographic map. Instead of being mapped in terms of latitude and longitude, prominent places were usually located in relation to other places, which were, of course, similarly positioned. Distances could not be measured with any accuracy at this time, so these maps were liable to gross errors.
The early maps in the Making Maps, Mapping History exhibit provide a capsulized view of the growth of geographical knowledge of the Great Lakes region. As noted above, Sansons map was the first to display all five of the Great Lakes. Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, the cosmographer of the Republic of Venice, used information supplied by Jesuit missionaries in a 1688 map that was the first accurate depiction of the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River. French cartographer Guillaume De LIsle further refined the image and provided an outline that was not substantially improved until surveyors entered the region in the nineteenth century.
The first official government surveys of the Great Lakes were hydrographic surveys conducted by the British Admiralty under the direction of Capt. Henry W. Bayfield. Bayfield spent his entire career surveying the St. Lawrence River and the Great Lakes, beginning with Lake Superior in 1816. The lake-shore city of Bayfield, Wis., was named in honor of this pioneer surveyor.
One of the first acts of the new government of the United States was to establish a system for the orderly settlement of its western lands. Under the Ordinance of 1785, land surveyors went into the western territories in advance of settlement to divide the land into townships of 36 square- mile sections. Though mapping was not the governments primary aim, the surveys provided ample grist for the mapmakers mill, and the regions were, for the first time, mapped with considerable accuracy. The federal government, however, was not yet in the business of making maps for the public. That was left to enterprising individuals, such as Samuel Morrison, Elisha Dwelle and Joshua Hathaway, who produced one of the first topographical maps of the Wisconsin Territory in 1837.
The surveys of the General Land Office served as the basis for the mapping of much of the Great Lakes region from around 1800, when the surveys began, until about 1890, when the U.S. Geological Survey began to map the region again. In some cases, however, the old surveys were not entirely superseded until the mid-20th century. The distinctive feature of maps based on these surveys is the invariable presence of the township grid.
As population and commerce in the Great Lakes region grew, the federal government assumed responsibility for charting the lakes for navigation. The U.S. Lake Survey began in 1841 with an appropriation of $15,000. Before the Civil War, the work was conducted by officers of the Corps of Topographical Engineers. Its initial survey was completed in 1882, but the need for contin- uous revisions caused it to be reactivated a few years later. The Topographical Engineers merged with the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers in 1863, and the Lake Survey remained in the hands of the Corps of Engineers until 1970, when it became part of the newly formed National Ocean Survey (now known as the National Ocean Service).
The U.S. Lake Survey conducted far more rigorous surveys than those of the General Land Office, which used instruments no more sophisticated than a surveyors compass and a Gunters chain. The Lake Survey used an array of precision instruments and employed triangulation to form the geographic framework of the maps. Triangulation allowed the transfer of geographical coordinates from point to point throughout the system and, for the first time, geographical locations were determined with precision. Inland navigation prompted Congress to order a variety of government surveys. During the era of canal building, surveys like the one for the Portage Canal were common. Most of them were conducted by the Corps of Engineers, as were the surveys of the great rivers, such as the Mississippi.
The degree of accuracy accorded Great Lakes navigators was generally not matched on land for many years to come. The task of precisely mapping the United States by covering it with large-scale topographic quadrangle maps was given to the newly formed U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) in the 1880s. John Wesley Powell, the second director of the USGS, stated that the mapping of the United States could be accomplished in 25 years, but that goal was not accomplished until the 1980s. The first topographic maps of Wisconsin appeared in the 1890s, when much of the southeastern part of the state was surveyed. The surveys were quickly done, however, and most of the sheets needed at least minor revision within the next decade. Despite a rapid start, the topographic mapping of Wisconsin bogged down and ultimately was not completed until 1983. Mapping standards changed entirely with the application of aerial photography around 1930. Following World War II, all Wisconsin topographic sheets were derived from photographs.
Today, polar-orbiting satellites with thematic mappers can, in a single day, record images that reveal Great Lakes water quality and temperature, the streets and large buildings of urban areas, and the general health of forests, wetlands and farmlands, including the identity of such crops as corn, hay and alfalfa. The detailed precision of todays computerized Space Age technology no doubt would have astounded Nicolas Sanson—but the seventeenth-century mapmakers ability to create a fairly accurate map of a world he had only heard and read about is equally astounding to twenty-first-century mapmakers.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1746 J B D Anville Large Rare Antique Map of North America Pre French Indian War
-
Title : Amerique Septentrionale Publiee sous les Auspices de Monseigneur le Duc d Orleans.. Par Le Snr. D Anville MDCCXLVI
- Ref #: 17010
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 42 1/2in x 37in (1.08m x 940mm)
- Date : 1746
Description:
This large important original copper plate engraved antique map of North America, in 12 sheets joined, was engraved in 1746 - dated in the cartouche - and was published by Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D Anville in his Elephant Folio Atlas Generale.
This map was instrumental in instructing the European Colonial powers of the time, England France & Spain the importance of dominating the New World, that ultimately led to the French and Indian War of 1754–63. This conflict determined the political direction of North America leading to the American War of Independence in 1775 and ultimately the formation of The United States of America.
To illustrate the importance of cartography in the mid eighteenth century, especially that of North America, a J B D Anville map is essential. D Anville dominated 18th century European cartography with many of his cartographical achievements, especially in North America, copied by many of his contemporaries such as Kitchen, Sayer, Homann, Seutter, Mitchell and others .
He was one of the first to leave blank spaces in his maps, where knowledge was scant or insufficient. His representation of the great lakes is superior to that of his contemporary John Mitchell, responsible for publishing one of the most famous mid 18th century maps of North America, A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America on 8 sheets in 1755 and remained the standard map of North America up until the end of the 18th century. (Ref: Tooley, Printed maps of America, 104; The Mapping of America 316)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 42 1/2in x 37in (1.08m x 940mm)
Plate size: - 34 1/2in x 33 1/2in (875m x 850mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small wormholes in left margin repaired, not affecting the image
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Age toning
Background:
The French and Indian War (1754–63) comprised the North American theatre of the worldwide Seven Years War of 1756–63. It pitted the colonies of British America against those of New France. Both sides were supported by military units from their parent countries, as well as by American Indian allies. At the start of the war, the French North American colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British North American colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on the Indians. The European nations declared war on one another in 1756 following months of localized conflict, escalating the war from a regional affair into an intercontinental conflict.
The name French and Indian War is used mainly in the United States. It refers to the two enemies of the British colonists, the royal French forces and their various American Indian allies. The British colonists were supported at various times by the Iroquois, Catawba, and Cherokee, and the French colonists were supported by Wabanaki Confederacy members Abenaki and Mikmaq, and Algonquin, Lenape, Ojibwa, Ottawa, Shawnee, and Wyandot.
British and other European historians use the term the Seven Years War, as do English-speaking Canadians. French Canadians call it La guerre de la Conquête (the War of the Conquest) or (rarely) the Fourth Intercolonial War.
Fighting took place primarily along the frontiers between New France and the British colonies, from Virginia in the south to Newfoundland in the north. It began with a dispute over control of the confluence of the Allegheny River and Monongahela River called the Forks of the Ohio, and the site of the French Fort Duquesne in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The dispute erupted into violence in the Battle of Jumonville Glen in May 1754, during which Virginia militiamen under the command of 22-year-old George Washington ambushed a French patrol.
In 1755, six colonial governors in North America met with General Edward Braddock, the newly arrived British Army commander, and planned a four-way attack on the French. None succeeded, and the main effort by Braddock proved a disaster; he lost the Battle of the Monongahela on July 9, 1755 and died a few days later. British operations failed in the frontier areas of Pennsylvania and New York during 1755–57 due to a combination of poor management, internal divisions, effective Canadian scouts, French regular forces, and Indian warrior allies. In 1755, the British captured Fort Beauséjour on the border separating Nova Scotia from Acadia, and they ordered the expulsion of the Acadians (1755–64) soon afterwards. Orders for the deportation were given by William Shirley, Commander-in-Chief, North America, without direction from Great Britain. The Acadians were expelled, both those captured in arms and those who had sworn the loyalty oath to His Britannic Majesty. Indians likewise were driven off the land to make way for settlers from New England.
The British colonial government fell in the region of modern Nova Scotia after several disastrous campaigns in 1757, including a failed expedition against Louisbourg and the Siege of Fort William Henry; this last was followed by Indians torturing and massacring their British victims. William Pitt came to power and significantly increased British military resources in the colonies at a time when France was unwilling to risk large convoys to aid the limited forces that they had in New France, preferring to concentrate their forces against Prussia and its allies in the European theater of the war. Between 1758 and 1760, the British military launched a campaign to capture the Colony of Canada (part of New France). They succeeded in capturing territory in surrounding colonies and ultimately the city of Quebec (1759). The British later lost the Battle of Sainte-Foy west of Quebec (1760), but the French ceded Canada in accordance with the Treaty of Paris (1763).
The outcome was one of the most significant developments in a century of Anglo-French conflict. France ceded to Great Britain its territory east of the Mississippi. It ceded French Louisiana west of the Mississippi River (including New Orleans) to its ally Spain in compensation for Spains loss to Britain of Florida. (Spain had ceded Florida to Britain in exchange for the return of Havana, Cuba.) Frances colonial presence north of the Caribbean was reduced to the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, confirming Great Britains position as the dominant colonial power in eastern North America.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.