Military (4)
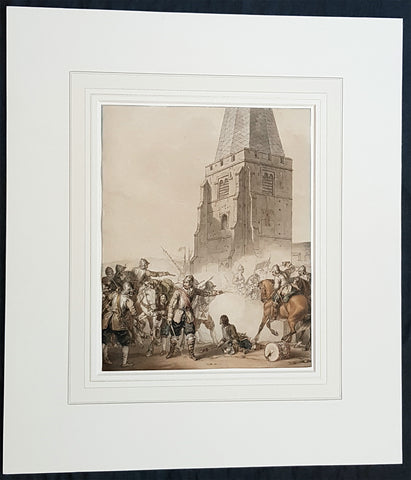
1810 John Augustus Atkinson Original Water Colour Art of an English War Skirmish
Antique Map
- Title : (A Civil War Skirmish)
- Ref #: 93444
- Size: 17in x 15in (430mm x 365mm)
- Date : 1810
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully executed original pen, pencil and watercolour picture of an English Civil War battle scene was painted by John Augustus Atkinson in ca 1810.
Atkinson was known for his battle scene art works during his time at the St Petersburg Court in Russia as well as his Napoleonic battle scenes from the early 19th century.
Atkinson is held in high esteem as a watercolourist, and was elected as a member of the Society of Painters in Water Colours in 1808. He has works of art held at many prestigious museums in Russia, Europe and the UK, such as the Tate, Royal Watercolour Society, National Maritime Museum and many more listed below. He also sells on the open market with this piece last sold in 2004.
Professionally matted and can be easily removed if required.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 17in x 15in (430mm x 365mm)
Plate size: - 9 3/4in x 8in (247mm x 203mm)
Margins: - Min 0in (0mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (Roundheads) and Royalists (Cavaliers) principally over the manner of Englands governance and part of the wider Wars of the Three Kingdoms. The first (1642–1646) and second (1648–1649) wars pitted the supporters of King Charles I against the supporters of the Long Parliament, while the third (1649–1651) saw fighting between supporters of King Charles II and supporters of the Rump Parliament. The war ended with Parliamentarian victory at the Battle of Worcester on 3 September 1651.
Unlike other civil wars in England, which were mainly fought over who should rule, these conflicts were also concerned with how the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland were to be governed. The outcome was threefold: the trial and execution of Charles I (1649); the exile of his son, Charles II (1651); and the replacement of English monarchy with, at first, the Commonwealth of England (1649–1653) and then the Protectorate, which as the Commonwealth of England, Scotland, and Ireland unified the British Isles under the personal rule of Oliver Cromwell (1653–1658) and briefly his son Richard (1658–1659). The execution of Charles I was particularly notable given that an English king had never been executed before. In England, the monopoly of the Church of England on Christian worship was ended, while in Ireland the victors consolidated the established Protestant Ascendancy. Constitutionally, the wars established the precedent that an English monarch cannot govern without Parliaments consent, although the idea of Parliamentary sovereignty was only legally established as part of the Glorious Revolution in 1688.
Atkinson, John Augustus 1775 - 1830
Atkinson was an English artist, engraver and watercolourist.
He was born in London and at the age of 9, in 1784, went to live with his uncle, the famous engraver James Walker, in St Petersburg, Russia. Walker was engraver to the empress Catherine the Great 1729 - 1796 and encouraged Atkinson to study art, seeing a talent in him. Atkinson was well placed in St Petersburg to study art, being surrounded by the many collections of Catherine and the Russian Nobility, the richest in Europe. It is known that Atkinson was encouraged by Catherine herself along with and her son & later Emperor of Russia Paul I 1754 - 1801. Paul later commissioned Atkinson to paint large pieces from Russian history that can be seen in many Museums today around the world.
After the death of Paul in 1801, Atkinson returned to England and in 1803 published A Picturesque Representation of the Manners, Customs, and Amusements of the Russians, in 100 plates, drawn and etched by himself. He also painted in watercolours and in 1808 was elected to the Society of Painters in Water Colours. Many of his works, during the Napoleonic wars, were of naval subjects. He painted many battle scenes including a Battle of Waterloo, which was engraved by John Burnet.
His last contribution to the Royal Academy exhibition was in 1829. He died on 25 March 1830 in London.
Selected Works
• Carriage on Sledges 1803 Art Gallery of Greater Victoria, British Columbia
• A Russian Village 1804 Art Gallery of Greater Victoria, British Columbia
• Golubtza 1804 Art Gallery of Greater Victoria, British Columbia
• Village Amusements 1804 Art Gallery of Greater Victoria, British Columbia
• Scene from Tom Jones Courtauld Institute of Art, London
• The Slack Rope Courtauld Institute of Art, London
• A Belgian Waggon with Four Horses Tate Gallery, London
• Illustrations to Ossian The Huntington Library, California
• Heaving a Lead 1807 National Maritime Museum
• Greenwich Pensioners 1808 National Maritime Museum
• Skating, 1810 Tyne & Wear Museums, England
• Ships of the Reign of King Edward IV 1812 - Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco
• 42nd Highlanders at Waterloo Courtauld Institute of Art, London
• British Sailors Boarding a Man of War 1815 National Maritime Museum
1853 - 1857 Elephant Folio Album w/ 328 Antique Maps & Prints of The Crimea War - Unique
Antique Map
- Title : Crimean War Maps, Prints & Views
- Date : 1853 - 57
- Size: 24in x 18in (610mm x 455mm) Elephant Folio
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 35600
Description:
This is a unique and very comprehensive visual record of the Crimean War (1853 - 1856 & 57) in a huge Elephant Folio Album.
The album consists of 163 double pages with 328 original maps, prints and views of the War tipped in chronological order. These are mainly from the Illustrated London News, from the Wars beginning in 1853 to its end in 1856 through to the Coronation of Alexander II in 1857 and some of the first recipients of the Victoria Cross.
My impression is that the album was professionally organised and assembled possibly by a political or historical organisation of the time, in the mid 19th century.
This album is extremely large measuring 28 inches x 18 inches (62cm x 46cm) when closed and weighs approx. 14 Kg.
The Album contains; (in more detail directly below)
- 71 views of various battles during the conflict.
- 94 Portraits & prints of the leaders, generals, & personnel who were in charge and soldiers, sailors who participated in the war.
- 47 views of various cities and towns from the participating countries England, Russia, Crimea, Turkey etc.
- 63 prints of naval fleets, battleships, sea battles, landings & evacuations..
- 15 Maps of various regions and conflicts
- 25 victory scenes in Britain
- 39 prints of portraits and views of the Coronation of Alexander II
- 4 Pages of recipients from both Army & Navy, of the first Victoria Cross.
Battle Views (Battle of Kars, Kinburn, Sebastopol, Malakoff, Tchernaya, Sveaborg, Gheisk, Hango-Head, Narva, Balaclava, Inkerman, Charge of Light Cavalry Balaclava, Alma, Odessa, Crondstat, Citate, Oltenitza, Kalafat)
Prints of leaders, generals and soldiers (British, Russian, Turkish, Greek, French, Austrian, Peace Talks Paris, Congress of Vienna, Allied Naval Command, Marshall Pelissier, Wounded, Hospitals, Sir De Lacy Evans, Nicolas Emperor of Russia, Royal Marines, Lord Raglan, Napoleon III, Commanders of Allied Armies in the East, Sultan of Turkey, Marshal St Arnaud, French Cavalry, French Infantry, British Infantry, British Navy, Sir Charles Napier, Rear Admiral Corry, & Plumridge, British Cavalry & Artillery Officers, Scots Guards, Royal marines, British Cavalry, Coldstream Guards, Grenadier Guards, Omer Pacha, General Prim)
Views of cities & towns (Balaclava, Kars, Sebastopol, Sveaborg, Helsingborg, Kiel, Copenhagen, Crondstat, St Petersberg, Kerch, Inkermann, Eupatoria, Alma, Coast of Crimea, Varna Bay, Odessa and Coast, Constantinople, Oltenitza, Sinope)
Fleets, battleships & sea battles (HMS Wellington, Steamers, British Fleet, Baltic Fleet, Gun Boats, Nystad, Sebastopol, Spithead, Portsmouth, Flying Squadron, Trafalgar and Resolution, landing French Troops at Gallipoli, Duke of Wellingtons Flagship, Turkish Fleet in Biospheres, English & French Fleet in Besika Bay, HMS Neptune)
Maps (Crimea & Black Sea region, Russia-Turkey, Constantinople, Austria-Russia, Spithead review of Fleet, Sea of Azoff, Kerch, River Alma to Balaklava, Plan of Sebastopol, Seat of War in the Crimea, Sebastopol & Balaklava, Picturesque map of the seat of war, Battle of Alma, The Ottoman Empire)
Florence Nightingale (Treating wounded, visiting wounded Balaclava)
Victory Scenes in England (illuminations, Parades, Queen, Brighton, Hyde Park, Awarding Medals, The Guards, Fireworks, Landing in Kalamita Bay)
The Album is huge Elephant Folio measuring 24in x 18in (610mm x 455mm) and weighing about 13kg (29lbs) The contemporary half morocco boards are worn, rubbed and detached from the internals that on the whole are clean and tight with occasional spotting and repairs with no loss.
Also included with the album is the following loose prints, maps and newspaper clippings;
- 47 prints and views from ILN on the British Expedition into Abyssinia in 1868.
- 39 prints, views and maps from the ILN and The Graphic on the 1882 Anglo-Egyptian War.
- 60 Newspaper clipping from 1882 of The Times, Evening Standard, Daily News and other papers again on the Anglo Egyptian War.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable.
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24in x 18in (610mm x 455mm) each
Plate size: - 24in x 18in (610mm x 455mm) each
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
External Boards: - Worn, slit spine, scuffing detached from internals
Internal pages: - Overall clean, some spotting, light offsetting to some pages, several small repairs without loss
Background: The Crimean War was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between the Russian Empire and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom, and Sardinia-Piedmont.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the decline of the Ottoman Empire (the "Eastern Question"), the expansion of the Russian Empire in the preceding Russo-Turkish Wars, and the British and French preference to preserve the Ottoman Empire to maintain the balance of power in the Concert of Europe. The flashpoint was a disagreement over the rights of Christian minorities in Palestine, then part of the Ottoman Empire, with the French promoting the rights of Roman Catholics, and Russia promoting those of the Eastern Orthodox Church.
The churches worked out their differences with the Ottomans and came to an agreement, but both the French Emperor Napoleon III and the Russian Tsar Nicholas I refused to back down. Nicholas issued an ultimatum that demanded the Orthodox subjects of the Ottoman Empire be placed under his protection. Britain attempted to mediate and arranged a compromise to which Nicholas agreed. When the Ottomans demanded changes to the agreement, Nicholas recanted and prepared for war.
In July 1853, Russian troops occupied the Danubian Principalities (now part of Romania but then under Ottoman suzerainty). On 16 October 1853, having obtained promises of support from France and Britain, the Ottomans declared war on Russia. Led by Omar Pasha, the Ottomans fought a strong defensive campaign and stopped the Russian advance at Silistra (now in Bulgaria). A separate action on the fort town of Kars, in the Ottoman Empire, led to a siege, and an Ottoman attempt to reinforce the garrison was destroyed by a Russian fleet at the Battle of Sinop in November 1853.
Fearing the growth of influence of the Russian Empire, the British and French fleets entered the Black Sea in January 1854. They moved north to Varna in June 1854 and arrived just in time for the Russians to abandon Silistra. In the Baltic, near the Russian capital of Saint Petersburg, an Anglo-French fleet instituted a naval blockade and bottled up the outnumbered Russian Baltic Fleet, causing economic damage to Russia by blockading trade while also forcing the Russians to keep a large army guarding St. Petersburg from a potential allied attack.
After a minor skirmish at Köstence (now Constanța), the allied commanders decided to attack Russia's main naval base in the Black Sea, Sevastopol, in Crimea. After extended preparations, allied forces landed on the peninsula in September 1854 and marched their way to a point south of Sevastopol after they had won the Battle of the Alma on 20 September 1854. The Russians counterattacked on 25 October in what became the Battle of Balaclava and were repulsed, but the British Army's forces were seriously depleted as a result. A second Russian counterattack at Inkerman ended in a stalemate.
By 1855, the Italian Kingdom of Sardinia sent an expeditionary force to Crimea, siding with France, Britain and the Ottoman Empire. The front settled into the Siege of Sevastopol, involving brutal conditions for troops on both sides. Smaller military actions took place in the Caucasus (1853–1855), the White Sea (July–August 1854) and the North Pacific (1854–1855).
Sevastopol finally fell after eleven months, after the French assaulted Fort Malakoff. Isolated and facing a bleak prospect of invasion by the West if the war continued, Russia sued for peace in March 1856. France and Britain welcomed the development, owing to the conflict's domestic unpopularity. The Treaty of Paris, signed on 30 March 1856, ended the war. It forbade Russia to base warships in the Black Sea. The Ottoman vassal states of Wallachia and Moldavia became largely independent. Christians in the Ottoman Empire gained a degree of official equality, and the Orthodox Church regained control of the Christian churches in dispute.
The Crimean War was one of the first conflicts in which military forces used modern technologies such as explosive naval shells, railways and telegraphs. The war was also one of the first to be documented extensively in written reports and in photographs. The war quickly became a symbol of logistical, medical and tactical failures and of mismanagement. The reaction in Britain led to a demand for the professionalisation of medicine, most famously achieved by Florence Nightingale, who gained worldwide attention for pioneering modern nursing while she treated the wounded.
The Crimean War marked a turning point for the Russian Empire. The war weakened the Imperial Russian Army, drained the treasury and undermined Russia's influence in Europe. The empire would take decades to recover. Russia's humiliation forced its educated elites to identify its problems and recognise the need for fundamental reforms. They saw rapid modernisation as the sole way to recover the empire's status as a European power. The war thus became a catalyst for reforms of Russia's social institutions, including the abolition of serfdom and overhauls in the justice system, local self-government, education and military service. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
The Illustrated London News (ILN)
In 1842, Herbert Ingram, a young printer and newsagent from Nottingham, arrived in London. As a newsagent he noticed that when on the rare occasions that newspapers included woodcuts, their sales increased. He therefore came to the conclusion that it would be possible to make a good profit from a magazine that included a large number of illustrations.
Herbert Ingram discussed the proposal with his friend, Mark Lemon, the editor of Punch magazine. With Lemon as his chief adviser, the first edition of the Illustrated London News appeared on 14th May 1842. Costing sixpence, the magazine had sixteen pages and thirty-two woodcuts. The first edition included pictures of the war in Afghanistan, a train crash in France, a steamboat explosion in Canada and a fancy dress ball at Buckingham Palace.
Ingram was a staunch Liberal who favored social reform. He announced in the London Illustrated News that the concern of the magazine would be \\\"with the English poor\\\" and the \\\"three essential elements of discussion with us will be the poor laws, the factory laws, and the working of the mining system\\\". Later Herbert Ingram was to become MP for Boston and until his death in 1860 continued his campaign for social reform in the House of Commons.
The London Illustrated News was an immediate success and the first edition sold 26,000 copies. Within a few months it was selling over 65,000 copies a week. Special events were important to the success of the London Illustrated News. The magazine did very well during the Exhibition 1851 and over 150,000 copies were sold of the edition that reported the funeral of the Duke of Wellington. The Crimean War caused a further boast to sales and by 1863 it was selling over 300,000 copies a week. This was far higher than other journals. For example, newspapers such as the Daily News only sold 6,000 copies at this time, and even the largest selling newspaper, The Times only sold 70,000 copies. In the Christmas Number of The Illustrated London News, 1855, the first pictures in color were published.
In the year 1879, The ILLUSTRATED LONDON NEWS claimed to be the fastest woodcut-printing establishment in the world. The Ingram Rotary machine had been invented. It printed both sides of the paper at once and turned out 6,500 copies per hour. It required only four men to operate it, whereas thirty men and five machines were needed previously
 The ILN held a commanding position in the market place. It was seriously challenged by The GRAPHIC in 1870. Although it never reached the circulation of the ILN. it did take a good market share until the turn of the century.
Please note all items auctioned are genuine, we do not sell reproductions. A Certificate of Authenticity (COA) can be issued on request.
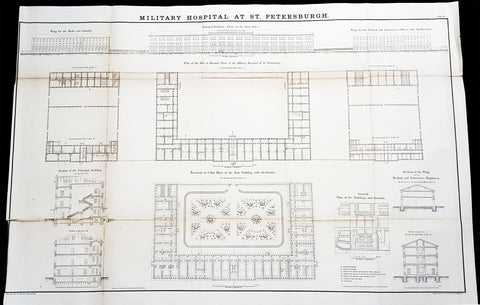
1856 Delafield Antique Architectural Plan SM Kirov Medical Academy St Petersburg
Antique Map
- Title : Military Hospital at St Petersburg
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 90139
- Size: 36in x 24in (915mm x 610mm)
Description:
This very large original lithograph print, an architectural plan of the S.M. Kirov Military Medical Academy in St Petersburg, Russia - during the time of the Crimean War and just prior to the American Civil War - was engraved by John T Bowen & co. of Philadelphia and was published in the 1856 edition of Captain Richard Delafields Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856.
In early 1855, Captain Richard Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 36in x 24in (915mm x 610mm)
Plate size: - 36in x 24in (915mm x 610mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
The S. M. Kirov Military Medical Academy (Военно-медицинская академия имени С. М. Кирова) is the oldest school of military medicine in Saint Petersburg and the Russian Federation. Senior medical staff are trained for the Armed Forces and conduct research in military medical services.
The origins of S.M. Kirov Military Medical Academy go back to the years of Peter the Great. In 1715 by the Tsars order the Admiralty Hospital in the Vyborg Side of Saint Petersburg was founded. In 1717 next to in the Land Military Hospital was opened. Since 1773 surgical schools attached to both hospitals were operating. In 1786 those schools were consolidated into the Main Medical College. It became the principal training center for army and fleet physicians.
Unofficially, the year 1714 is considered the foundation year of the academy. The Medical and Surgical Academy was established by the order of Emperor Paul I of 18/29 December 1798 on the initiative of Baron Alexei Vasilyev, General Director of the Medical College. At the same time a Neoclassical building for the Academy was designed by Antonio Porta. It was decorated with a set of panel paintings by Giuseppe Bernasconi.
Ranked as one of the best educational institutions in the Russian Empire, it was known as the Imperial Medical and Surgical Academy from 1808. According to the order of Emperor Alexander I, a member of the Medical and Surgical Academy had the rights, liabilities, and benefits of a member of the Academy of Sciences.
Sir James Wylie, a Scottish baronet, managed the academy between 1808 and 1838. His contributions have been commemorated with a monument which stood in front of the academy until the October Revolution. The monument was designed in 1859 by David Jensen. It was later relocated and replaced with a statue of Hygieia.
In 19th century the Imperial Medical and Surgical Academy played a major role in the development of Russian natural science and medicine. In 1840 — 1856 one of its professors was Nikolay Pirogov, considered the founder of field surgery.
Since 1861 Sergey Botkin, one of Pirogovs disciples, worked at the Academy. He is considered one of the founders of modern Russian medical science and education. Botkin introduced triage, pathological anatomy, and post mortem diagnostics into Russian medical practice.
In 1881 the Academys official name was changed into the Imperial Military Medical Academy. In the late 19th century, its physiology laboratory, founded by Ivan Sechenov, was at the forefront of medical research. Ivan Romanovich Tarkhanov conducted some important experiments there.
In 1890 — 1901 the Academys President was Viktor Pashutin, one of the founders of the pathophysiologic school in Russia and of pathophysiology as an independent scientific discipline.
The Nobel-prize winning physiologist Ivan Pavlov graduated from the Academy in 1879 with Gold Medal award. Since 1895 he headed Department of Physiology at the Academy for three decades.
In 1904 — 1924 Nikolai Kravkov, the founder of Russian national school of pharmacologists, headed the Academys Department of Pharmacology.
In 1903 — 1936 one of the Academys professors was Sergey Fedorov, the founder of the largest national school of surgery and «the father of Russian urology».
The academy was also among the pioneers of medical education for women, launching the courses for nurse-midwives in 1872. Nadezhda Suslova, the first female physician in Russia, attended Sechenovs classes at the academy. A school of gymnastics (now the Military Institute of Physical Culture) was launched in 1909.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
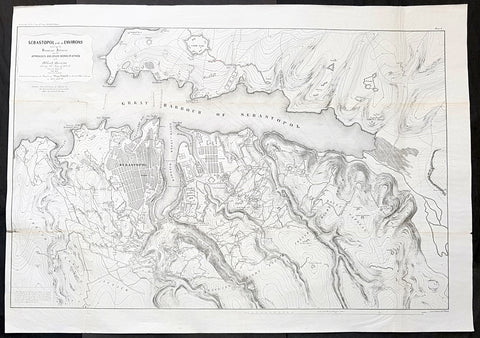
1856 Delafield Large Antique Lithograph Map Siege of Sevastopol Crimea, 1854-55
- Title : Sebastopol and ts Environs showing the Russian Defences and the Approaches and other Works of Attack of the Allied Armies during the Seige of 1854-55 from the Report of Gen. Niel Chief of the French Eng. prepared to accompany the report of Major Delafield on the art of War in Europe in 1854, 55 & 56
- Date : 1856
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 90124
- Size: 41in x 29in (1.040m x 735mm)
Description:
This large, scarce, original lithograph antique map of the defences of the city of Sevastopol, on the Crimean Peninsula on the Black Sea, during the Crimean War and the siege of Sevastopol in 1854-55, was published by the American Army Officer Major Richard Delafield in his 1856 report to the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856 The lithography was completed by Bowen & Co of Philadelphia. Very rare map in VG condition.
An amazing very large lithograph map, highly detailed, illustrating the Russian defences of the city of Sevastopol and the attack position of the British, French & Turkish attacking positions.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 41in x 29in (1.040m x 735mm)
Plate size: - 41in x 29in (1.040m x 735mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Small repair along left fold, folds as issued
Verso: - Several folds re-enforced with archival tape
Background:
Siege of Sevastopol (1854–1855)
The siege of Sevastopol (at the time the siege of Sebastopol) lasted from October 1854 until September 1855, during the Crimean War. The allies (French, Ottoman, and British) landed at Eupatoria on 14 September 1854, intending to make a triumphal march to Sevastopol, the capital of the Crimea, with 50,000 men. The 56-kilometre traverse took a year of fighting against the Russians. Major battles along the way were Alma (September 1854), Balaklava (October 1854), Inkerman (November 1854), Tchernaya (August 1855), Redan (September 1855), and, finally, Sevastopol (September 1855). During the siege, the allied navy undertook six bombardments of the capital, on 17 October 1854; and on 9 April, 6 June, 17 June, 17 August, and 5 September 1855.
Sevastopol is one of the classic sieges of all time. The city of Sevastopol was the home of the Tsardefencess Black Sea Fleet, which threatened the Mediterranean. The Russian field army withdrew before the allies could encircle it. The siege was the culminating struggle for the strategic Russian port in 1854–55 and was the final episode in the Crimean War.
During the Victorian Era, these battles were repeatedly memorialized. The siege of Sevastopol was the subject of Crimean soldier Leo Tolstoydefencess Sebastopol Sketches and the subject of the first Russian feature film, Defence of Sevastopol. The Battle of Balaklava was made famous by Alfred, Lord Tennysondefencess poem defencesThe Charge of the Light Brigadedefences and Robert Gibbdefencess painting The Thin Red Line. A panorama of the siege itself was painted by Franz Roubaud.
Delafield, Richard Major General 1798 - 1873
Delafield was a United States Army officer for 52 years. He served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy for 12 years. At the start of the American Civil War, then Colonel Delafield helped equip and send volunteers from New York to the Union Army. He also was in command of defences around New York harbor from 1861 to April 1864. On April 22, 1864, he was promoted to Brigadier General in the Regular Army of the United States and Chief of Engineers. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866, reconfirmed due to a technicality on July 14, 1866. He retired from the US Army on August 8, 1866. He later served on two commissions relating to improvements to Boston Harbor and to lighthouses. He also served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution.
Delafield served as assistant engineer in the construction of Hampton Roads defences from 1819–1824 and was in charge of fortifications and surveys in the Mississippi River delta area in 1824-1832. While superintendent of repair work on the Cumberland Road east of the Ohio River, he designed and built Dunlaps Creek Bridge in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, the first cast-iron tubular-arch bridge in the United States. Commissioned a major of engineers in July 1838, he was appointed superintendent of the Military Academy after the fire of 1838 and served till 1845. He designed the new buildings and the new cadet uniform that first displayed the castle insignia. He superintended the construction of coast defences for New York Harbor from 1846 to 1855.
In the beginning of 1855, Delafield was appointed by the Secretary of War, Jefferson Davis a head of the board of officers, later called The Delafield Commission, and sent to Europe to study the European military. The board included Captain George B. McClellan and Major Alfred Mordecai. They inspected the state of the military in Great Britain, Germany, the Austrian Empire, France, Belgium, and Russia, and served as military observers during the Crimean War. After his return in April 1856, Delafield submitted a report which was later published as a book by Congress, Report on the Art of War in Europe in 1854, 1855, and 1856. The book was suppressed during the American Civil War due to fears that it would be instructive to Confederate engineers as it contained multiple drawings and descriptions of military fortifications.
Delafield served as superintendent of the Military Academy again in 1856-1861. In January 1861, he was succeeded by Captain Pierre G. T. Beauregard, who was dismissed shortly after Beauregards home state of Louisiana seceded from the Union, and Delafield returned as superintendent serving until March 1, 1861. In the beginning of the Civil War he advised the governor of New York Edwin D. Morgan during the volunteer force creation. Then, in 1861–1864, he was put in charge of New York Harbor defences, including Governors Island and Fort at Sandy Hook. On May 19, 1864, he was commissioned a brigadier-general after replacing Joseph Gilbert Totten, who had died, as the Chief of Engineers, United States Army Corps of Engineers, on April 22, 1864. He stayed in charge of the Bureau of Engineers of the War Department until his retirement on August 8, 1866. On March 8, 1866, President Andrew Johnson nominated Delafield for appointment to the grade of brevet major general in the Regular Army of the United States, to rank from March 13, 1865, and the United States Senate confirmed the appointment on May 4, 1866 and reconfirmed it due to a technicality on July 14, 1866.After retirement Delafield served as a regent of the Smithsonian Institution and a member of the Lighthouse Board. He died in Washington, D.C. on November 5, 1873.
The Jamaican and English nurses who treated the wounded during these battles were much celebrated, most famously Mary Seacole and Florence Nightingale.