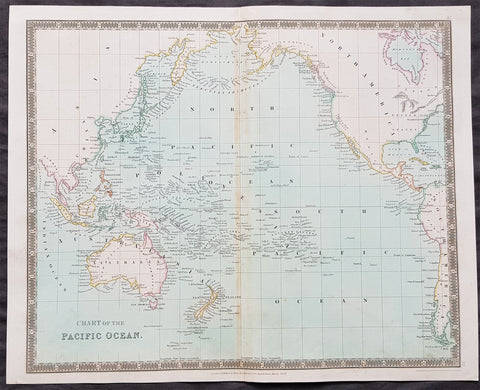
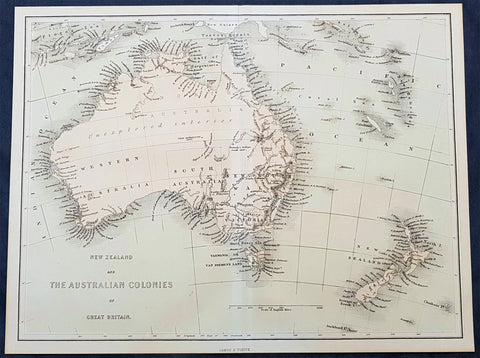
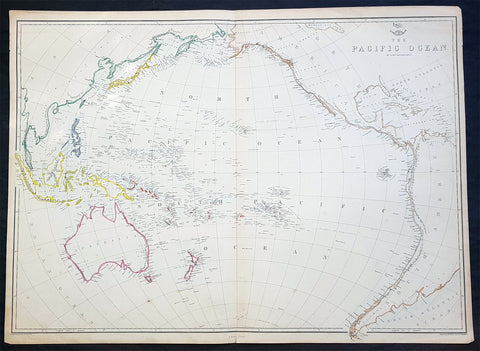
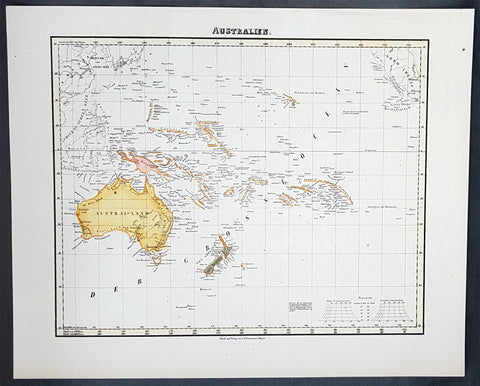
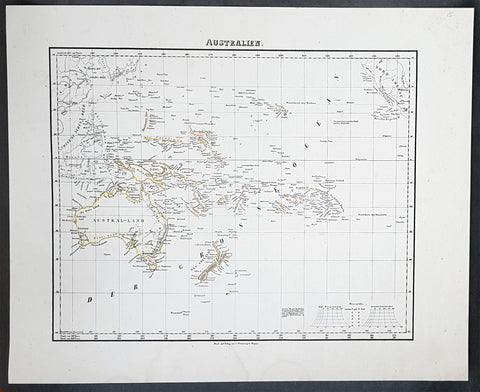
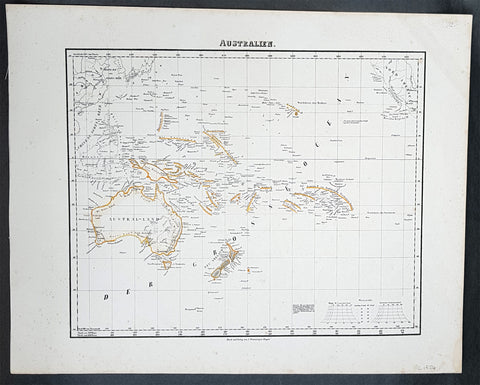
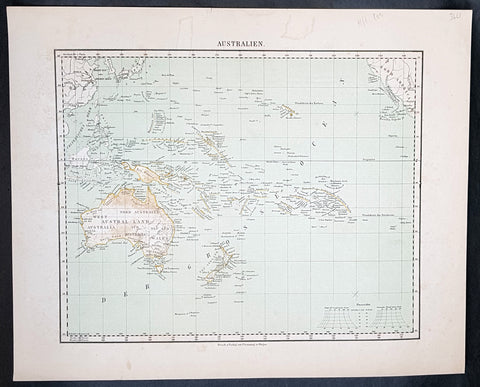
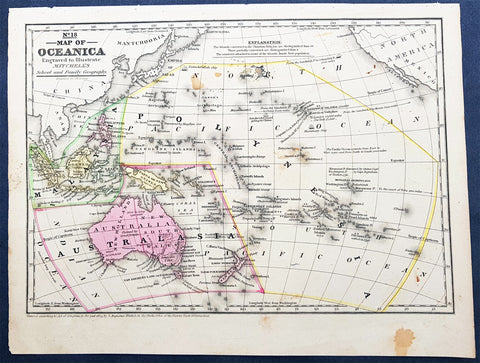
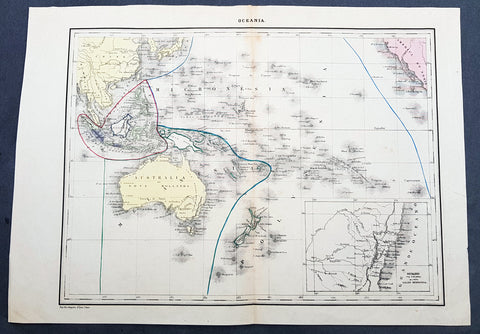
Australia/Oceania (23)
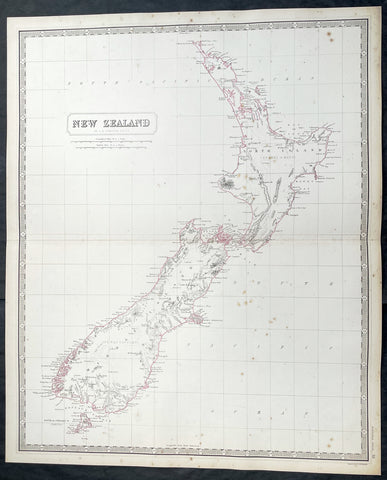
1774, 1777 & 1785 Capt James Cook 3 Atlas Volumes 1st Editions 204 Maps & Prints
- Title : 1. Figure du Banks 2. Premier Voyage De Cook 3. Troisieme Voyage De Cook
- Ref #: 93498, 93499, 93500
- Size: 4to (Quatro)
- Date : 1774; 1777; 1785
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
A unique and rare opportunity to acquire all three of Captain James Cooks 1st French edition Atlases (4to, Quatro), published to accompany the publication of his 3 voyages of discovery in 1774, 1777 & 1785. The atlases contain a total of 204 large folding, double page and single page maps and prints. It is very rare to find all three atlases complete and available together at the same time.
The contents of all three atlases are in fine condition, with a fresh, heavy impression and clean paper of all maps and prints.
As stated there are 204 maps and prints 51 in the 1st volume, 66 in the second volume and 87 in the second volume. Please view the images above, that include a few images of the 204 maps and prints as well as an itemized list of each volume.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 4to (Quatro)
Plate size: - 4to (Quatro)
Margins: - 4to (Quatro)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Some scuffing and wear to boards & spines
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Timeline First Voyage 1768 - 1771:
In 1768 Cook was chosen to lead an expedition to the South Seas to observe the Transit of Venus and to secretly search for the unknown Great Southern Continent (terra australis incognita).
Cook and his crew of nearly 100 men left Plymouth (August 1768) in the Endeavour and travelled via Madeira (September), Rio de Janiero (November-December) and Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) to Tahiti.
At Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) Cooks men went ashore and met the local people whom Cook thought perhaps as miserable a set of People as are this day upon Earth. Joseph Bankss party collected botanical specimens but his two servants, Thomas Richmond and George Dorlton, died of exposure in the snow and cold. Leaving Tierra del Fuego Endeavour rounded Cape Horn and sailed into the Pacific Ocean.
Sir Joseph Banks wrote about the homes of the Fuegans
..…huts or wigwams of the most unartificial construction imaginable, indeed no thing bearing the name of a hut could possibly be built with less trouble. They consisted of a few poles set up and meeting together at the top in a conical figure, these were covered on the weather side with a few boughs and a little grass, on the lee side about one eighth part of the circle was left open and against this opening was a fire made.......(Banks, Journal I, 224, 20th January 1769)
Samuel Wallis on the ship Dolphin discovered Tahiti in 1767. He recommended the island for the Transit of Venus observations and Cook arrived here in April 1769. Cook, like Wallis two years before him, anchored his ship in the shelter of Matavai Bay on the western side of the island.
In Matavai Bay Cook established a fortified base, Fort Venus, from which he was to complete his first task – the observation of the Transit of Venus (3rd June 1769). The fort also served as protection for all the important scientific and other equipment which had to be taken ashore as:
.......great and small chiefs and common men are firmly of opinion that if they can once get possession of an thing it immediately becomes their own…the chiefs employd in stealing what they could in the cabbin while their dependents took every thing that was loose about the ship…...(Joseph Banks).
Theft by some native peoples plagued Cooks voyages.
Cook and his crew experienced good relations with the Tahitians and returned to the islands on many occasions, attracted by the friendly people of this earthly paradise. On arrival Cook had set out the rules, including:
.....To endeavour by every fair means to cultivate a friendship with the Natives and to treat them with all imaginable humanity....
Just as Cook was planning to leave Tahiti two members of Endeavours crew decided to desert, having strongly attached themselves to two girls, but Cook recovered them.
Cook sailed around the neighbouring Society Islands and took on board the Tahitian priest, Tupaia, and his servant, Taiata. Endeavour left the Society Island in August 1769.
Tupaia acted as interpreter when they came into contact with other Polynesian peoples and helped Cook to make a map of the Pacific islands. This showed Cook the location of islands arranged according to their distance from Tahiti and indicated Tupaias and Polynesian knowledge of navigation and their skill as great mariners.
Cook sailed in search of the Southern Continent (August-October 1769) before turning west to New Zealand. The first encounters with the native Maori of New Zealand in October were violent, their warriors performing fierce dances, or hakas, in attempts to threaten and challenge the ships crew. Some of their warriors were killed when Cooks men had to defend themselves. Eventually relations improved and Cook was able to trade with the Maori for fresh supplies.
Exploring different bays and rivers along the way Cook circumnavigated New Zealand and was the first to accurately chart the whole of the coastline. He discovered that New Zealand consisted of two main islands, north (Te Ika a Maui) and south (Te Wai Pounamu) islands (October 1769-March 1770).
The artist Sydney Parkinson described three Maori who visited the Endeavour on 12th October 1769:
......Most of them had their hair tied up on the crown of their heads in a knot…Their faces were tataowed, or marked either all over, or on one side, in a very curious manner, some of them in fine spiral directions…
This Maori wears an ornamental comb, feathers in a top-knot, long pendants from his ears and a heitiki, or good luck amulet, around his neck.
At the northern end of the south island Cook anchored the ship in Ship Cove, Queen Charlotte Sound, which became a favourite stopping place on the following voyages. Parkinson noted:
......The manner in which the natives of this bay (Queen Charlotte Sound) catch their fish is as follows: - They have a cylindrical net, extended by several hoops at the bottom, and contracted at the top; within the net they stick some pieces of fish, then let it down from the side of the canoe and the fish, going in to feed, are caught with great ease.....(Parkinson, Journal, 114)
In Queen Charlottes Sound Cook visited one of the many Maori hippah, or fortified towns.
........The town was situated on a small rock divided from the main by a breach in a rock so small that a man might almost Jump over it; the sides were every where so steep as to render fortifications iven in their way almost totally useless, according there was nothing but a slight Palisade…in one part we observed a kind of wooden cross ornamented with feathers made exactly in the form of a crucifix cross…we were told that it was a monument to a dead man.......
Endeavour left New Zealand and sailed along the east coast of New Holland, or Australia, heading north (April-August 1770). Cook started to chart the east coast and on 29th April landed for the first time in what Cook called Stingray, later, Botany Bay.
The ship struck the Great Barrier Reef and was badly damaged (10 June). Repairs had to be carried out in Endeavour River. (June-August 1770). The first kangaroo to be sighted was recorded and shot.
The inhabitants of New Holland were very different from the people Cook had come across in other Pacific lands. They were darker skinned than the Maori and painted their bodies:
......They were all of them clean limnd, active and nimble. Cloaths they had none, not the least rag, those parts which nature willingly conceals being exposed to view compleatly uncovered......(Joseph Banks)
Tupaia could not make himself understood and at first the aborigines were very wary of the visitors and not at all interested in trading.
Joseph Banks recorded the fishing party observed at Botany Bay on 26 April 1770. He wrote:
......Their canoes… a piece of Bark tied together in Pleats at the ends and kept extended in the middle by small bows of wood was the whole embarkation, which carried one or two…people…paddling with paddles about 18 inches long, one of which they held in either hand.....(Banks, Journal II, 134)
Endeavour left Australia and sailed via the Possession Isle and Endeavour Strait for repairs at Batavia, Java (October-December 1770). Although the crew had been quite healthy and almost free from scurvy, the scourge of sailors, many caught dysentery and typhoid and over thirty died at Batavia or on the return journey home via Cape Town, South Africa (March-April 1771). The ship arrived off Kent, England (July 1771).
The voyage successfully recorded the Transit of Venus and largely discredited the belief in a Southern Continent. Cook charted the islands of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia and the scientists and artists made unique records of the peoples, flora and fauna of the different lands visited.
Timeline - Second Voyage 1772 - 1775
In July 1772 Resolution, commanded by Captain Cook, and Discovery, commanded by Lieutenant Furneaux, set sail from Britain, via Madiera (Jul-Aug) and Cape Town, South Africa (Oct-Nov), towards the Antarctic in search of the Great Southern Continent.
During January 1773 the ships took on fresh water, charts of the voyage being marked with:
......Here we watered our Ship with Ice the 1st. Time 26S 44W and Here we compleated our Water/26S 20W but became separated in thick fog: Here we parted company…. and The Resolutions Track after we parted Company on the 8 of February 1773......
The ships became the first known to have crossed the Antarctic Circle (17 January 1773). On 9th January Cook wrote:
.......we hoisted out three Boats and took up as much as yielded about 15 Tons of Fresh Water, the Adventure at the same time got about 8 or 9 and all this was done in 5 or 6 hours time; the pieces we took up and which had broke from the Main Island, were very hard and solid, and some of them too large to be handled so that we were obliged to break them with our Ice Azes before they could be taken into the Boats...... Cook, Journals II, 74.)
The ships met again in New Zealand (February-May 1773) and set off to explore the central Pacific, calling at Tahiti (August), where, from the island of Raiatea, they took aboard Omai who returned with the Adventure to England (7 September).
After visiting Amsterdam and Middelburg, two islands that Cook called the Friendly Islands (Tongan group) (October) the ships became separated and never met again. Both ships returned separately to New Zealand. (November) A boats crew from the Adventure were killed by Maori (17 December) and the ship sailed for Britain, arriving July 1774.
Cook on Resolution attempted another search for the Great Southern Continent (November 1773), crossing the Antarctic Circle on 20th December 1773. However, the ice and cold soon forced him to turn north again and he made another search in the central Pacific for the Great Southern Continent. In January 1774 he turned south again, crossing the Antarctic Circle for the second time. Captain Cooks Journal, 2nd January 1774.
Cook sailed north, arriving at Easter Island in March 1774. Cook was too ill to go ashore but a small party explored the southern part of the island. The artist William Hodges painted a group of the large statues of heads (moia) for which the island has become famous.
Cook then sailed to the Marquesas (March); Tahiti (April) and Raiatea (June); past the Cook Islands and Niue, or Savage Islands as Cook called them; Tonga (June); Vatoa, the only Fijian Island visited by Cook (July); New Hebrides (July-August); New Caledonia (September) and Norfolk Island (October); before returning to New Zealand (October 1774).
Not all the peoples of the islands visited by Cook were friendly and when his ship approached Niue the local people would not let his crew ashore. Cook wrote:
.......The Conduct and aspect of these Islanders occasioned my giving it the Name of Savage Island, it lies in the Latitude of 19 degrees 1 Longitude 169 degrees 37 West, is about 11 Leagues in circuit, of a tolerable height and seemingly covered with wood amongst which were some Cocoa-nutt trees......(Cook, Journals II, 435, 22 June 1774.)
En route for New Zealand, Cook sailed west and explored the islands which he called the New Hebrides, now known as Vanuatu, arriving on 17 July 1774. The people were Melanesian, not Polynesian, and spoke different languages and had different customs. Cook recorded:
........The Men go naked, it can hardly be said they cover their Natural parts, the Testicles are quite exposed, but they wrap a piece of cloth or leafe round the yard (nautical slang for the penis) which they tye up to the belly to a cord or bandage which they wear round the waist just under the Short ribs and over the belly and so tight that it was a wonder to us how they could endure it.......(Cook, Journals II, 464, 23 July 1774)
Cook sailed past or visited nearly all the islands in the group, including landfalls at Malekula, Tanna and Erromango. He later moved on to New Caledonia.
Cooks reception by the New Hebrideans was generally hostile. At Erromango during the landing on 4th August 1774 the marines had to open fire when the natives tried to seize the boat and started to fire missiles. Cook wrote:
....…I was very loath to fire upon such a Multitude and resolved to make the chief a lone fall a Victim to his own treachery…happy for many of these poor people not half our Musquets would go of otherwise many more must have fallen.......(Cook, Journals II, 479, 4th August 1774)
Some of Cooks crew were slightly injured but several natives were wounded and their leader killed. Back on the ship Cook had a gun fired to frighten off the islanders and decided to depart.
Cook left New Zealand to return to Britain via the Southern Ocean in November 1774 and arrived in Tierra del Fuego, South America, in December. Cook took on stores and spent the holiday in what he called Christmas Sound. He described the area:......except those little tufts of shrubbery, the whole country was a barren Tack (or Rock) doomed by Nature to everlasting sterility......(Cook, Ms Journal PRO Adm 55/108)
Cook left South America in early January 1775 and set off across the southern Atlantic for Cape Town, South Africa. On the way he tried to confirm the location of a number of islands charted by Alexander Dalrymple on an earlier voyage. On 17 January 1775 Cook arrived at the cold, bleak, glaciated island he called South Georgia and spent 3 days charting it before sailing on.
Cook headed east and in late January came across the South Sandwich Islands that he again charted and then sailed on to Cape Town, arriving in late March 1775. He then headed across the Atlantic via St. Helena and Ascension Island (May), the Azores (July) and landed at Portsmouth on 30th July 1775.
On his return Cook became a national hero. He was presented to the King, made a member of the Royal Society and received its Copley Medal for achievement. Cook was promoted to post-captain of Greenwich Hospital and wrote up his account of the voyage. This did not mean retirement for Cook who went on his third and final voyage the following year.
The second voyage was one of the greatest journeys of all time. During the three years the ships crews had remained healthy and only four of the Resolutions crew had died. Cook disproved the idea of the Great Southern Continent; had become the first recorded explorer to cross the Antarctic Circle; and had charted many Pacific islands for the first time.
Timeline - Third Voyage 1776 - 1780
In 1776 Cook sailed in a repaired Resolution (July) to search for the North West Passage and to return Omai to his home on Huahine in the Society Islands.
He sailed via the Canary Islands and was joined at Cape Town, South Africa, by the Discovery, commanded by Charles Clerke.
The Discovery was the smallest of Cooks ships and was manned by a crew of sixty-nine. The two ships were repaired and restocked with a large number of livestock and set off together for New Zealand ( December).
Cook sailed across the South Indian Ocean and confirmed the location of Desolation Island, later known as Kerguelen Island. Cook wrote of Christmas Harbour where he first anchored on 25th December 1776:
........I found the shore in a manner covered with Penguins and other birds and Seals…so fearless that we killed as ma(n)y as we chose for the sake of their fat or blubber to make Oil for our lamps and other uses… Here I displayd the British flag and named the harbour Christmas harbour as we entered it on that Festival........(Cook, Journals III, i, 29-32)
Cook sailed east, arriving at Van Diemens Land/Tasmania (January 1777) and Queen Charlottes Sound, New Zealand (February). The Maori were wary at first, expecting Cook to take revenge for the killing of members of the Adventures crew in 1773, but instead Cook befriended the leader of the attack.
The ships stayed for nearly two weeks in New Zealand, restocking with wild celery and scurvy grass and trading with the local Maori who set up a small village in Ship Cove. Cook set off around the islands of the south Pacific (February), visiting the Cook Islands (April); Tongan Islands (July); and Tahiti (August-December 1777)
In 1778 Cook visited the Hawaiian islands, or Sandwich Islands as he named them, for the first time. Cook wrote:
........We no sooner landed, that a trade was set on foot for hogs and potatoes, which the people gave us in exchange for nails and pieces of iron formed into some thing like chisels….At sun set I brought every body on board, having got during the day Nine tons of water….about sixty or eighty Pigs, a few Fowls, a quantity of potatoes and a few plantains and Tara roots.......(Cook, Journals III, i. 269 & 272)
In February 1778 Cook sailed from the Hawaiian Islands across the north Pacific to the Oregan coast of North America. He travelled up the coast in bad weather until he found a safe harbour, Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island, Canada. There he refitted the ships, explored the area and developed relations with the local people.
Cook described a village there, probably Yoquot:
….their houses or dwellings are situated close to the shore…Some of these buildings are raised on the side of a bank, theses have a flooring consisting of logs supported by post fixed in the ground….before these houses they make a platform about four feet broad…..so allows of a passage along the front of the building: They assend to this passage (along the front of the building) by steps, not unlike some at our landing places in the River Thames........(Cook, Journals III, i, 306)
Cook left Nootka Sound in April 1778 and sailed north along the Alaskan coast looking for inlets that might lead to the Northwest passage but was then forced to turn south. By July he had rounded the Alaskan Peninsula and was able to sail north again, visiting the Chukotskiy Peninsula, Russia, before heading out into the Bering Sea.
Cook described the summer huts, or yarangas, of the Chukchi people as:
.........pretty large, and circular and brought to a point at the top; the framing was of slight poles and bone, covered with the skins of Sea animals…About the habitations were erected several stages ten or twelve feet high, such as we had observed on some part of the American coast, they were built wholly of bones and seemed to be intended to dry skins, fish &ca. upon, out of reach of their dogs........(Cook, Journals III, I, 413)
After entering the Bering Sea on 11th August 1778, Cook crossed the Arctic Circle and went as far north as latitude 70 degrees 41 North before being forced back by the pack ice off Icy Cape, Alaska. On the ice all around the ships were large numbers of walruses. About a dozen of these huge animals were killed to replenish the supplies of fresh meat and to provide oil for the lamps.
Cook had to turn west and worked his way down the Russian coast, eventually heading south and east into Norton Sound, Alaska, in September 1778. He wrote of their very brief encounter with the inhabitants of Norton Sound:
....…a family of the Natives came near to the place where we were taking off wood…I saw no more than a Man, his wife and child…...(Cook, Journals III, I, 438)
After a short period spent searching for the Northwest Passage Cook realised that it was too late in the year to make any progress and so sailed for warmer winter quarters in the Hawaiian Islands, arriving there in December 1778.
After circumnavigating the big island of Hawaii for over a month the ships finally anchored in Kealakekua Bay on 16th January 1779. The Hawaiians in over 1000 canoes came out to welcome them, the arrival of the ships coinciding with celebrations to mark the religious festival of Makahiki to the god Lono. The Hawaiians seem to have treated Cook as a personification of the god and at first relations were good on this second visit. However, relationships became strained and Cook left the island on 4th February 1779.
When Cook left Hawaii his ships ran into gales which broke a mast, forcing him to return to Kealakekua Bay for repairs on 11th February. This time the native people were less friendly and stole the cutter of the Discovery. The next day, the 14th February 1779, Cook went ashore to take the Hawaiian king into custody pending the return of the cutter but a fight developed and Cook, four of his marines and a number of natives were killed. Cooks remains were buried at sea in Kealakekua Bay.
Charles Clerke took over command of the stunned expedition and explored the other Hawaiian islands before sailing north to search for the North-West Passage. The ships called at Kamchatka, Russia, (April-June) where they were welcomed by the governor, Behm, at Bolsheretsk. Behm took news of the expedition and Cooks death overland to St. Petersburg from where it reached Europe and Britain.
Having made another voyage into the Arctic in search of the Northwest Passage (June-July) the ships returned to Kamchatka in August. In November they set off sailing south along the east coast of Japan, between Taiwan and the Phillipines and arrived at Macao, China, in December.
In January 1780 the expeditions left for home, crossing the Indian Ocean, calling at Cape Town (April-May) and arriving back in Stromness, Orkney, in August but not returning to London until October 1780.
News of Cooks death reached Britain in January 1780, ahead of the return of Resolution and Discovery in October 1780. The voyage was written up and published and Cooks life gradually commemorated in articles, books, medals and monuments.
The achievements of the voyage were overshadowed by the deaths of both Cook and his second-in-command, Clerke. The main purpose of the voyage, the discovery of the Northwest Passage, was not realised but large tracts of the Pacific and Arctic coasts of America and Russia were charted.
Early attempts to summarise the life of Cook appeared in the popular press soon after news of his death reached Britain. Articles in journals such as the Westminster Magazine, published in January 1780, included Biographical Anecdotes of Capt. Cook, charting his life from his birth in Marton, North Yorkshire. The first published biography of Cook, Life of Captain James Cook, by Andrew Kippis, appeared a few years later in 1788.
1774 Cook & Hawkesworth Antique Atlas of Australia, New Zealand 52 Maps & Prints
- Title : Cartes et figures des voyages entrepris par ordre de sa Majesté Britannique, actuellement régnante ; pour faire des découvertes dans l'hémisphère méridional, et successivement exécutés par le Commodore Byron, le Capitaine Carteret, le Capitaine Wallis & le Capitaine Cook dans les vaisseaux. MDCCLXXIV (1774)
- Size: 4to (Quatro)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1774
- Ref #: 35632
Description:
This original antique Atlas containing 52 maps and prints, as called for, from some of the foremost explorers of the mid 18th century, including Commodore Byron, Captain Carteret, Captain Wallis & Captain James Cook, was published as the 1st French edition of Cartes et figures des voyages entrepris par ordre de sa Majesté Britannique: (Maps and Figures of Travels undertaken by Order of his Present Reigning British Majesty) in 1774, published after only a year after the 1st English edition by John Hawkesworth.
The 52 prints and maps contained in this atlas chart in maps, prints and plans, the progression in the exploration of the South Seas of the 4 explorers. But there is of course, the standout amongst these 4 explorers and that is of course Captain James Cook.
At the time of the publication of this tome, Cook had returned from his first voyage of exploration to The South Pacific, becoming the first European to survey and chart the coastline of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia. But at this point Cook was not as famous as he was destined to become, after completing 2 more voyages of exploration, and in turn becoming the most famous explorer of his era.
The majority of this atlas contains the prints and maps dedicated to Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery including the two famous maps, one of New Zealand and the other the East Coast of Australia. All voyages can be tracked from the first large folding map of the South Seas, at the beginning of the Atlas, that illustrates the tracks on Cook and the other 3 explorers.
In-4 binding in half-calf, spine with five bands with gilding boxes and title label complete with 52 folding & single plates
Spine & boards in poor condition with lack of leather and scratched covers, contents tights with plates in very good condition.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 4to (Quatro)
Plate size: - 4to (Quatro)
Margins: - 4to (Quatro)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning - Maps & Prints
Plate area: - Folds as issued - Maps & Prints
Verso: - Folds as issued - Maps & Prints
Background:
Capt. Cook First Voyage 1768 - 1771:
In 1768 Cook was chosen to lead an expedition to the South Seas to observe the Transit of Venus and to secretly search for the unknown Great Southern Continent (terra australis incognita).
Cook and his crew of nearly 100 men left Plymouth (August 1768) in the Endeavour and travelled via Madeira (September), Rio de Janiero (November-December) and Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) to Tahiti.
At Tierra del Fuego (January 1769) Cooks men went ashore and met the local people whom Cook thought perhaps as miserable a set of People as are this day upon Earth. Joseph Bankss party collected botanical specimens but his two servants, Thomas Richmond and George Dorlton, died of exposure in the snow and cold. Leaving Tierra del Fuego Endeavour rounded Cape Horn and sailed into the Pacific Ocean.
Sir Joseph Banks wrote about the homes of the Fuegans
..…huts or wigwams of the most unartificial construction imaginable, indeed no thing bearing the name of a hut could possibly be built with less trouble. They consisted of a few poles set up and meeting together at the top in a conical figure, these were covered on the weather side with a few boughs and a little grass, on the lee side about one eighth part of the circle was left open and against this opening was a fire made.......(Banks, Journal I, 224, 20th January 1769)
Samuel Wallis on the ship Dolphin discovered Tahiti in 1767. He recommended the island for the Transit of Venus observations and Cook arrived here in April 1769. Cook, like Wallis two years before him, anchored his ship in the shelter of Matavai Bay on the western side of the island.
In Matavai Bay Cook established a fortified base, Fort Venus, from which he was to complete his first task – the observation of the Transit of Venus (3rd June 1769). The fort also served as protection for all the important scientific and other equipment which had to be taken ashore as:
.......great and small chiefs and common men are firmly of opinion that if they can once get possession of an thing it immediately becomes their own…the chiefs employd in stealing what they could in the cabbin while their dependents took every thing that was loose about the ship…...(Joseph Banks).
Theft by some native peoples plagued Cooks voyages.
Cook and his crew experienced good relations with the Tahitians and returned to the islands on many occasions, attracted by the friendly people of this earthly paradise. On arrival Cook had set out the rules, including:
.....To endeavour by every fair means to cultivate a friendship with the Natives and to treat them with all imaginable humanity....
Just as Cook was planning to leave Tahiti two members of Endeavours crew decided to desert, having strongly attached themselves to two girls, but Cook recovered them.
Cook sailed around the neighbouring Society Islands and took on board the Tahitian priest, Tupaia, and his servant, Taiata. Endeavour left the Society Island in August 1769.
Tupaia acted as interpreter when they came into contact with other Polynesian peoples and helped Cook to make a map of the Pacific islands. This showed Cook the location of islands arranged according to their distance from Tahiti and indicated Tupaias and Polynesian knowledge of navigation and their skill as great mariners.
Cook sailed in search of the Southern Continent (August-October 1769) before turning west to New Zealand. The first encounters with the native Maori of New Zealand in October were violent, their warriors performing fierce dances, or hakas, in attempts to threaten and challenge the ships crew. Some of their warriors were killed when Cooks men had to defend themselves. Eventually relations improved and Cook was able to trade with the Maori for fresh supplies.
Exploring different bays and rivers along the way Cook circumnavigated New Zealand and was the first to accurately chart the whole of the coastline. He discovered that New Zealand consisted of two main islands, north (Te Ika a Maui) and south (Te Wai Pounamu) islands (October 1769-March 1770).
The artist Sydney Parkinson described three Maori who visited the Endeavour on 12th October 1769:
......Most of them had their hair tied up on the crown of their heads in a knot…Their faces were tataowed, or marked either all over, or on one side, in a very curious manner, some of them in fine spiral directions…
This Maori wears an ornamental comb, feathers in a top-knot, long pendants from his ears and a heitiki, or good luck amulet, around his neck.
At the northern end of the south island Cook anchored the ship in Ship Cove, Queen Charlotte Sound, which became a favourite stopping place on the following voyages. Parkinson noted:
......The manner in which the natives of this bay (Queen Charlotte Sound) catch their fish is as follows: - They have a cylindrical net, extended by several hoops at the bottom, and contracted at the top; within the net they stick some pieces of fish, then let it down from the side of the canoe and the fish, going in to feed, are caught with great ease.....(Parkinson, Journal, 114)
In Queen Charlottes Sound Cook visited one of the many Maori hippah, or fortified towns.
........The town was situated on a small rock divided from the main by a breach in a rock so small that a man might almost Jump over it; the sides were every where so steep as to render fortifications iven in their way almost totally useless, according there was nothing but a slight Palisade…in one part we observed a kind of wooden cross ornamented with feathers made exactly in the form of a crucifix cross…we were told that it was a monument to a dead man.......
Endeavour left New Zealand and sailed along the east coast of New Holland, or Australia, heading north (April-August 1770). Cook started to chart the east coast and on 29th April landed for the first time in what Cook called Stingray, later, Botany Bay.
The ship struck the Great Barrier Reef and was badly damaged (10 June). Repairs had to be carried out in Endeavour River. (June-August 1770). The first kangaroo to be sighted was recorded and shot.
The inhabitants of New Holland were very different from the people Cook had come across in other Pacific lands. They were darker skinned than the Maori and painted their bodies:
......They were all of them clean limnd, active and nimble. Cloaths they had none, not the least rag, those parts which nature willingly conceals being exposed to view compleatly uncovered......(Joseph Banks)
Tupaia could not make himself understood and at first the aborigines were very wary of the visitors and not at all interested in trading.
Joseph Banks recorded the fishing party observed at Botany Bay on 26 April 1770. He wrote:
......Their canoes… a piece of Bark tied together in Pleats at the ends and kept extended in the middle by small bows of wood was the whole embarkation, which carried one or two…people…paddling with paddles about 18 inches long, one of which they held in either hand.....(Banks, Journal II, 134)
Endeavour left Australia and sailed via the Possession Isle and Endeavour Strait for repairs at Batavia, Java (October-December 1770). Although the crew had been quite healthy and almost free from scurvy, the scourge of sailors, many caught dysentery and typhoid and over thirty died at Batavia or on the return journey home via Cape Town, South Africa (March-April 1771). The ship arrived off Kent, England (July 1771).
The voyage successfully recorded the Transit of Venus and largely discredited the belief in a Southern Continent. Cook charted the islands of New Zealand and the east coast of Australia and the scientists and artists made unique records of the peoples, flora and fauna of the different lands visited.
Vice-Admiral John Byron (1723-1786) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is known for his circumnavigation of the globe aboard the HMS Dolphin, completing one of the first British expeditions to achieve this feat. His account of the voyage, "The Narrative of the Honourable John Byron," influenced subsequent explorations. Byron's naval career included service in the Seven Years' War and the American Revolutionary War.
Rear-Admiral Philip Carteret (1733-1796) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is best known for his role as the captain of HMS Swallow during the first circumnavigation of the globe. Carteret's expedition, which took place from 1766 to 1769, aimed to explore and map uncharted regions of the Pacific Ocean. His discoveries included the Carteret Islands and the Pitcairn Islands. Carteret's voyage greatly contributed to the knowledge of Pacific geography and exploration during that time.
Samuel Wallis (1728-1795) was a British naval officer and explorer. He is renowned for leading the first recorded European expedition to visit Tahiti and for his significant contributions to the exploration of the Pacific Ocean. In 1766, Wallis commanded HMS Dolphin on a voyage funded by the British Admiralty. During the expedition, he discovered and named several islands, including Tahiti, which he encountered in June 1767. Wallis's visit to Tahiti marked the beginning of sustained European contact with the island and its inhabitants. His exploration efforts and subsequent reports greatly expanded European knowledge of the Pacific region. Wallis's achievements laid the foundation for future explorations and influenced subsequent voyages of exploration in the Pacific.
John Hawkesworth 1715 -1775
An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cooks view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Cook , Capt. James 1728-1779
James Cook was born on 27 October 1728 in Marton, England. His father was a poor farm labourer who had worked his way up to Overseer. James began as a farm labourer and grocer\\\'s assistant. He soon found employment on the Baltic sea in a Collier (coal transport ship) at the age of 18.
During the war with the French in 1755, James Cook enlisted as an Able Seaman on the Eagle. Within a month he was promoted, because of outstanding ability, to Masters Mate. Four years later he was promoted to Master. In command of his own ship, James Cook performed a crucial charting of the St. Lawrence River, which made possible the great amphibious assault upon Quebec City in 1759. In 1763 he was given command of the schooner Grenville to survey the eastern coasts of Canada over a four year period. These excellent charts were used up until the early part of the 20th century.
James Cook was selected to lead a 1768 expedition to observe the transit of Venus, and to explore new lands in the Pacific Ocean. In his first Pacific voyage, James Cook rounded Cape Horn in the Endeavour and reached Tahiti on 3 June 1769. After recovering a necessary scientific instrument stolen by the natives, the transit of Venus was successfully observed. The Endeavour then spent six months charting New Zealand. James Cook next explored and claimed possession of eastern Australia. Returning to England, on 12 June 1771, via New Guinea, Java and the Cape of Good Hope, the crew suffered an appalling 43% fatality rate. James Cook thus became very concerned about crew health on subsequent voyages. He instituted compulsory dietary reforms that were copied by many other ship captains.
The object of Captain Cook\\\'s second Pacific Ocean voyage was to confirm the existence of a theorized Great Southern Continent. His ship the Resolution, accompanied by the Adventure, departed Plymouth on 13 July 1772 and sailed around the Cape of Good Hope. Beset by ice, he was unable to reach Antarctica. Although its existence was suspected, James Cook demonstrated, by traversing large areas of the south Pacific, that it would have to be a frigid wasteland, and not an economically productive addition to the British empire. James Cook charted many of the South Pacific islands with the incredible accuracy of 3 miles. This accuracy was made possible by a new and highly accurate clock. The two ships returned to England, via Cape Horn, on 29 July 1775. The experimental diets and close attention to cleanliness had a miraculous effect: out of a crew of 118, only one man was lost to disease! Since public interest was high, the many paintings by the artists were widely displayed and published as engravings. James Cook was also awarded the Copley Gold Medal and elected as a fellow of the Royal Society.
The third great voyage is especially significant to the history of the west coast of North America. Captain Cook and his men were primarily searching for the Northwest Passage from the Pacific Ocean to the Atlantic Ocean. They departed Plymouth on 12 July 1776 in the Resolution and the Discovery.
The ships sailed around the Cape of Good Hope to reach the west coast of America in February of 1778. They continued north along the coast in haste to the Bering Sea and Bering Strait in an attempt to pass through the Arctic Ocean during the summer season. Foiled by ice, James Cook returned to Hawaii to prepare for another attempt at the Northwest Passage the next season. Soon after they had departed, a storm damaged the foremast of the Resolution and forced a return to Kealakekua Bay for repairs. Unfortunately, they had previously overstayed their welcome and relations became tense. The theft of a ship\\\'s cutter led Captain Cook to put ashore to demand the return of the boat. A fight broke out and James Cook was killed on 14 Feb 1779 by angry natives. Although his men made another attempt at the Northwest Passage, they were unsuccessful. The expedition did identify the possibilities of trade with the coastal American natives for otter seal furs, which could then be bartered for Chinese goods that were highly prized in England.
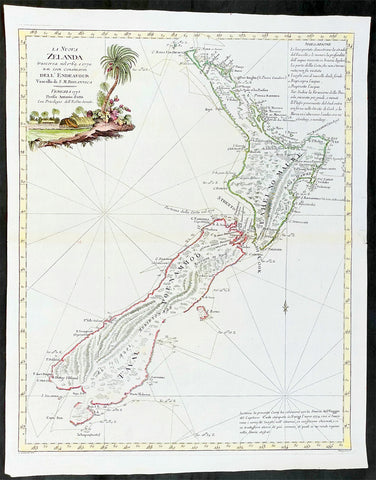
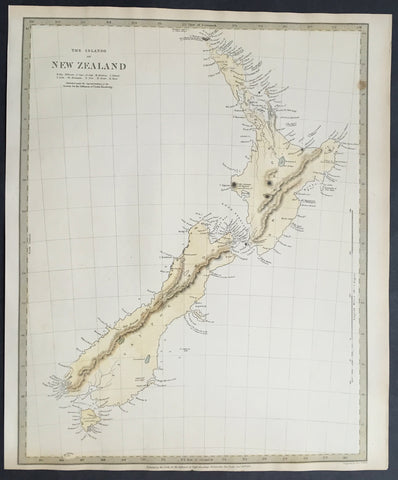
1778 Antonio Zatta Antique Map of New Zealand af. Captain James Cook - Beautiful
- Title : La Nuova Zelanda trascorsa nel 1769 e 1770 d'al Cook Comandante dell' Endeavour Vascello di S. M. Britannica . . . 1778
- Ref #: 93527
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
- Date : 1778
Description:
This impressive original hand coloured copper-plate engraved very early antique map of New Zealand, after Captain James Cook, was engraved in 1778 (the first edition with a second dated 1791) was published by Antonio Zatta in his 1779 edition of Atlante Novissimo
This is a beautifully engraved map after Captain James Cooks surveys of 1769. Cook published the first compete map of NZ in 1774, with this more decorative map being published by Zatta some 4 years later. The map contains all of Cooks coastal survey detail with some details of the interior of the islands. Also included are the tracks of Cooks ship HMS Endeavour as he surveyed the coast as well as his approach and exit from New Zealand. Beautiful original hand colour, with a heavy impression denoting an early pressing.
The maps of Venetian publisher Antonio Zatta are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 14in (455mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land "Nieuw Zeeland" after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasman's place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including 'Cape Maria van Diemen' (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the 'Three Kings' islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiralty's choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via "Secret Instructions" to be opened once at sea.
Cook's party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cook's intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavour's voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cook's crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavour's return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cook's second voyage, and was related to Cook's wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawke's Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavor's crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cook's "Banke's Island" is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the "Isle Solander" to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cook's first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cook's chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cook's very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
Zatta, Antonio fl. 1757 - 1797
Antonio Zatta was a prominent Italian editor, cartographer, and publisher. Little is known about his life beyond his many surviving published works. It is possible that he was born as early as 1722 and lived as late as 1804. He lived in Venice and his work flourished between 1757 and 1797. He is best known for his atlas, Atlante Novissimo (1779-1785), and for his prolific output of prints and books that were both precisely made and aesthetically pleasing. Zatta clearly had a large network from which to draw information; this is how he was able to publish the first glimpse of the islands visited by Captain Cook in the Atlante Novissimo.
Zattas maps are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. His re-engraving and publication of John Mitchells famous map of North America A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America in 1778, is considered one of the best re-issues of this seminal, landmark map .
......He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.... (Portinaro & Knirsch, The Cartography of North America, 1500-1800, p. 319).
Zatta was among the leaders in the eighteenth-century revival of fine printing in Italy and his choice of the text of Raynal to support his re-issue of Mitchells Map, is not surprising. Anne Palms Chalmers describes Zatta as a sardonic writer with the focus of a certain amount of political controversy (Venetian Book Design in the Eighteenth Century, The Metropolitan Museum of Art Bulletin, New Series, Vol. 29, No. 5, January 1971, pp. 226-235). Chalmers describes Zattas printing and design as harmonious in composition with ornament unified by style, quality of line, and tone of printing.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
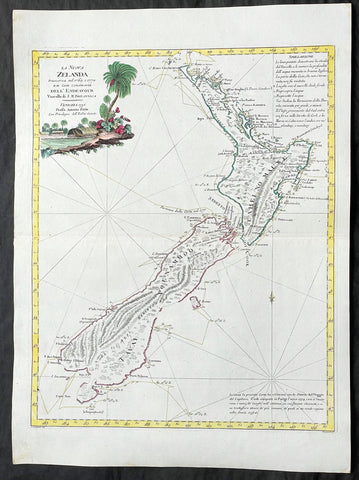
1778 Antonio Zatta Antique Map of New Zealand af. Captain James Cook - Magnificent
Antique Map
- Title : La Nuova Zelanda trascorsa nel 1769 e 1770 d'al Cook Comandante dell' Endeavour Vascello di S. M. Britannica . . . 1778
- Ref #: 17023
-
Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Size: 21 1/4in x 15 1/2in (540mm x 400mm)
- Date : 1778
Description:
This impressive original hand coloured copper-plate engraved very early antique map of New Zealand, after Captain James Cook, was engraved in 1778 (the first edition with a second dated 1791) was published by Antonio Zatta in his 1779 edition of Atlante Novissimo. (This is one of the best examples of this early New Zealand map I have see to date)
This is a beautifully engraved map after Captain James Cooks surveys of 1769. Cook published the first compete map of NZ in 1774, with this more decorative map being published by Zatta some 4 years later. The map contains all of Cooks coastal survey detail with some details of the interior of the islands. Also included are the tracks of Cooks ship HMS Endeavour as he surveyed the coast as well as his approach and exit from New Zealand. Beautiful original hand colour, with a heavy impression denoting an early pressing.
The maps of Venetian publisher Antonio Zatta are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 21 1/4in x 15 1/2in (540mm x 400mm)
Plate size: - 18in x 14in (455mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land "Nieuw Zeeland" after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasman's place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including 'Cape Maria van Diemen' (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the 'Three Kings' islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiralty's choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via "Secret Instructions" to be opened once at sea.
Cook's party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cook's intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavour's voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cook's crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavour's return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cook's second voyage, and was related to Cook's wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawke's Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavor's crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cook's "Banke's Island" is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the "Isle Solander" to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cook's first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cook's chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cook's very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
Zatta, Antonio fl. 1757 - 1797
Antonio Zatta was a prominent Italian editor, cartographer, and publisher. Little is known about his life beyond his many surviving published works. It is possible that he was born as early as 1722 and lived as late as 1804. He lived in Venice and his work flourished between 1757 and 1797. He is best known for his atlas, Atlante Novissimo (1779-1785), and for his prolific output of prints and books that were both precisely made and aesthetically pleasing. Zatta clearly had a large network from which to draw information; this is how he was able to publish the first glimpse of the islands visited by Captain Cook in the Atlante Novissimo.
Zattas maps are noteworthy for their fine craftsmanship and high aesthetics. His re-engraving and publication of John Mitchells famous map of North America A Map of the British and French Dominions in North America in 1778, is considered one of the best re-issues of this seminal, landmark map .
......He was probably the most important Italian map publisher of the late eighteenth century and is responsible for a large number of atlases and single maps of considerable aesthetic and scientific merit.... (Portinaro & Knirsch, The Cartography of North America, 1500-1800, p. 319).
Zatta was among the leaders in the eighteenth-century revival of fine printing in Italy and his choice of the text of Raynal to support his re-issue of Mitchells Map, is not surprising. Anne Palms Chalmers describes Zatta as a sardonic writer with the focus of a certain amount of political controversy (Venetian Book Design in the Eighteenth Century, The Metropolitan Museum of Art Bulletin, New Series, Vol. 29, No. 5, January 1971, pp. 226-235). Chalmers describes Zattas printing and design as harmonious in composition with ornament unified by style, quality of line, and tone of printing.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
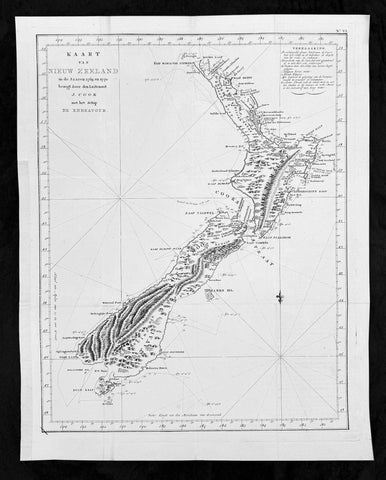
1774 Captain James Cook Antique Map, 1st Printed Chart of New Zealand. Dutch Ed. - Scarce
- Title : Kaart van Nieuw Zeeland in de Jaaren 1769 en 1770 bezogt door den Luitenant J Cook met het Schip De Endeavour (Chart of New Zealand explored in 1769 and 1770 by Lieutenant. J. Cook Commander of his Ship Endeavour)
- Date : 1774
- Size: 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 35674
Description:
This magnificent large original copper plate engraved scarce antique map, the first printed chart of New Zealand by Captain James Cook, during his circumnavigation of the South Pacific in 1769-70, was published in the 1st Dutch edition of Hawkeworths Voyages in 1774 by Reiner Arrenberg Reizen Rondom de Weereld Ondernomen op Bevell van Zyne Majesteit den Tans Regeerenden Koning van Groot-Brittanje tot Het Doen van Ontdekkingen ... J. Hawkesworth Uit Het Engelsch Vertaalt,
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 21in x 16 1/2in (530mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/4in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 394mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasmans place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including Cape Maria van Diemen (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the Three Kings islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiralty\\\'s choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cooks party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cooks intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavours voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cooks crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavours return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The chart and its publication
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cooks second voyage, and was related to Cooks wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawkes Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavors crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cooks Bankes Island is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the Isle Solander to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cooks first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cooks chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cooks very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
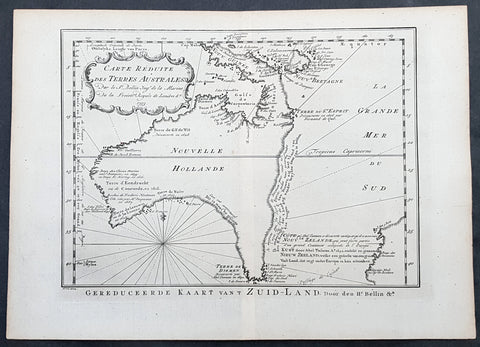
1753 Jacques Nicolas Bellin Antique Map of Australia & New Zealand, Pre Captain Cook
- Title : Carte Reduite des Terres Australes pour Servir a l Histoire des Voyages...1753
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1753
- Ref #: 80279
Description:
This important, early original copper-plate engraved antique map of Australia, New Zealand & New Guinea, one of the earliest near complete maps dedicated to the Island Continent, by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved by Jakob van der Schley in 1753 - date engraved in the title cartouche - and was published by Abbé Prévosts in the 1755 Dutch edition of Histoire Géneral des Voyages.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 3/4in x 8 1/2in (295mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
This is one of the few maps prior to the mid 18th century to focus specifically on the Australian continent & surrounding islands, prior to Captain James Cooks famous first voyage to the south pacific, under secret instruction from the British Admiralty, between 1768 & 1771.
Mainland Australia is connected to both Tasmania (Terre de Van Diemen) and Papua New Guinea (Nouv. Guinee) Along the imaginary eastern coastline is a note that reads: I suppose that the land of Diemen can join with the land of Terre du St Esprit, but this is without proof. A partial coastline of New Zealand is shown peeking out of the corner of the map, with a note of discovery along the western coastline by Abel Tasman in 1642 and speculation that it might be part of a great southern continent, Terra Australis.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley 1715 - 1779 was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for La Vie de Marianne by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763), published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747. He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme, published in The Hague in 1740. Most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages are signed by van der Schley.
This is an important map of Australia depicting the interesting theories & misconceptions of the great southern land just prior to the extensive exploration & discoveries of the region in the later part of the 18th century. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
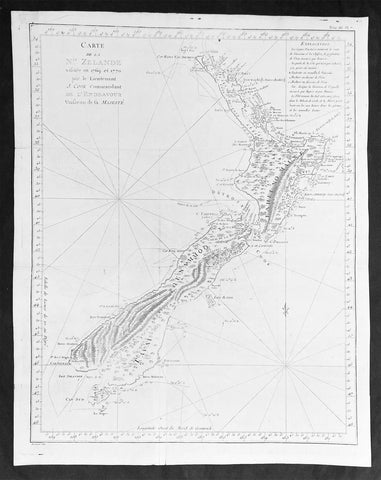
1774 Captain James Cook Antique Map, 1st Printed Chart of New Zealand
- Title : Carte de la Nle. Zelande visitée en 1769 et 1770 par le Lieutenant J. Cook Commandant de l'Endeavour vasseau de sa Majesté.
- Date : 1774
- Size: 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in (520mm x 420mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 27004
Description:
This magnificent large original copper plate engraved scarce antique map, the first printed chart of New Zealand by Captain James Cook, during his circumnavigation of New Zealand in 1769-70, was published in the 1st French edition of Hawkeworths Voyages in 1774.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 16 1/2in (520mm x 420mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/4in x 15 1/2in (490mm x 394mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued, professional restoration of tear to center of map, no loss
Verso: - Folds as issued, professional restoration of tear to center of map, no loss
Background:
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasman\\\'s place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including \\\'Cape Maria van Diemen\\\' (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the \\\'Three Kings\\\' islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiralty\\\'s choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cook\\\'s party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cook\\\'s intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavour\\\'s voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cook\\\'s crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavour\\\'s return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasmans place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including Cape Maria van Diemen (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the Three Kings islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiraltys choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cooks party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cooks intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavours voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cooks crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavours return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The chart and its publication
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cooks second voyage, and was related to Cooks wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawkes Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavors crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cooks Bankes Island is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the Isle Solander to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cooks first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cooks chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cooks very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
1795 (1806) Canzler Large Antique Map Australia, Ulimaroa, New Zealand SE Asia
- Title : Karte vom Funften Erdtheil oder Polynaesien-Inselwelt oder Australien oder Sudindien (Map of the fifth earth or Polynesia or Australia or South India.)
- Size: 24 1/4in x 20 1/2in (615mm x 520mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1795 (1806)
- Ref #: 93121
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved, antique map of Australia, New Zealand and SE Asia by Friedrich Gottlieb Canzler in 1795, was published by the Homann Firm in 1806.
A distinct map with the short lived alternative name of Ulimaroa for New Holland, given by Canzler after Daniel Djurberg mistakenly interperated the New Zealand Maori word, Olhemaroa, from Cooks diary, for Australia. The real interpretation being Long Hand, the Maori name for New Caledonia.
There are two records in Cooks diary relating to Ulimaroa....
5th Feb 1769....This place we concluded to be the land difcovered by Tafman, which he called Cape Maria Van Diemen, and finding thefe people fo intelligent, we inquired farther, if they knew of any country befides their own: they anfwered, that they never had vifisted any other, but that their anceftors had told them, that to the N.W. by N., or N.N.W. there was a country of great extent, called Ulimaroa, which people had failed in a very large canoe
5th Feb 1770.....When we were under fail, our old man aTopaa came on board to take his leave of us, and as we were ftill defirous of making farther enquiries whether any memory of Tafman had been preferved among thefe people, Tupia was directed to afk him whether he had ever heard that fuch a veffel as ours had vifited the country. To this he replied in the negative, but faid, that his anceftors had told him there had once come to this place a fmall veffel, from a distant country, called Ulimaroa, in which were four men, who, upon coming on fhore, were all killed: upon being afked where this diftant land lay, he pointed to the northward. Of Ulimaroa we had heard fome-thing before, from people about the Bay of Iflands, who faid that their anceftors had vifisted it; and Tupia had alfo talked to us of Ulimaroa.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24 1/4in x 20 1/2in (615mm x 520mm)
Plate size: - 24 1/2in x 19in (620mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Ulimaroa was a name given to Australia by the Swedish geographer and cartographer Daniel Djurberg in 1776. Djurberg adapted the name from Olhemaroa, a Māori word found in Hawkesworths edition of Captain James Cook and Sir Joseph Banks journals which is thought to have been a misunderstood translation — the Māori were actually referring to Grand Terre, the largest island of New Caledonia. Djurberg believed the name meant something like big red land, whereas modern linguists believe it meant long hand — echoing the geography of Grand Terre. The spurious name continued to be reproduced on certain European maps, particularly some Austrian, Czech, German and Swedish maps, until around 1820, including in Carl Almqvists 1817 novel Parjumouf Saga ifrån Nya Holland (Stockholm, 1817).
Canzler, Friedrich Gottlieb 1764-1811
Friedrich Gottlieb Canzler was born in Wolgast, Sweden in 1764. He graduated from the school in his hometown and from 1781 to 1783 the Sundische Gymnasium in Stralsund . He then studied history , geography , statistics and the Swedish language at the University of Göttingen . After completing his studies, he also received his doctorate and habilitation in Göttingen, and worked as a Privatdozent for history, geography, statistics and cameralistics .
In addition, he published in Göttingen from July 1789 to February 1791 the General Political State Newspaper for all Stands, for which he ran his own university and newspaper printing plant, and founded in 1797 an Academic Reading Museum. Two years later he was appointed Professor of Statistics, State Economics, Cameral, Financial and Commerz Sciences at the University of Greifswald where he worked until his death in 1811.
Selected Works:
- New magazine for recent history, Earth and ethnology. Leipzig 1790
- English language teaching for Germans. Göttingen 1796
- General Litteraturarchiv for history, geography and statistics. Leipzig 1792-1798 (as publisher)
- Map of the fifth earth or Polynesia or Australia or South India. Nuremberg 1795, 1805 and 1806 (as well as 1813 with corrections by Christian Gottlieb Reichard)
- Front India or Hindostan or East India on the side of the Ganges. Nuremberg 1804
1774 James Cook Large Antique Map of The South Seas, Australia, New Zealand etc
- Title : Carte d une Partie de la Mer du Sud Contenant les Decouvertes de Vaisseaux de sa Majeste Le Dauphin, Commodore Byron La Tamar, Capitne. Mouats 1765 Le Dauphin, Capitne. Wallis Le Swallow, Capitne. Cartaret, 1767 et l Endeavour, Lieutenant Cook 1769
- Ref #: 17034
- Size: 28 1/2in x 18 3/4in (725mm x 475mm)
- Date : 1774
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map, a chart of the voyage tracks of Captain James Cook during his first voyage of discovery of Australia & NZ, and 4 other explorers to the South Seas from 1765 to 1771. It was engraved by Robert Benard and published in the 1774 French translation of John Hawkesworths publication An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks.
The 5 Voyages, with Captains, ships & tracks are;
1. 1764-66 - HMS Dolphin under Command of Commodore John Byron, completed the first circumnavigation of the globe under two years.
2. 1764-1766 - HMS Tamar under Command of Captain Patrick Mouat, accompanied Commodore John Byron & HMS Dolphin on 1764-66 circumnavigation of the world.
3. 1766-68 - HMS Dolphin under Command of Captain Samuel Wallis, completed another circumnavigation & was the first European to visit Tahiti & the Society Islands.
4. 1766-68 - HMS Swallow under Command of Captain Philip Carteret, who accompanied HMS Dolphin under the command of Samuel Wallis to circumnavigate the world.
5. 1769-71 - HMS Endeavour, under Command of Lieutenant James Cook (later Captain) completed a the mapping of Tahiti & the Society Islands, New Zealand & the East Coast of Australia.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, brown, pink, red, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28 1/2in x 18 3/4in (725mm x 475mm)
Plate size: - 27in x 15in (685mm x 380mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued, light toning along folds
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light toning along folds
Verso: - Folds as issued, light toning along folds
Background:
Commodore John Byron 1723 – 1786 was a British Royal Navy officer and politician.He circumnavigated the world as a commodore with his own squadron in 1764-1766. He fought in battles in The Seven Years War and the American Revolution. He rose to Vice Admiral before his death in 1786.
Captain Patrick Mouat. Commanded HMS Tamer on a voyage of discovery with Commodore John Byron between 1764-66. HMS Tamar was a sloop, mounting sixteen guns: ninety men, three lieutenants, and two and twenty petty officers.
Captain Samuel Wallis 1728 – 1795 was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean. Was given the command of HMS Dolphin in 1751 as part of an expedition led by Philip Carteret in the Swallow with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan, Wallis continuing to Tahiti, which he named King George the Third\'s Island in honour of the King in June 1767.
Captain Philip Carteret 1733 – 1796 was a British naval officer and explorer who participated in two of the Royal Navys circumnavigation expeditions in 1764–66 and 1766–69.
Captain James Cook is considered one of the most talented Surveyors & Map Makers of any age, for Cook, the production of a new chart was his principal reason for going to sea. His charts were aimed at fellow seamen so he incorporated as much information as possible while employing an economy of style and little elaboration. The quality of his charts can be confirmed by the fact that some survey details from Newfoundland to New Zealand & Australias East Coast could still be safely used over one hundred years later. His last piece of the New Zealand hydrographic chart was only removed in the 1990s.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
Robert Bénard 1734 – 1777 was an 18th-century French engraver.
Specialized in the technique of engraving, Robert Ménard is mainly famous for having supplied a significant amount of plates (at least 1,800) to the Encyclopédie by Diderot & d Alembert from 1751.
Later, publisher Charles-Joseph Panckoucke reused many of his productions to illustrate the works of his catalog.
1856 A K Johnston Large Antique Map of New Zealand
- Title : New Zealand by A K Johnston
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 27003
- Size: 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Description:
This original large hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of New Zealand was published by A K Johnston in the 1856 edition of his National atlas of historical, commercial, and political geography.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning
Plate area: - Light age toning
Verso: - Light age toning
Background:
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasmans place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including Cape Maria van Diemen (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the Three Kings islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiraltys choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cooks party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cooks intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavours voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cooks crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavours return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The chart and its publication
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cooks second voyage, and was related to Cooks wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawkes Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavors crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cooks Bankes Island is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the Isle Solander to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cooks first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cooks chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cooks very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
1856 A K Johnston Large Antique Map of New Zealand
- Title : New Zealand by A K Johnston
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93438
- Size: 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Description:
This original large hand coloured steel plate engraved antique map of New Zealand was published by A K Johnston in the 1856 edition of his National atlas of historical, commercial, and political geography.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 21 1/2in (635mm x 545mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
The first printed chart of New Zealand.
New Zealand (or Aotearoa, as the Maori call it) had been first encountered by Europeans in the early 1640s, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman named the land Nieuw Zeeland after the Dutch province. Importantly, Tasman only sailed up the west coast of the North Island and had little notion as to the nature of the islands or their broader geographical context. A small number of Tasmans place names were preserved by Cook (and remain in place to this day), including Cape Maria van Diemen (the northernmost point of the North Island) and the Three Kings islets, where Cook and his men celebrated the Christmas of 1769-the first Europeans to visit the islands for nearly 130 years.
Captain James Cook (1728-1779) is considered to be the greatest explorer of the eighteenth century and was the finest maritime cartographer of the Age of Enlightenment. Having first worked on coal colliers and then distinguished himself as a surveyor in Eastern Canada, in 1768 he became the British Admiraltys choice to lead an unprecedented voyage of discovery. The central impetus for the expedition was to observe the Transit of Venus from Tahiti and then to proceed to explore Terra Australis Incognita, the supposedly rich southern continent. Whereas the first part of the voyage was to be conducted under the auspices of international scientific cooperation, the second part was entirely clandestine and was only communicated to Cook via Secret Instructions to be opened once at sea.
Cooks party left Plymouth in August 1768 aboard the converted coal collier HMS Endeavor and proceeded to Tahiti by way of Cape Horn. They arrived in time to observe the Transit of Venus, which occurred June 3, 1769. Cook then proceeded towards New Zealand, to the coordinates recorded by Tasman. As New Zealand was quite conceivably part of Terra Australis, it was Cooks intention to carefully explore and map the region.
On October 6, 1769, the Endeavor sighted the North Island (Te Ika a Maui) at Turanga Nui, which Cook renamed Poverty Bay. He and his crew had arrived on the opposite shore to where Tasman had met the island. Cook proceeded to the South Island (Te Wai Pounamu), carefully mapping both landmasses with a running survey. He used soundings, visual observations, and triangulation regulated by astronomical observations to create his manuscript charts.
Despite being constantly buffeted by wind and rain, and after having some hostile relations with the Maori that resulted in Maori deaths, Cook and his crew managed to circumnavigate both the North and South Islands, proving that they were separate islands divided by the Cook Strait. They also proved the islands were not connected to any southern continent. On March 31, 1770, Cook wrote in his journal that the Endeavours voyage:
…must be allowed to have set a side the most, if not all, the arguments and proofs that have been advanced by different Authors to prove that there must be a Southern Continent; I mean to the northward of 40 degrees South, for what may lay to the Southward of that Latitude I know not (Cook, Journals I, 290).
The Endeavor left New Zealand at Cape Farewell, sailing west towards Australia, where Cooks crew would become the first Europeans to explore that region. In total, they had surveyed over 2,400 miles of New Zealand coastline in six months.
Upon the Endeavours return to England in July 1771, Cook became a national hero. He would go on to lead two further voyages that would succeed in illuminating most of the Pacific Ocean to European eyes. On the second expedition, Cook would put to rest the myth of a southern continent. On the third, he kick started the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest of North America while searching for the Northwest Passage. He was killed by Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay in 1779.
The chart and its publication
Cook returned to England with over 300 manuscript charts and coastal views. The original manuscript chart of New Zealand is now held by the British Library (Add MS 7085, f. 16-7). The chart was drawn, at least in part, by Isaac Smith (1752-1831), a draftsman of considerable skill who worked with Cook in Newfoundland, sailed on the Endeavour and Cooks second voyage, and was related to Cooks wife. Of the New Zealand chart, Cook wrote:
The Chart which I have drawn will best point out the figure and extent of these Islands…beginning at Cape Palliser and proceed round Aehei no mouwe (North Island) by the East Cape &ca. The Coast between these two Capes I believe to be laid down pretty accurate both in its figure and the Course and distance from point to point. The oppertunities I had and the methods I made use on to obtain these requesites were such as could hardly admit of an error… some few places however must be excepted and these are very doubtfull …(Cook, Journals I, 275-6)
The overall delineation is impressively accurate, correctly capturing many of the bays and promontories, and making insightful observations of the interior. Many of the names given by Cook survive to this day, including the Alps, (the great mountain chain of the South Island), Mount Egmont (the volcano on the North Island, also known as Mount Taranaki), the Bay of Islands, the Bay of Plenty, Hawkes Bay, and most intriguingly, Cape Kidnappers (a point on the North Island where Maori warriors attempted to abduct a member of the Endeavors crew).
There are a few errors, conspicuous only because of the otherwise superb accuracy of the chart. Notably, Cooks Bankes Island is in fact a peninsula, part of the South Island. Further south, what looks like a possible peninsula is actually Stewart Island, with the Isle Solander to the west. Also, some portions of coast line remain un-surveyed due to adverse conditions or distraction. For example, the portion of coastline near Bankes Island is but a dotted line because Lieutenant Gore had thought he sighted land to the southeast. Upon sailing toward it, the promontory proved to be clouds. Despite such mistakes, the chart is remarkably thorough.
The present chart was printed as part of the official account of Cooks first voyage, which was edited by the literary critic John Hawkesworth and underwritten by the British Admiralty. An Account of the Voyages undertaken by the order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere… (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1773) recounted the voyages not only of Cook, but of Byron, Wallis, and Carteret who had also ventured to the Pacific for the Royal Navy earlier in the 1760s. It was engraved by John Abraham Bayly (fl. 1755-1794), a London-based engraver who specialized in cartographic work.
In 1816, the British Hydrographic Office began to reprint the map for its vessels. The chart was continuously consulted into the twentieth century. Due to this longevity, its extraordinary origins, and its important place in the founding of New Zealand as a British colony, Cooks chart is considered to be the most important single map in the history of New Zealand. Due to the complexity of the assignment and the great accuracy of the survey, it is also considered to be one of Cooks very finest maps, and one of the truly great achievements of Enlightenment cartography.
1838 SDUK Large Antique Map of New Zealand - 1st edition
- Title :The Islands of New Zealand....Published by the SDUK...Nov 26th 1838
- Ref #: 61040
- Size: 16in x 13in (400mm x 330mm)
- Date : 1838
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original hand coloured antique map* of New Zealand was engraved in 1838 (1st edition) - dated at the bottom of the map - by J & C W Walker and was published in the Baldwin & Cradock edition of theSociety For the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (SDUK) Atlas.
Background: The map covers the entire island country from Cape Reinga (C. Maria Van Diemen) to Stewart Island. Various cities, towns, rivers, mountains, bays and several other topographical details are noted with relief shown by hachure.
In 1840, after the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi, the British annexed New Zealand as part of the Australian colony of New South Wales. However, it separated from New South Wales to become a colony in its own right in 1841. This map was originally copyrighted in 1838, but was issued in Volume two of Chapman and Hall's 1844 edition of Maps of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge
The SDUK produced two landmark volumes in cartography in the first half of the 19th century. The first volume concentrated on areas of the old world, Europe, Africa, Great Britain etc. The second volume contained maps of the new world, America, South Asia, including US state maps, colonies of Australia, South Africa, South America etc. Also included were some of the finest engraved town and city plans published at that time.
The SDUK was published in its entirety or in part by many publishers including Baldwin and Cradock 1829-32, Chapman & Hall in 1844, Charles Knight & co. 1846 – 1852. G. Cox published the SDUK between 1852-3, Stanford 1857-70 and later revised edition were also published after Stanford.
This is a finely engraved map with beautiful original colour t on strong, clean paper. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 13in (400mm x 330mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1808 Wilkinson Antique Map of East Coast of Australia, New Zealand, inset Sydney
- Title : New South Wales New Zealand New Hebrides...Published Dec 12th 1808
- Ref #: 9003
- Size: 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
- Date : 1808
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the east coast of Australia, New Zealand and the Solomon Islands - with inset maps of Lord Howe Island, Norfolk Island & Port Jackson - was published in 1808 by Robert Wilkinson - the date is included in the title - in his wideley acclaimed General Atlas of the World published between 1794 and 1816.
This is a finely engraved copper-plate map with beautiful original hand colouring on strong stable paper. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 11in (330mm x 280mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 10in (320mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1888 Pic Atlas Large Antique Map of the North Island of New Zealand
- Title : General Map of The North Island of New Zealand
- Ref #: 50321
- Size: 28in x 18in (710mm x 460mm)
- Date : 1888
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique map of the North Island of New Zealand was engraved in 1888 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - by Alex J Scally and was published in the extremely significant Australian & New Zealand publicationThe Picturesque Atlas of Australasia between 1886-88. Also includes an index to the map on the verso giving names and locations of places on the map.
These maps were some of the best maps published at the time in the "Modern" look. The colour is bright, the engraving extremely fine and the paper heavy and stable.
The Picturesque Atlas of Australasia was published in Sydney between 1886-88. Many of its over 700 wood-engraved illustrations were specially commissioned works by leading Australian artists.
It was released in 42 separate editions usually bound into three large volumes and sold a remarkable 50,000 copies.
Its publication was one of the most significant cultural projects in nineteenth-century Australia. Writers, artists, academics and politicians came together to prepare a book of unprecedented grandeur and ambition, and a publishing company was established to produce and publish it. The seven hundred engravings on steel and wood contained in the Picturesque Atlas were among the finest engravings to be found anywhere in the world at this time.
The Atlas was a collegial project, staffed by a large number of artists and garnering an unusual number of contributors for one work. Lightly supervised by the former Sydney Morning Herald editor Andrew Garran it was lavishly produced at the Wynyard Square headquarters of the Atlas company. It had the services of the Melburnian journalist and public figure James Smith who wrote much of the Victorian and Tasmanian material, and W.H. Traill wrote extensively about Queensland. It was not, of course, an Atlas is the usual sense of the word, maps playing a comparatively minor role. But use of Atlas in the title, Hughes-d'Aeth notes, gave a sense of the scale of the publication both in terms of comprehensiveness and format. As the author points out, calling it an Atlas carries a promise of the exactitude of the relationship between the subject and its representation, and also bears a sense of the acquisitiveness that shadows the imperial phase of cartography.
There were only thirty maps in the Atlas's 800 pages, but there were hundreds of pictures. This is where much of the ideological work of the Atlas was completed and this is where Paper Nation concentrates its analysis. Its first task is to unravel the linguistic ball of string that is the word 'picturesque'. Though Humphrey Repton and Uvedale Price had their opinions, Hughes-d'Aeth is quite right to pick William Gilpin out of the line-up of suspicious aesthetes, for it was he who really popularised the idea of travelling in search of picturesque views. Paper Nation's dissection of the term picturesque is particularly aware of the term's adaptation to colonial usage, and its mutations through time. The picturesque took on an increasingly acquisitive edge, as admiration of the beauty of the land was joined by a concern to exploit it. A 'deep reverence for production' can be seen in the Picturesque Atlas's many illustrations of mines, factories and agricultural processes. The slag heaps of a mine were now as 'picturesque' as a fern-filled valley, but this does mean that the term was evacuated of all meaning. Rather the aesthetic appropriation of the land and its material exploitation were part of a continuum of colonial attitudes, and it was the duty of the Picturesque Atlas to affirm and re-affirm the rightness of European habitation and progress. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, yellow, green, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 28in x 18in (710mm x 460mm)
Plate size: - 28in x 18in (710mm x 460mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1834 Henry Teesdale Antique Map The Pacific, Australia, New Zealand, Nth America
- Title : Chart of The Pacific Ocean.....London Published by Henry Teesdale & co. High Holborn March 1834
- Ref #: 50303
- Size: 17 1/2in x 14in (445mm x 355mm)
- Date : 1834
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of the Pacific Ocean, Australia, New Zealand, to North & South America by John Dower was engraved in 1834 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published in the 1835 edition of Henry Teesdales A New General Atlas of the World. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 19in x 15 1/2in (485mm x 395mm)
Plate size: - 17 1/2in x 14 1/2in (445mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Teesdale & co., Henry fl 1828-1843
Teesdale was a prominent London publisher and founding fellow of the Royal Geographical Society. He produced large-scale maps and charts and a number of fine atlases in the early part of the nineteenth century. He employed the most skilled draftsmen and engravers and his maps are renowned for precise detail and fine coloring
1856 James Virtue Antique Map of New Zealand and the Colonies of Australia
- Title : New Zealand and the Australian Colonies of Great Britain James S Virtue
- Size: 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1856
- Ref #: 93052
Description:
This original lithograph antique map of New Zealand and the Colonies of Australia was published by James Virtue in 1856, just after Victorian statehood in 1851 and just prior to Queensland statehood in 1859.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 10in (330mm x 255mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
A highly detailed map just prior to the gold and population boom of both Australia and New Zealand, with much of Australia unexplored in the center.
Virtue, George & James
George Virtue (1794 – 1868) was a 19th-century London publisher, well known for printing engravings. His publishing house was located at 26 Ivy Lane, Paternoster Row, London, EC
Virtue selected accomplished artists, employed the best engravers, and produced books that were rarely surpassed in elegance and correctness for the period. Chief among his publications were the following, all illustrated by William Henry Bartlett: Switzerland, by William Beattie, 2 vols. 1836; Scotland, by W. Beattie, 1838; The Waldenses, by W. Beattie, 1838; American Scenery, 2 vols. 1840; Description of the Beauties of the Bosphorus, by Julia Pardoe, 1840; and The Danube, its History and Scenery, by W. Beattie, 1844. Virtue created a prodigious business, issuing upwards of twenty thousand copper and steel engravings through his career.
In 1848, Virtue purchased two magazines. One was an art publication, The Art Union, which had been founded in 1839 by Hodgson & Graves, then purchased in 1847 by Chapman & Hall. The second purchase was controlling interest in Sharpe\\\\\\\'s London Magazine, a literary and cultural magazine, Arthur Hall publisher. In 1849, Virtue renamed the art magazine The Art Journal and, in time, it became known as the premier art publication of Great Britain. Also in 1849, he created a new firm with Arthur Hall called Arthur Hall, Virtue & Co
James Sprent Virtue (1829 – 1892) inherited the publishing business from his father, George, after his retirement in 1855
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
1860 Edward Weller Large Antique Map of The Pacific - Australia to California
- Title : The Pacific Ocean
- Ref #: 70063
- Size: 26 1/2in x 19in (675mm x 490mm)
- Date : 1860
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original steel plate engraved hand coloured antique map by Edward Weller was published in the 1860 edition of The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, Green, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 19in (675mm x 490mm)
Plate size: - 26 1/2in x 19in (675mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Weller, Edward 1819 – 1884
Weller was a London-based engraver, cartographer and publisher, working from offices in Red Lion Square and later, Bloomsbury. Amongst his considerable portfolio were various atlases, many of which focussed on the educational publishing market. Having established his credentials as an engraver of finely detailed works, he sold maps to be published in a number of regular magazines and pamphlets, perhaps the best known being The Dispatch Atlas; a compilation of maps Weller had already published in The Weekly Dispatch. Although Weller usually engraved the maps himself, he did work in partnership with others, particularly John Dower for this 1858 and 1863 volume. Weller also published The Crown Atlas in 1871.
The Dispatch Atlas featured well over one hundred superbly detailed steel plate engraved maps, usually with simplistic, single colour outline hand colouring, and a distinctive header style. Most English counties featured, some of which were divided onto separate sheets, affording space to engrave in even greater detail. The maps of North and South Devonshire for example include such details as individual property names, as do those of the Northern and Southern parts of Hampshire.
After Wellers death in 1884, many of these astonishingly detailed plates were sold on to other map makers, including George Washington Bacon, who, whilst retaining the level of detail, expanded the printing area of each plate, adding more precise and varied hand colouring in keeping with the final decades of the century.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 40973
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 31988
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 31975
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1854 Handtke & Flemming Antique Map of Australia, New Zealand, Pacific
- Title : Australien
- Date : 1854
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 32163
- Size: 17in x 14in (430mm x 355mm)
Description:
This hand coloured original steel-plate engraved antique highly detailed map of Australia, New Zealand, & The Pacific by Friedrich Handtke in 1854, was published in the Complete hand atlas of the recent description of the earth over all parts of the earth, Carl Flemming, Glougau.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14in (405mm x 355mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
Background:
Australia is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world\'s sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australias capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country\'s other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.
Australia was inhabited by indigenous Australians for about 60,000 years before the first British settlement in the late 18th century. It is documented that Aborigines spoke languages that can be classified into about 250 groups. After the European discovery of the continent by Dutch explorers in 1606, who named it New Holland, Australia\'s eastern half was claimed by Great Britain in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation to the colony of New South Wales from 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day. The population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the 1850s most of the continent had been explored and an additional five self-governing crown colonies established. On 1 January 1901, the six colonies federated, forming the Commonwealth of Australia. Australia has since maintained a stable liberal democratic political system that functions as a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy comprising six states and ten territories.
Being the oldest, flattest and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils, Australia has a landmass of 7,617,930 square kilometres. A megadiverse country, its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east and mountain ranges in the south-east. A gold rush began in Australia in the early 1850s, which boosted the population of the country. Nevertheless, its population density, 2.8 inhabitants per square kilometre, remains among the lowest in the world. Australia generates its income from various sources including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and manufacturing. Indigenous Australian rock art is the oldest and richest in the world, dating as far back as 60,000 years and spread across hundreds of thousands of sites.
The first recorded European sighting of the Australian mainland, and the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent (in 1606), are attributed to the Dutch. The first ship and crew to chart the Australian coast and meet with Aboriginal people was the Duyfken captained by Dutch navigator, Willem Janszoon. He sighted the coast of Cape York Peninsula in early 1606, and made landfall on 26 February at the Pennefather River near the modern town of Weipa on Cape York. The Dutch charted the whole of the western and northern coastlines and named the island continent New Holland during the 17th century, but made no attempt at settlement. William Dampier, an English explorer and privateer, landed on the north-west coast of New Holland in 1688 and again in 1699 on a return trip. In 1770, James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast, which he named New South Wales and claimed for Great Britain.
With the loss of its American colonies in 1783, the British Government sent a fleet of ships, the First Fleet, under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, to establish a new penal colony in New South Wales. A camp was set up and the flag raised at Sydney Cove, Port Jackson, on 26 January 1788, a date which became Australia\'s national day, Australia Day. A British settlement was established in Van Diemens Land, now known as Tasmania, in 1803, and it became a separate colony in 1825. The United Kingdom formally claimed the western part of Western Australia (the Swan River Colony) in 1828. Separate colonies were carved from parts of New South Wales: South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. The Northern Territory was founded in 1911 when it was excised from South Australia. South Australia was founded as a free province—it was never a penal colony. Victoria and Western Australia were also founded free, but later accepted transported convicts. A campaign by the settlers of New South Wales led to the end of convict transportation to that colony; the last convict ship arrived in 1848.
1839 Samuel Augustus Mitchell Antique Map of New Holland, New Zealand & Oceania
- Title : No 18 Map of Oceania...Entered according to Act of Congress in the year 1839 by S Augustus Mitchell
- Date : 1839
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 32148
- Size: 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Description:
This detailed original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique map of New Holland - Australia, New Zealand, Polynesia & Micronesia, Oceania by Samuel Augustus Mitchell in 1839 - dated - was published in Mitchells School and Family Geography
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light soiling
Plate area: - Light soiling
Verso: - Light soiling
Background:
Early map of Australia and Oceania, the east coast is still referred to as NSW, with no sign of development of Melbourne or Victoria with New Zealand listing early Cook & Maori place names.
1840 P & A Lapie Antique Map of New Holland, New Zealand & Central Coast of NSW
- Title : Oceania
- Date : 1840
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 21425
- Size: 17in x 12in (430mm x 305mm)
Description:
This detailed original hand coloured lithograph map of Australia, New Zealand, Polynesia & Micronesia - Oceania - with an inset map of part of the coast of Sydney, NSW from Double Bay to Shoal Bay by Pierre & Alexandrie Lapie was published as a single map Kaeppelin & Co. in 1840.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 12in (430mm x 305mm)
Plate size: - 17in x 12in (430mm x 305mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Early map of Australia and Oceania, the east coast is still referred to as NSW, with no sign of development of Melbourne or Victoria with New Zealand listing early Cook & Maori place names. The inset map of the central NSW coast is still largely lacking in detail past Bathurst, with Australia Felix noted in the south.
Lapie, Pierre & Alexandre
Pierre M. Lapie 1779 - 1850 and his son Alexandre Emile Lapie 1809 - 1850 were French cartographers and engravers active in the early part of the 19th century. The Lapies were commissioned officers in the French army holding the ranks of Colonel and Captain, respectively. Alexander enjoyed the title of First Geographer to the King, and this title appears on several of his atlases. Both father and son were exceptional engravers and fastidious cartographers. Working separately and jointly they published four important atlases, an 1811 Atlas of the French Empire (Alexander), the 1812 Atlas Classique et Universel (Pierre), the Atlas Universel de Geographie Ancienne et Modern (joint issue), and the 1848 Atlas Militaire (Alexander). They also issued many smaller maps and independent issues. All of these are products of exceptional beauty and detail. Despite producing many beautiful maps and atlases, the work of the Lapie family remains largely underappreciated by most modern collectors and map historians. The later 19th century cartographer A. H. Dufour claimed to be a student of Lapie, though it is unclear if he was referring to the father or the son. The work of the Lapie firm, with its precise engraving and informational density, strongly influenced the mid-19th century German commercial map publishers whose maps would eventually dominate the continental market.