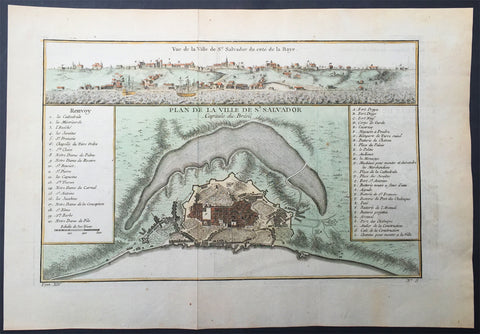
Sold (332)
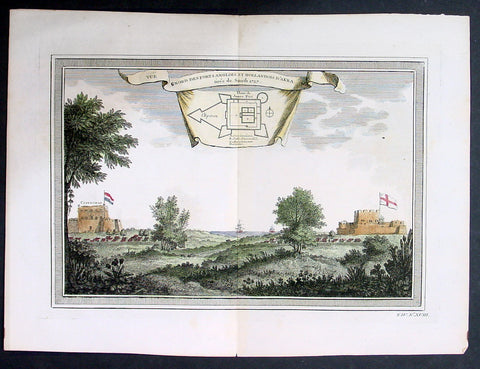
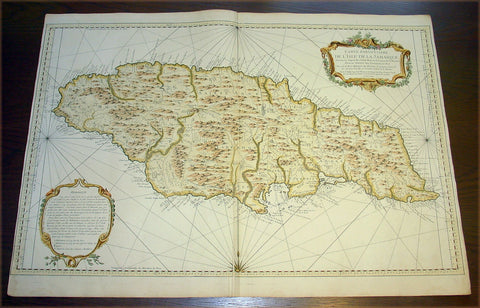
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Print British & Dutch Forts in Accra, Ghana West Africa
- Title: Vue Nord Des Forts Anglois et Hollandois D Akara tiree de Smith 1727
- Date: 1755
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 21933
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique print view of the British & Dutch forts located in the city of Accra, Ghana West Africa by Jakob van Schley in 1755, was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1789.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, blue, red
General color appearance: - authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8 1/2in (305mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Accra is the capital and most populous city of the Greater Accra Region and the Republic of Ghana.
The main Ga group known as the Tumgwa We led by Ayi Kushie arrived by sea. When the Guan (Lartehs) on the coast saw them on their canoes at sea, they looked like ants. Hence, the Lartehs refer to them as Nkran (ants). Nkran was later corrupted by the Danes to Akra, then to present-day Accra. Nkran in the Ga language is Gaga, thus they also started calling themselves Ga. Due to their sheer numbers, the indigenous Lartehs thus relocated to the Akuapem ridge. The Ga are also part of the main Guan group that started the initial migration from the Nubia Empire.
Initially, Accra was not the most prominent trading centre; the trade hubs of the time were the ports at Ada and Prampram, along with the inland centres of Dodowa and Akuse. The Dutch built the nearby outposts of Ussher Fort while the British and the Swedes built James Fort and Christiansborg castles, respectively. By the 17th century, Portugal, France and Denmark, had constructed forts in the city.
Britain gradually acquired the interests of all other countries beginning in 1851, when Denmark sold Christiansborg (which they had acquired from the Swedes) and their other forts to the British. The Netherlands was the last to sell out, in 1871. In 1873, after decades of tension between the British and Ashantis of the peninsula country Ashantiland, the British attacked and virtually destroyed the Ashantiland and Ashanti Region capital of Kumasi. The British then captured Accra in 1874, and in 1877, at the end of the second Anglo-Asante War, Accra replaced Cape Coast as the capital of the British Gold Coast. This decision was made because Accra had a drier climate relative to Cape Coast. Until this time, the settlement of Accra was confined between Ussher Fort to the east and the Korle Lagoon to the west.
As the newly established Gold Coast\'s administrative functions were moved to Accra (1877), an influx of British colonial administrator and settlers grew around the Christiansborg (modern Osu, Ministries, Ridge, Labone, and Cantonments) began, and the city began to expand to accommodate the new residents. Victoriaborg was formed in the late 19th century as an exclusively European residential neighbourhood, located to the east of the city limits of the time. The boundaries of Accra were further stretched in 1908. This expansion entailed the creation of a native-only neighbourhood, intended to accommodate members of the native population as a means of relieving congestion problems in the overcrowded city centre. Adabraka was thus established to the north of the city
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Print View of Niagara Falls, Canada & America
- Title: Cataracte de Niagara
- Date: 1755
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 61104
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique print a view of Niagara Falls, Canada & America by Jakob van Schley in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Niagara Falls is the collective name for three waterfalls that straddle the international border between Canada and the United States; more specifically, between the province of Ontario and the state of New York. They form the southern end of the Niagara Gorge.
A number of figures have been suggested as first circulating an eyewitness description of Niagara Falls. The Frenchman Samuel de Champlain visited the area as early as 1604 during his exploration of Canada, and members of his party reported to him the spectacular waterfalls, which he described in his journals. The Finnish-Swedish naturalist Pehr Kalm explored the area in the early 18th century and is credited with the first scientific description of the falls. The consensus honoree for the first description is the Belgian missionary Louis Hennepin, who observed and described the falls in 1677, earlier than Kalm, after traveling with the explorer Rene-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, thus bringing the falls to the attention of Europeans. Further complicating matters, there is credible evidence the French Jesuit missionary Paul Ragueneau visited the falls some 35 years before Hennepin\'s visit, while working among the Huron First Nation in Canada. Jean de Brébeuf also may have visited the falls, while spending time with the Neutral Nation.
In 1762, Captain Thomas Davies, a British Army officer and artist, surveyed the area and painted the watercolor, An East View of the Great Cataract of Niagara, the first eyewitness painting of the falls.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11n x 8in (280mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \"La Vie de Marianne\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévost\'s Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
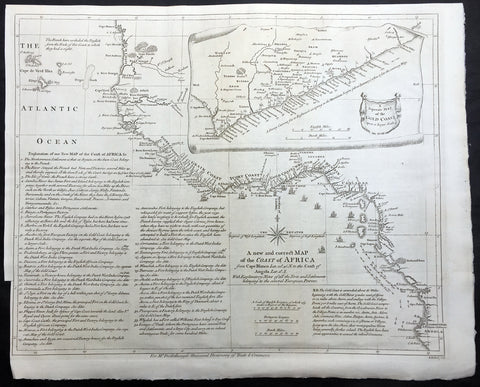
1755 Seale & Postlethweyt Large Antique Map Trade Routes & Forts of West Africa
- Title : A New and Correct Map of the Coast of Africa from Cape Blance to the Coast of Angola with Explanatory Notes of all the Forts and settlements belonging to the several European Powers
- Ref #: 92347
- Size: 20 1/2in x 17in (520mm x 430mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved, highly detailed original antique map of the west coast of Africa from Senegal To Angola - with a separate inset map of the Gold Coast was engraved by William Seale - after Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D'Anville - and was published in Malachy Postlethweyt's monumental 2 Volume Dictionary of Trade & Commerce published between 1751 & 1774.
Incredibly detailed map with an in-depth explanation of the different commercial interests of the European countries from Senegal referred to as the Gum Coast, Sierra Leone & Liberia known as the grain coast, Ivory coast, Ghana & Benin known as the Gold Coast all the way down to Angola.
The extensive text, bottom left, gives a detailed explanation to the different trades undertaken in which areas on the West Coast of Africa. This also included the unfortunate Slaves Trade, Ivory, Gold and Grain as well as local & European settlements and forts.
A truly fascinating insight into a vast region of Africa that was so crucial to the commerce and wealth of Western Europe.
Malachy Postlethweyt's Dictionary of Trade & Commerce:
A monumental dictionary of trade and commerce. It is based in part on the Dictionnaire universel de Commerce (Paris: 1723-30) of Jacques Savary de Bruslon, under whose name it is often catalogued, but has been adapted by Postlethwayt for a British audience, with substantial enlargements and improvements, and entirely new material relating to England and her colonies. Postlethwayt devoted twenty years to the preparation of the dictionary, which was first published in 1751-55 & includes a description of British affairs in North America since the peace of 1763.
As with his other works, the dictionary demonstrates Postlethway’s deep commitment to the expansion and strengthening of English trade. Included are entries for geographical locations (Africa, Antilles, Canada, Japan, Louisiana, &c.), products (brandy, cardamom, codfish, diamonds, sugar, &c.), trading companies (Dutch East India Company, English African Company, &c.), treaties of commerce, and a vast range of other information of value to merchants (bankruptcy, currency, bills of exchange, brokerage, exportation, landed interest, privateering, &c.). The Dictionary is also important for containing almost the whole substance of Richard Cantillon’s Essay on Commerce, its first appearance in print.
Background: Being part of the Mediterranean world, the northern coasts of the African continent as far as the Straits of Gibraltar and even round to the area of the Fortunate Isles (the Canaries) were reasonably well known and quite accurately mapped from ancient times. In particular, Egypt and the Nile Valley were well defined and the Nile itself was, of course, one of the rivers separating the continents in medieval T-O maps. Through Arab traders the shape of the east coast, down the Red Sea as far as the equator, was also known but detail shown in the interior faded into deserts with occasional mountain ranges and mythical rivers. The southern part of the continent, in the Ptolemaic tradition, was assumed to curve to the east to form a land-locked Indian Ocean. The voyages of the Portuguese, organized by Henry the Navigator in the fifteenth century, completely changed the picture and by the end of the century Vasco da Gama had rounded the Cape enabling cartographers to draw a quite presentable coastal outline of the whole continent, even if the interior was to remain largely unknown for the next two or three centuries.
The first separately printed map of Africa (as with the other known continents) appeared in Munster's Geographia from 1540 onwards and the first atlas devoted to Africa only was published in 1588 in Venice by Livio Sanuto, but the finest individual map of the century was that engraved on 8 sheets by Gastaldi, published in Venice in 1564. Apart from maps in sixteenth-century atlases generally there were also magnificent marine maps of 1596 by Jan van Linschoten (engraved by van Langrens) of the southern half of the continent with highly imaginative and decorative detail in the interior. In the next century there were many attractive maps including those of Mercator/Hondius (1606), Speed (1627), Blaeu (1 630), Visscher (1636), de Wit (c. 1670), all embellished with vignettes of harbours and principal towns and bordered with elaborate and colourful figures of their inhabitants, but the interior remained uncharted with the exception of that part of the continent known as Ethiopia, the name which was applied to a wide area including present-day Abyssinia. Here the legends of Prester John lingered on and, as so often happened in other remote parts of the world, the only certain knowledge of the region was provided by Jesuit missionaries. Among these was Father Geronimo Lobo (1595-1678), whose work A Voyage to Abyssinia was used as the basis for a remarkably accurate map published by a German scholar, Hiob Ludolf in 1683. Despite the formidable problems which faced them, the French cartographers G. Delisle (c. 1700-22), J. B. B. d'Anville (1727-49) and N. Bellin (1754) greatly improved the standards of mapping of the continent, improvements which were usually, although not always, maintained by Homann, Seutter, de Ia Rochette, Bowen, Faden and many others in the later years of the century. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 20 1/2in x 17in (520mm x 430mm)
Plate size: - 19 1/2in x 15 1/2in (495mm x 395mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom left margin cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
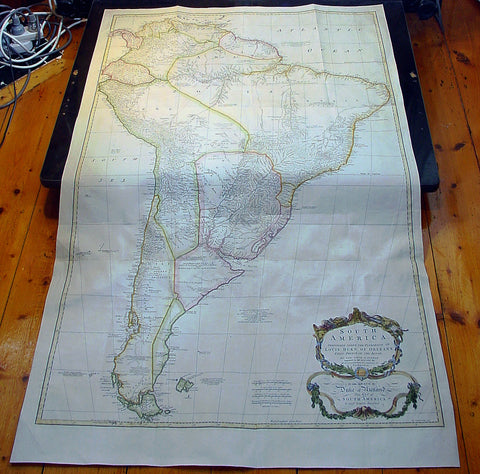
1755 Thomas Bowen & D' Anville Large Antique Map of South America
- Title : South America Performed Under The Patronage of Louis Duke of Oreleans....T. Bowen 1755
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92345
- Size: 51 1/2in x 31 1/2in (1.31mm x 800mm)
Description:
This very large 3 sheet joined copper-plate engraved original antique map of South America was engraveClaude Ptolemydd by Thomas Bowen in 1755 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - and was published by Solomon Bolton for Malachy Postlethweyt's 2 Volumes publication of Dictionary of Trade & Commercepublished in 1757.
The cartographical detail was borrowed from the same Jean-Baptiste Bourguinon D'Anville map published in the 1760 edition of his large elephant folio atlas Atlas Generale.
Background:
This map from the second edition of this famous dictionary, based in part on the Dictionaries universel de Commerce (Paris: 1723-30) of Jacques Savary de Bruslon, under whose name it is often catalogued, but was adapted by Postlethwayt for a British audience, with substantial enlargements and improvements, and entirely new material relating to England and her colonies. Postlethwayt devoted twenty years to the preparation of the dictionary, which was first published in 1751-55. The dictionary included a description of British affairs in North America since the peace of 1763. As with his other works, the dictionary demonstrates Postlethway’s deep commitment to the expansion and strengthening of English trade. Included are entries for geographical locations (Africa, Antilles, Canada, Japan, Louisiana, &c.), products (brandy, cardamom, codfish, diamonds, sugar, &c.), trading companies (Dutch East India Company, English African Company, &c.), treaties of commerce, and a vast range of other information of value to merchants (bankruptcy, currency, bills of exchange, brokerage, exportation, landed interest, privateering, &c.).
The Dictionary is also important for containing almost the whole substance of Richard Cantillon’s Essay on Commerce, its first appearance in print (see Henry Higgs’1931 edition and translation of Cantillon). The substantial maps, engraved by T.Kitchin and R.S.Seale after J.B.B. D’Anville and S.Bolton, depict Europe (4 sheets), Asia (8 sheets), North America (4 sheets), South America (3 sheets), and Africa (3 sheets). (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 51 1/2in x 31 1/2in (1.31mm x 800mm)
Plate size: - 48 1/2in x 30 1/2in (1.23mm x 770mm)
Margins: - min. 1in (25m)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light creasing along folds
Verso: - None
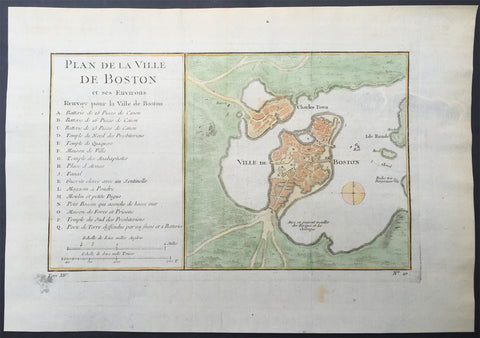
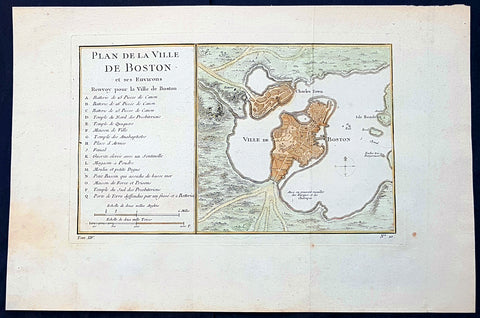
1756 Bellin Antique Map - Plan of The City of Boston & Charlestown
- Title : Plan De La Ville De Boston
- Ref #: 61096
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of Boston and surrounding areas - one of the earliest obtainable maps of the city - by Jacques-Nicholas Bellin in 1756 was published in the 1757 French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
Background:
Beautifully hand coloured map with great street and building detail in both Boston and Charlestown, showing parts of Ronde Isle and the mainland. Important buildings and areas identified in the index at the left of the map. Including three cannon batteries, the Presbyterian Church, the Quaker temple, the Anabaptist Church, the City Hall, the Armory, Faneuil Hall (Spelled Fanal), etc. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 7 1/4in (280mm x 185mm)
Margins: - Min ½in (7mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
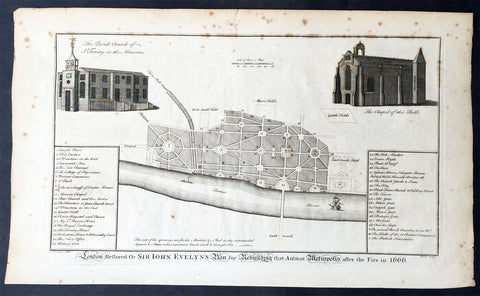
1756 Cole Maitland Antique Map, Evelyns Plan For London after Great Fire of 1666
- Title : London Restored or Sir John Evelyns Plan for Rebuilding the Antient Metropolis after the Fire in 1666
- Ref #: 26338
- Size: 16in x 9 1/2in (410mm x 245mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This fine original antique print a plan for the rebuilding of London by Sir John Evelyn after the great Fire Of London in 1666 - was engraved by Benjamin Cole and published in the 1756 edition of The History of London from its Foundation to the Present Time...', by William Maitland, Osborne & Shipton and Hodges, London
Great Fire of London (1666)
The Great Plague was immediately followed by another catastrophe, albeit one which helped to put an end to the plague. On the Sunday, 2 September 1666 the Great Fire of London broke out at one o'clock in the morning at a bakery in Pudding Lane in the southern part of the City. Fanned by an eastern wind the fire spread, and efforts to arrest it by pulling down houses to make firebreaks were disorganised to begin with. On Tuesday night the wind fell somewhat, and on Wednesday the fire slackened. On Thursday it was extinguished, but on the evening of that day the flames again burst forth at the Temple. Some houses were at once blown up by gunpowder, and thus the fire was finally mastered. The Monument was built to commemorate the fire: for over a century and a half it bore an inscription attributing the conflagration to a "popish frenzy"
The fire destroyed about 60% of the City, including Old St Paul's Cathedral, 87 parish churches, 44 livery company halls and the Royal Exchange. However, the number of lives lost was surprisingly small; it is believed to have been 16 at most. Within a few days of the fire, three plans were presented to the king for the rebuilding of the city, by Christopher Wren, John Evelyn and Robert Hooke.
Wren proposed to build main thoroughfares north and south, and east and west, to insulate all the churches in conspicuous positions, to form the most public places into large piazzas, to unite the halls of the 12 chief livery companies into one regular square annexed to the Guildhall, and to make a fine quay on the bank of the river from Blackfriars to the Tower of London. Wren wished to build the new streets straight and in three standard widths of thirty, sixty and ninety feet. Evelyn's plan differed from Wren's chiefly in proposing a street from the church of St Dunstan's in the East to the St Paul's, and in having no quay or terrace along the river. These plans were not implemented, and the rebuilt city generally followed the streetplan of the old one, and most of it has survived into the 21st century.
Nonetheless, the new City was different from the old one. Many aristocratic residents never returned, preferring to take new houses in the West End, where fashionable new districts such as St. James's were built close to the main royal residence, which was Whitehall Palace until it was destroyed by fire in the 1690s, and thereafter St. James's Palace. The rural lane of Piccadilly sprouted courtiers mansions such as Burlington House. Thus the separation between the middle class mercantile City of London, and the aristocratic world of the court in Westminster became complete.
In the City itself there was a move from wooden buildings to stone and brick construction to reduce the risk of fire. Parliament's Rebuilding of London Act 1666 stated "building with brick [is] not only more comely and durable, but also more safe against future perils of fire". From then on only doorcases, window-frames and shop fronts were allowed to be made of wood.
Christopher Wren's plan for a new model London came to nothing, but he was appointed to rebuild the ruined parish churches and to replace St Paul's Cathedral. His domed baroque cathedral was the primary symbol of London for at least a century and a half. As city surveyor, Robert Hooke oversaw the reconstruction of the City's houses. The East End, that is the area immediately to the east of the city walls, also became heavily populated in the decades after the Great Fire. London's docks began to extend downstream, attracting many working people who worked on the docks themselves and in the processing and distributive trades. These people lived in Whitechapel, Wapping, Stepney and Limehouse, generally in slum conditions.
In the winter of 1683–4 a frost fair was held on the Thames. The frost, which began about seven weeks before Christmas and continued for six weeks after, was the greatest on record. The Revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685 led to a large migration on Huguenots to London. They established a silk industry at Spitalfields.
At this time the Bank of England was founded, and the British East India Company was expanding its influence. Lloyd's of London also began to operate in the late 17th century. In 1700 London handled 80% of England's imports, 69% of its exports and 86% of its re-exports. Many of the goods were luxuries from the Americas and Asia such as silk, sugar, tea and tobacco. The last figure emphasises London's role as an entrepot: while it had many craftsmen in the 17th century, and would later acquire some large factories, its economic prominence was never based primarily on industry. Instead it was a great trading and redistribution centre. Goods were brought to London by England's increasingly dominant merchant navy, not only to satisfy domestic demand, but also for re-export throughout Europe and beyond.
William III, a Dutchman, cared little for London, the smoke of which gave him asthma, and after the first fire at Whitehall Palace (1691) he purchased Nottingham House and transformed it into Kensington Palace. Kensington was then an insignificant village, but the arrival of the court soon caused it to grow in importance. The palace was rarely favoured by future monarchs, but its construction was another step in the expansion of the bounds of London. During the same reign Greenwich Hospital, then well outside the boundary of London, but now comfortably inside it, was begun; it was the naval complement to the Chelsea Hospital for former soldiers, which had been founded in 1681. During the reign of Queen Anne an act was passed authorising the building of 50 new churches to serve the greatly increased population living outside the boundaries of the City of London. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 9 1/2in (410mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 13 3/4in x 8 1/4in (350mm x 210mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light spotting in margins
Plate area: - Light spotting
Verso: - Light spotting
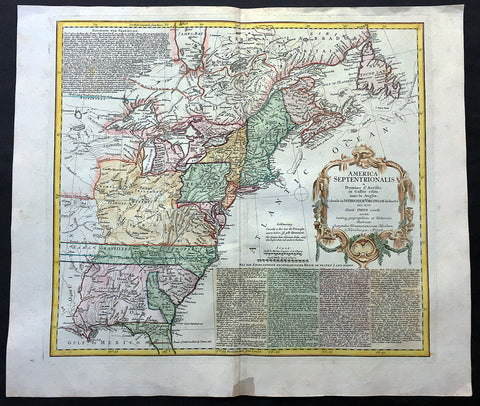
1756 Homann Large Antique Map of The Colonial United States - French Indian War
- Title : America Septentrionalis a Domino d'Anville in Galliis edita nunc in Anglia Coloniis in Interiorem Virginiam….1756
- Ref #: 61007
- Size: 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique 1st edition map of the Colonial United States United States was engraved in 1756 - dated - and was published by the Homann firm.
This is a wonderful and important map with beautiful hand colour, a dark impression on heavy sturdy paper. This map is the 1st edition and was reprinted with political changes in 5 different editions until the 1790's
Background: This is an important, informative and interesting map of colonial North America at the outset of the French & Indian War. The map is incredibly detailed with historical text on British and French claims in North America as well as cartographical details on cities, towns, rivers, Indian settlements and many other features.
Cartographically the map shows both the British and French possessions but from the British perspective. The map is based on the cartography of both J B D' Anville & Thomas Jefferys', using the latters map of 1755 for the political boundaries.
Some of the interesting features include, a truncated Pennsylvania and oversized Virginia, as well as the massive stretch of land in North Carolina designated Earl Granville's property, which extends to the Mississippi. Also shown is a very early Georgia, chartered in 1754.The boundary of New York crosses Lakes Ontario, Huron and Erie to include the lower peninsula of Michigan.
The map is beautifully adorned with a large rococo cartouche and the extensive text in German, describes the British claims and French encroachments, that led to the inevitable conflict.
The French and Indian War is the common American name for the war between Great Britain and France in North America from 1754 to 1763. In 1756, the war erupted into the world-wide conflict known as the Seven Years' War and thus came to be regarded as the North American theater of that war. In Canada, it is usually just referred to as the Seven Years' War, although French Canadians often call it La guerre de la Conquête ("The War of Conquest"). In Europe, there is no specific name for the North American part of the war. The name refers to the two main enemies of the British colonists: the royal French forces and the various Native American forces allied with them, although Great Britain also had Native allies.
The war was fought primarily along the frontiers separating New France from the British colonies from Virginia to Nova Scotia, and began with a dispute over the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers, the site of present-day Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The dispute erupted into violence in the Battle of Jumonville Glen in May 1754, during which Virginia militiamen under the command of George Washington ambushed a French patrol. British operations in 1755, 1756 and 1757 in the frontier areas of Pennsylvania and New York all failed, due to a combination of poor management, internal divisions, and effective French and Indian offense. The 1755 capture of Fort Beauséjour on the border separating Nova Scotia from Acadia was followed by a British policy of deportation of its French inhabitants, to which there was some resistance.
After the disastrous 1757 British campaigns (resulting in a failed expedition against Louisbourg and the Siege of Fort William Henry, which was followed by significant atrocities on British victims by Indians), the British government fell, and William Pitt came to power. Pitt significantly increased British military resources in the colonies, while France was unwilling to risk large convoys to aid the limited forces it had in New France, preferring instead to concentrate its forces against Prussia and its allies in the European theatre of the war. Between 1758 and 1760, the British military successfully penetrated the heartland of New France, with Montreal finally falling in September 1760.
The outcome was one of the most significant developments in a century of Anglo-French conflict. France ceded French Louisiana west of the Mississippi River to its ally Spain in compensation for Spain's loss to Britain of Florida (which Spain had given to Britain in exchange for the return of Havana, Cuba). France's colonial presence north of the Caribbean was reduced to the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, confirming Britain's position as the dominant colonial power in the eastern half of North America. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 24in x 21in (610mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 20 1/2in x 18 3/4in (520mm x 475mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom margin centerfold re-joined
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
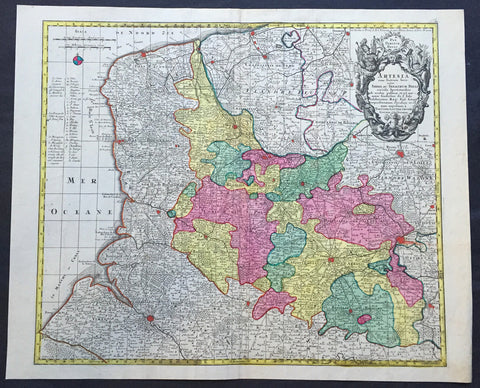
1756 Lotter Large Antique Map Artois & Pas-De-Calais & Flanders region of France
- Title : Artesia...Tob. Conradi Lotter
- Ref #: 50168
- Size: 25in x 20in (635mm x 510mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Artois & Pas-De-Calais and Flanders region of France & Belgium was engraved by Tobias Conrad Lotter in 1756.
The map centres on the city of Arras north to Dunkirk, south to Abbeville and east to Douai (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 21in (635mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 22 ½in x 19 ½in (570mm x 495mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1756 Maitland Large Antique Print of Temple Church London, Knights Templars
- Title : The South East Prospect of the Temple Church
- Ref : 26261
- Size: 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 245mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine hand coloured original antique print of SE view of Temple Church, London was engraved by Benjamin Cole and published in the 1756 edition of The History of London from its Foundation to the Present Time...', by William Maitland, Osborne & Shipton and Hodges, London.
The Temple Church is a late 12th-century church in the City of London located between Fleet Street and the River Thames, built by the Knights Templar as their English headquarters. During the reign of King John (1199–1216) it served as the royal treasury, supported by the role of the Knights Templars as proto-international bankers. It is jointly owned by the Inner Temple and Middle Temple Inns of Court, bases of the English legal profession. It is famous for being a round church, a common design feature for Knights Templar churches, and for its 13th and 14th century stone effigies. It was heavily damaged by German bombing during World War II and has since been greatly restored and rebuilt. The area around the Temple Church is known as the Temple and nearby formerly in the middle of Fleet Street stood the Temple Bar, an ornamental processional gateway. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Red, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 9 1/2in (380mm x 245mm)
Plate size: - 13 3/4in x 8 1/4in (350mm x 210mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
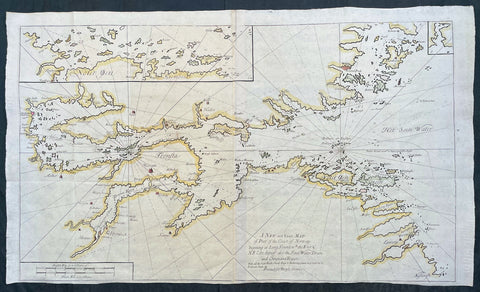
1756 Mount & Page Large Maritime Map of Oslofjord - Oslo to Fredrikstad Norway
- Title : A New and Exact Map of Part of the Coast of Norway beginning at Long Sound wth. the East & N E Coast thereof; also the Soen Water Dram and Christiana Rivers ..., printed for Benyan Crowe
- Ref #: 17033
- Size: 41 1/2in x 24 1/4in (1.045m x 615mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique Maritime map or chart of the Oslofjord body of water stretching from Oslo to Fredrikstad, Norway was published in by Mount and Page in the 1756 edition of The English pilot : Describing the sea-coasts, capes, headlands, soundings, sands, shoals, rocks and dangers : the bays, roads, harbours, rivers and ports in the whole northern navigation.... Specifically from the Second Part of the Atlas series on Northern Navigation containing 31 large folding maps engraved by Francis Lamb and Herman Moll.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 41 1/2in x 24 1/4in (1.045m x 615mm)
Plate size: - 35in x 23 1/4in (990mm x 590mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Bottom margin cropped to plate-mark
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
Background:
The English Pilot 1698 - 1803, was the first major sea-atlas produced in England and in its final form it consisted of five separate books, with the Fourth Book the first wholly English sea-atlas of American waters. Although the idea of the atlases originated with John Seller, he was involved in producing only the first two books. William Fisher and John Thornton produced The Fourth Book in 1689, and their successors Mount and Page continued to print it for over 100 years … Sellers proposal for a Sea Waggoner resulted in the production of The English Pilot, which consisted of five separate volumes with a common generic title. Book One included the southern navigation and Book Two the northern. Book Three was concerned with the Orient, Book Four with America, and Book Five contained Africa. Each book or volume has its own independent publishing history and appeared in numerous editions. The five separate books constitute a set only by virtue of the general title, and under that title The English Pilot is the first great sea-atlas produced in England. Of the five books, the fourth has the longest publication history and is the best known.
Mount & Page 1701 - 1790
Mount & Page was a firm of religious and maritime publishers that flourished in the eighteenth century. The name became well-known worldwide as an imprint of nautical charts.
The firm was founded in 1701 by Richard Mount (1654–1722) and Thomas Page (active 1700-1733). Mount had previously been in partnership with his father-in-law William Fisher (1631–1692) and inherited the business on the latter's death. As Mount & Page the firm flourished throughout the 18th century and made the fortunes of both families, helped by government contracts. Successive generations of Mounts and Pages worked in the business, and the families intermarried. One of its staple titles was Navigatio Britannica by John Barrow, published in 1750 and still being advertised in 1787.
By the 1760s, Richard Mount's grandson John Mount (1725–1786) was able to retire to Berkshire where he built Wasing Place. John's son William (1753–1815) was the last to work in the business, and later generations went into politics.
1756 Nicolas Bellin Antique Map of the City of Boston & Charlestown w/ Harbor
- Title : Plan De La Ville De Boston Et Ses Environs Renvoy pour la Ville de Boston...
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 93122
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10 1/2in (395mm x 270mm)
Description:
This original hand coloured antique map of Boston and surrounding areas - one of the earliest obtainable maps of the city - by Jacques Nicholas Bellin in 1756 - was published in the French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Beautifully hand coloured map with great street and building detail in both Boston and Charlestown, showing parts of Ronde Isle and the mainland. Important buildings and areas identified in an idex at the left of the map. Including three cannon batteries, the Presbyterian Church, the Quaker temple, the Anabaptist Church, the City Hall, the Armory, Faneuil Hall (Spelled Fanal), etc. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10 1/2in (395mm x 270mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 7 1/2in (285mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
Boston is the capital city and most populous municipality of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States.
Boston is one of the oldest cities in the United States, founded on the Shawmut Peninsula in 1630 by Puritan settlers from England. It was the scene of several key events of the American Revolution, such as the Boston Massacre, the Boston Tea Party, the Battle of Bunker Hill, and the Siege of Boston. Upon U.S. independence from Great Britain, it continued to be an important port and manufacturing hub as well as a center for education and culture.
In the 1820s, Boston\\\'s population grew rapidly, and the city\\\'s ethnic composition changed dramatically with the first wave of European immigrants. Irish immigrants dominated the first wave of newcomers during this period, especially following the Irish Potato Famine; by 1850, about 35,000 Irish lived in Boston. In the latter half of the 19th century, the city saw increasing numbers of Irish, Germans, Lebanese, Syrians, French Canadians, and Russian and Polish Jews settling in the city. By the end of the 19th century, Boston\\\'s core neighborhoods had become enclaves of ethnically distinct immigrants. Italians inhabited the North End, Irish dominated South Boston and Charlestown, and Russian Jews lived in the West End. Irish and Italian immigrants brought with them Roman Catholicism. Currently, Catholics make up Boston\\\'s largest religious community and the Irish have played a major role in Boston politics since the early 20th century; prominent figures include the Kennedys, Tip O\\\'Neill, and John F. Fitzgerald.
Between 1631 and 1890, the city tripled its area through land reclamation by filling in marshes, mud flats, and gaps between wharves along the waterfront. The largest reclamation efforts took place during the 19th century; beginning in 1807, the crown of Beacon Hill was used to fill in a 50-acre mill pond that later became the Haymarket Square area. The present-day State House sits atop this lowered Beacon Hill. Reclamation projects in the middle of the century created significant parts of the South End, the West End, the Financial District, and Chinatown.
After the Great Boston Fire of 1872, workers used building rubble as landfill along the downtown waterfront. During the mid- to-late 19th century, workers filled almost 600 acres of brackish Charles River marshlands west of Boston Common with gravel brought by rail from the hills of Needham Heights. The city annexed the adjacent towns of South Boston (1804), East Boston (1836), Roxbury (1868), Dorchester (including present day Mattapan and a portion of South Boston) (1870), Brighton (including present day Allston) (1874), West Roxbury (including present day Jamaica Plain and Roslindale) (1874), Charlestown (1874), and Hyde Park (1912). Other proposals were unsuccessful for the annexation of Brookline, Cambridge and Chelsea.
1756 Schley & Prevost Antique Print View The City of Manila, Philippines - Rare
- Title : Ville de Manille; De Stad Manilha
- Ref #: 61063
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1756
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured large, rare,original antique print a view of the Philippine city of Manila by Jakob van der Schley was published in the 1756 French & Dutch edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
This print is in fantastic condition on clean heavy paper with a clear heavy plate-mark indicating an early pressing.
This is a scarce and rarely seen print that was only published in a limited numbers of Prevost's Voyages.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for "La Vie de Marianne" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), "Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévost'sHistoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, blue, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11 1/2in x 8in (295mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (20mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
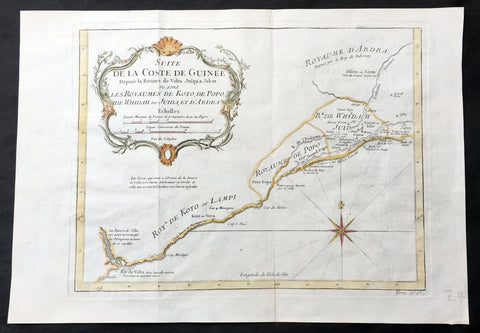
1757 Bellin Antique Map from Ghana to Togo, Benin & Nigeria in Western Africa
- Title : Suite de la Coste de Guinee...Les Royaumes de Koto, de Popo, De Whidah ou Juida Et D Ardra
- Size: 14in x 9 1/2in (355mm x 240mm)
- Ref #: 15985
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine large, original copper-plate engraved antique map from the Volta River in Ghana to Togo, Benin to Lagos in Nigeria (know early as Koto, Popo, Wydah & Juida) by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 9 1/2in (355mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8 1/2in (280mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
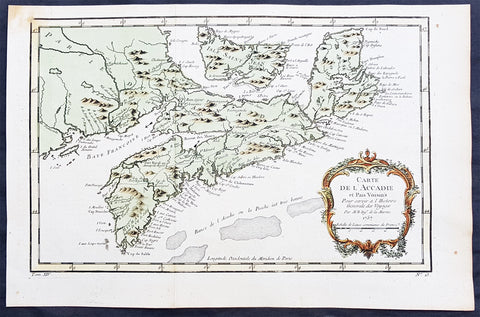
1757 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Arcadia in Nova Scotia, Canada
- Title : Carte De L' Accadie...Par M B. 1757
- Ref #: 61093
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)ea
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured originalantique map* of Arcadia, Nova Scotia, Canada by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1757 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published in the 1757 French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Background : Acadia was a colony of New France in north-eastern North America that included parts of eastern Quebec, the Maritime provinces, and modern-day Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17th and early 18th centuries, Norridgewock on the Kennebec River and Castine at the end of the Penobscot River were the southernmost settlements of Acadia. The actual specification by the French government for the territory refers to lands bordering the Atlantic coast, roughly between the 40th and 46th parallels. Later, the territory was divided into the British colonies which became Canadian provinces and American states. The population of Acadia included members of the Wabanaki Confederacy and descendants of emigrants from France (i.e., Acadians). The two communities intermarried, which resulted in a significant portion of the population of Acadia being Métis.
The first capital of Acadia, established in 1605, was Port-Royal. A British force from Virginia attacked and burned down the town in 1613 but it was later rebuilt nearby, where it remained the longest serving capital of French Acadia until the British Siege of Port Royal in 1710. Over seventy-four years there were six colonial wars, in which English and later British interests tried to capture Acadia starting with King William's War in 1689. During these wars, along with some French troops from Quebec, some Acadians, the Wabanaki Confederacy, and French priests continuously raided New England settlements along the border in Maine. While Acadia was officially conquered in 1710 during Queen Anne's War, present-day New Brunswick and much of Maine remained contested territory. Present-day Prince Edward Island (Île Saint-Jean) and Cape Breton (Île Royale) as agreed under Article XIII of the Treaty of Utrecht remained under French control. By militarily defeating the Wabanaki Confederacy and the French priests, present-day Maine fell during Father Rale's War. During King George's War, France and New France made significant attempts to regain mainland Nova Scotia. After Father Le Loutre's War, present-day New Brunswick fell to the British. Finally, during the French and Indian War (the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War), both Île Royale and Île Saint-Jean fell to the British in 1758.
Today, the term Acadia is used to refer to regions of North America that are historically associated with the lands, descendants, and/or culture of the former French region. It particularly refers to regions of The Maritimes with French roots, language, and culture, primarily in New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, the Magdalen Islands and Prince Edward Island, as well as in Maine It can also be used to refer to the Acadian diasporain southern Louisiana, a region also referred to as Acadiana. In the abstract, Acadia refers to the existence of a French culture in any of these regions.
People living in Acadia, and sometimes former residents and their descendants, are called Acadians, also later known as Cajuns after resettlement in Louisiana.
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 9in (345mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
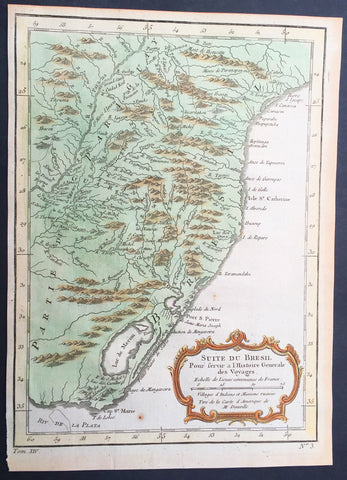
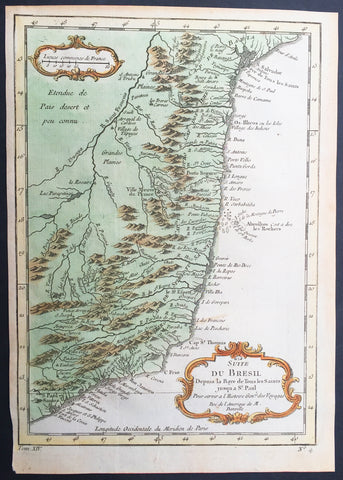
1755 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Brazil, Camarin to Cape St Marie
- Title : Suite du Bresil.
- Ref #: 61078
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Southern Brazil from from Camarin to Cape St Marie by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The land now called Brazil was claimed for the Portuguese Empire on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral. The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several tribes, most of whom spoke languages of the Tupi–Guarani family, and fought among themselves. Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, colonization effectively began in 1534, when King Dom João III of Portugal divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous Captaincy Colonies of Brazil.
However, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captaincy colonies proved problematic, and in 1549 the Portuguese king restructured them into the Governorate General of Brazil, a single and centralized Portuguese colony in South America. In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and European groups lived in constant war, establishing opportunistic alliances in order to gain advantages against each other. By the mid-16th century, cane sugar had become Brazil\'s most important exportation product, and slaves purchased in Sub-Saharan Africa, in the slave market of Western Africa (not only those from Portuguese allies of their colonies in Angola and Mozambique), had become its largest import, to cope with plantations of sugarcane, due to increasing international demand for Brazilian sugar
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline, and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony\'s economy, fostering a Brazilian Gold Rush which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world. This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and old settlers.
Portuguese expeditions known as Bandeiras gradually advanced the Portugal colonial original frontiers in South America to approximately the current Brazilian borders. In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union.
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the monopoly of Portugal\'s wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares, and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Conspiracy
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2in x 7in (240mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1755 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Brazil, San Salvador to Sao Paulo
- Title : Suite du Bresil
- Ref #: 61077
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Northern Brazil from San Salvador to Sao Paulo in the south by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The land now called Brazil was claimed for the Portuguese Empire on 22 April 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral. The Portuguese encountered indigenous peoples divided into several tribes, most of whom spoke languages of the Tupi–Guarani family, and fought among themselves. Though the first settlement was founded in 1532, colonization effectively began in 1534, when King Dom João III of Portugal divided the territory into the fifteen private and autonomous Captaincy Colonies of Brazil.
However, the decentralized and unorganized tendencies of the captaincy colonies proved problematic, and in 1549 the Portuguese king restructured them into the Governorate General of Brazil, a single and centralized Portuguese colony in South America. In the first two centuries of colonization, Indigenous and European groups lived in constant war, establishing opportunistic alliances in order to gain advantages against each other. By the mid-16th century, cane sugar had become Brazil\'s most important exportation product, and slaves purchased in Sub-Saharan Africa, in the slave market of Western Africa (not only those from Portuguese allies of their colonies in Angola and Mozambique), had become its largest import, to cope with plantations of sugarcane, due to increasing international demand for Brazilian sugar
By the end of the 17th century, sugarcane exports began to decline, and the discovery of gold by bandeirantes in the 1690s would become the new backbone of the colony\'s economy, fostering a Brazilian Gold Rush which attracted thousands of new settlers to Brazil from Portugal and all Portuguese colonies around the world. This increased level of immigration in turn caused some conflicts between newcomers and old settlers.
Portuguese expeditions known as Bandeiras gradually advanced the Portugal colonial original frontiers in South America to approximately the current Brazilian borders. In this era other European powers tried to colonize parts of Brazil, in incursions that the Portuguese had to fight, notably the French in Rio during the 1560s, in Maranhão during the 1610s, and the Dutch in Bahia and Pernambuco, during the Dutch–Portuguese War, after the end of Iberian Union.
The Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil had two objectives that would ensure colonial order and the monopoly of Portugal\'s wealthiest and largest colony: to keep under control and eradicate all forms of slave rebellion and resistance, such as the Quilombo of Palmares, and to repress all movements for autonomy or independence, such as the Minas Conspiracy
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, Yellow,
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 9in x 7in (230mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
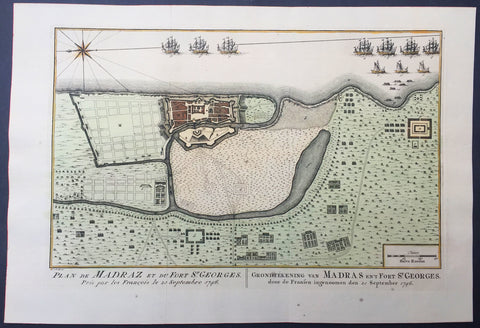
1757 Prevost & Schley Antique Map Ft St George Madras, Chennai, Tamil Nadu India
- Title : Plan de Madraz et du Fort St Georges. Pris par les Francois le 23 Septembre 1746
- Ref #: 61073
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a plan of the city of Chennai (Madras) the capital of Tamil Nadu, India and the old British Fort of St George (during the brief French occupation in 1746) - with separate Index of all the buildings and important places by Jakob van Schley in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Fort St George (or historically, White Town) is the name of the first English (later British) fortress in India, founded in 1644 at the coastal city of Madras, the modern city of Chennai. The construction of the fort provided the impetus for further settlements and trading activity, in what was originally an uninhabited land. Thus, it is a feasible contention to say that the city evolved around the fortress. The fort currently houses the Tamil Nadu legislative assembly and other official buildings.
The East India Company (EIC), which had entered India around 1600 for trading activities, had begun licensed trading at Surat, which was its initial bastion. However, to secure its trade lines and commercial interests in the spice trade, it felt the necessity of a port closer to the Malaccan Straits, and succeeded in purchasing a piece of coastal land, originally called Chennirayarpattinam or Channapatnam, from aVijayanagar chieftain named Damerla Chennappa Nayaka based in Chandragiri, where the Company began the construction of a harbour and a fort. The fort was completed on 23 April 1644 at a cost of £3000, coinciding with St George's Day, celebrated in honour of the patron saint of England. The fort, hence christened Fort St George, faced the sea and some fishing villages, and it soon became the hub of merchant activity. It gave birth to a new settlement area called George Town (historically referred to as Black Town), which grew to envelop the villages and led to the formation of the city of Madras. It also helped to establishEnglish influence over the Carnatic and to keep the kings of Arcot and Srirangapatna, as well as the French forces based at Pondichéry, at bay. In 1665, after the EIC received word of the formation of the newFrench East India Company, the fort was strengthened and enlarged while its garrison was increased. According to the 17th century traveller Thomas Bowrey, Fort St. George was:
"without all dispute a beneficiall place to the Honourable English India Company, and with all the Residence of theire Honourable Agent and Governour all of their Affaires Upon this Coast and the Coast of Gingalee, the Kingdoms also of Orixa, (Orissa) Bengala (Bengal), and Pattana (Patna), the said Governour and his Councell here resideigne, for the Honour of our English Nation keepinge and maintainneinge the place in great Splendour, Civil and good Government, Entertaineinge nobly all Foraign Embassadors, and provideinge great quantities of Muzlinge (Muslin) Callicoes (Calico) &c. to be yearly transported to England."
The Fort is a stronghold with 6 metres (20 ft) high walls that withstood a number of assaults in the 18th century. It briefly passed into the possession of the French from 1746 to 1749, but was restored to Great Britain under the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, which ended the War of the Austrian Succession.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12 mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
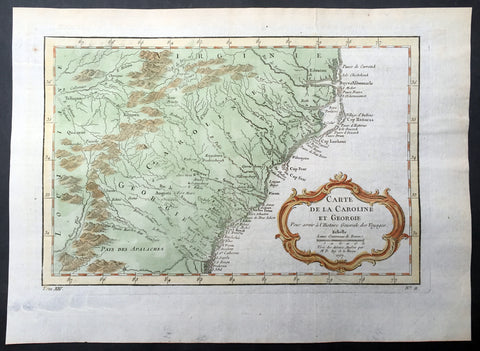
1757 Bellin Antique Map of Georgia, Carolinas, Virginia United States of America
- Title : Carte De La Caroline et Georgie...Par M B. 1757
- Ref #: 61095
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of Georgia, North & South Carolina by Jacques Nicolas Bellin, was engraved in 1757 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published in the 1757 French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8in (305mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
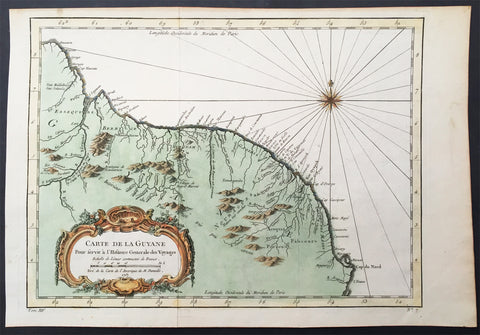
1757 Nicolas Bellin Original Antique Map of Guyana, South America
- Title : Carte De La Guyane...Par M B. 1757
- Ref #: 61099
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* of the Country of Guyana South America by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was engraved in 1757 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published in the 1757 French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12 mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
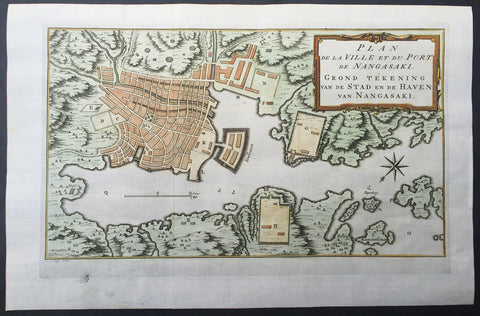
1757 Prevost & Schley Antique Map of The Port of Nagasaki, Japan - VOC, Deshima
- Title : Plan De La Ville et du Port du Nangasaki - Grond Tekening van de Stad en de Haven van Nangasaki
- Ref #: 61059
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a plan of the Japanese City & Port of Nagasaki by Jakob van Schley in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Oriented to the southeast, the map highlights principal points of interest and major buildings with the Deshima central to the map. The Deshima was an artificial island in the bay of Nagasaki where the Dutch East India Company (VOC) were allowed to trade with the representatives of the Shogun in Edo.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10in (395mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13 1/2in x 8 1/2in (345mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
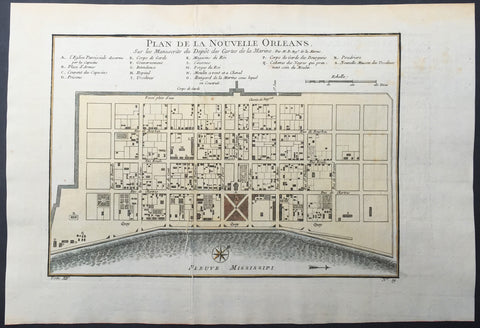
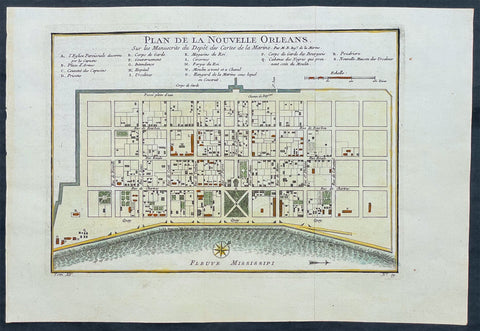
1757 Bellin Antique Map - Plan of The City of New Orleans, Louisiana, USA
- Title : Plan de la Nouvelle Orleans
- Ref #: 61088
- Size: 14 1/2in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1764
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* a scarce, early plan of the city of New Orleans, Louisiana by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was published in the 1757 French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Background: This scarce 1757 map by Bellin is one of the earliest obtainable maps of New Orleans. Oriented to the east, Bellin's map covers the original settlement of New Orleans along the Mississippi River and inland as far theFosse plein d'eau (roughly translated: 'Pit full of Water') near modern day Dauphine Street, and from modern day Iberville Street (shown but not named) to modern day Barracks Street (shown but not named). The map shows some 100 buildings with some 18 specifically identified via an alphabetically coded table set just above the map.
Among the locations noted in the key is one that provides an eerie echo of the slave trade. Item Q is identified as Cabanes des Negroes qui prennent soin Moulin or 'Cabins of Negros that care for mill.' Note how these cabins, as well as the adjacent mill, are both well outside the ordered structure of the city as well as conveniently located near the Corps de Garde des Bourgeois
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8in (280mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued, printers crease along left fold
Verso: - None
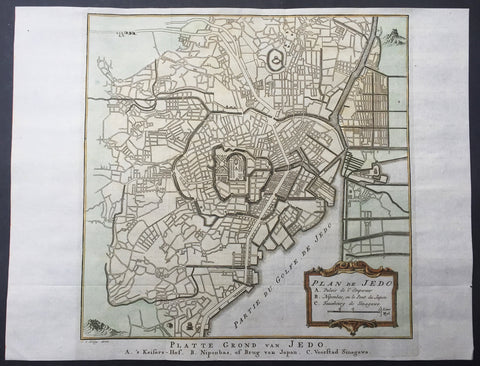
1757 Prevost & Schley Antique Map - Plan The City of Tokyo or Edo, Yeddo, Japan
- Title : Plan De Jedo
- Ref #: 61060
- Size: 14in x 10 1/2in (355mm x 260mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a plan of the Japanese Capital of Tokyo or Edo (Jedo) by Jakob van Schley in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
The map contains the location of 3 important areas in the title cartouche 1. The Emperors Palace 2. The Bridge of Japan 3. The Port of Jedo or Tokyo.
This map is cartographically based on a 1702 map of the same issued by Scheuchzer and Kaempfer, which itself is most likely based on Japanese maps. Centered on Edo Castle, this map depicts the whole of Edo as it existed, with numerous street shown but not named. Edo Castle itself is fancifully depicted as a French style formal garden. Possibly due to the cartographers inability to translate Japanese, the only three named locations on the map are Edo Castle, Japan Bridge, and the 'Faubourg de Sinagawa.' Here, in Sinagawa, the Tokugawa Shogunate maintained the Suzugamori Execution grounds where traitors to the state, criminals, and Christians were executed in an effort to contain 'spiritual pollution.
Edo also Yedo or Yeddo, is the ancient name of Tokyo. It was the seat of power for the Tokugawa shogunate, which ruled Japan from 1603 to 1868. During this period, it grew to become one of the largest cities in the world and home to an urban culture centered on the notion of a "floating world"
From the establishment of the Tokugawa bakufu headquarters at Edo, the town became the de facto capital and center of political power, although Kyoto remained the formal capital of the country. Edo grew from what had been a small, little-known fishing village in 1457 into the largest metropolis in the world with an estimated population of 1,000,000 by 1721.
Edo was repeatedly devastated by fires, with the Great Fire of Meireki in 1657 being the most disastrous. An estimated 100,000 people died in the fire. During the Edo period, there were about 100 fires mostly begun by accident and often quickly escalating and spreading through neighborhoods of wooden machiya which were heated with charcoal fires. Between 1600 and 1945, Edo/Tokyo was leveled every 25–50 years or so by fire, earthquakes, or war.
In 1868, when the shogunate came to an end, the city was renamed Tokyo ("eastern capital"). The emperor moved his residence to Tokyo, making the city the formal capital of Japan.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, orange
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm) Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 240mm)
Plate size: - 10 1/2in x 10 1/2in (260mm x 260mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1757 Bellin Antique Map The Colonial United States, Louisiana, Texas, New Mexico
- Title : Carte De La Louisiane...Par M B. 1757
- Ref #: 61094
- Size: 14in x 10in (365mm x 260mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map of The Colonial United States, from the Great Lakes to Louisiana, Texas and New Mexico was engraved in 1757 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published in the 1757 French edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (365mm x 260mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 230mm)
Margins: - min. 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1757 Bellin Antique Map & View of the City of Salvador, Brazil
- Title : Plan De La Ville de De St Salvador Capitale du Bresil
- Ref #: 61100
- Size: 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique map* and view of the Brazilian City of Salvador - with building index - by Jacques Nicolas Bellin was published in the 1757 French & Dutch edition of Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Background: Salvador, also known as São Salvador, Salvador de Bahia, and Salvador da Bahia (Brazilian Portuguese) is the capital of the Brazilian state of Bahia. With 2.9 million people (2013), it is the largest city proper in the Northeast Region and the 3rd-largest city proper in the country, after São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro.
Salvador lies on a small, roughly triangular peninsula that separates the Bay of All Saints from the Atlantic Ocean. The bay is the largest in Brazil and the 2nd-largest in the world. It was first reached by Gaspar de Lemos in 1501, just one year after Cabral's purported discovery of Brazil. During his second voyage for Portugal, the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci sighted the bay on All Saints' Day (November 1) 1502 and, in honor of the date and his parish church in Florence, he named it the Bay of the Holy Savior of All the Saints. The first European to settle nearby was Diogo Álvares Correia ("Caramuru"), who was shipwrecked off the end of the peninsula in 1509. He lived among the Tupinambá, marrying Guaibimpara and others. In 1531, Martim Afonso de Sousa led an expedition from Mount St Paul (Morro de São Paulo) and, in 1534,Francisco Pereira Coutinho, the first captain of Bahia, established the settlement of Pereira in modern Salvador's Ladeira da Barra neighborhood. Mistreatment of the Tupinambá by the settlers caused them to turn hostile and the Portuguese were forced to flee to Porto Seguro c. 1546. An attempted restoration of the colony the next year ended in shipwreck and cannibalism.
The present city was established as the fortress of Sao Salvador da Bahia de Todos os Santos ("Holy Savior of the Bay of All Saints") in 1549 by Portuguese settlers under Tomé de Sousa, Brazil's first governor-general. It is one of the oldest cities founded by Europeans in the Americas. From a cliff overlooking the Bay of All Saints, it served as Brazil's first capital and quickly became a major port for its slave trade and sugarcane industry. Salvador was long divided into an upper and a lower city, divided by a sharp escarpment some 85 meters (279 ft) high. The upper city formed the administrative, religious, and primary residential districts while the lower city was the commercial center, with a port and market.
In the Catholic Church, Brazil and the rest of the Portuguese Empire were initially administered as part of the Diocese of Funchal in Portugal but, in 1551, Salvador became the seat of the first Catholic diocese erected in Brazil. The first parish church was the mud-and-thatch Church of Our Lady of Help (Igreja da Nossa Senhora da Ajuda) erected by the Jesuits, which served as the first cathedral of the diocese until the Jesuits finished construction of the original basilica on the Terreiro de Jesus in 1553. Its bishop was made independent of Lisbon at the request of King Pedro II in 1676; he served as the primate of Congo and Angola until the elevation of Luanda on 13 January 1844 and still serves as the national primate of Brazil.
In 1572, the Governorate of Brazil was divided into the separate governorates of Bahia in the north and Rio de Janeiro in the south. These were reunited as Brazil six years later, then redivided from 1607 to 1613. By that time, Portugal had become united with Spain and was ruled from Madrid by its kings. In 1621, King Philip III replaced the Governorate of Brazil with the states of Brazil, still based in Salvador and now controlling the south, and the Maranhão, which was centered on São Luís and controlled what is now northern Brazil. As Spain was then prosecuting a war against the independence of the Dutch, the Dutch East and West India companies tried to conquer Brazil from them. Salvador played a strategically vital role against Dutch Brazil, but was captured and sacked by a West India Company fleet under Jacob Willekens and Piet Hein on 10 May 1624. Johan van Dorth administered the colony before his assassination, freeing its slaves. The city was recaptured by a Luso-Spanish fleet under Fadrique Álvarez de Toledo y Mendoza on 1 May 1625. John Maurice's two subsequent attempts to retake the town in April and May of 1638 were unsuccessful.
In 1763, the colonial administration was removed to Rio de Janeiro and elevated to a viceroyalty. Salvador remained the heart of the Recôncavo, Bahia's rich agricultural maritime district, but was largely outside Brazil's early modernization. The area formed a center of royal support against Pedro I's declaration of independence on September 7, 1822. Its elites initially remained loyal to the Portuguese crown while rebels from Cachoeira besieged them for a year until finally receiving Portugal's surrender of the town on July 2, 1823, which is now celebrated as Bahia Independence Day. The local elite was similarly hesitant during Manuel Deodoro da Fonseca's coup that established the republic by in 1889.
Owing to whales' use of the Bay of All Saints as a mating ground, Salvador became a large whaling port during the 19th century but the trade had already begun to fall off by the 1870s.
Under the empire and republic, however, the town slowly began to industrialize. In 1873, Brazil's first elevator, the powerful hydraulic Elevador Lacerda, was constructed to connect the city's upper and lower towns. Having undergone several upgrades, it continues in use. By the First World War, it was joined by a second elevato and Salvador was connected to four railroads: the Bahia & Alagoinhas to Joazeiro, the Bahia Central, the Nazareth Tramway, and a short line to Santo Amaro. Its central districts and the major suburbs of Bomsim and Victoria were served by four streetcar lines, which had begun to electrify. It also served as a port of call for most steamship lines trading between Europe and South America. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 14in x 10in (355mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12in x 8in (305mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
1757 Bellin Original Antique Map of Colonial States to New Mexico, North America
- Title : Carte De La Louisiane...Par M B. 1757
- Date : 1757
- Size: 15 1/2in x 10 1/2in (395mm x 265mm)
- Ref #: 70701
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique map of the Colonial United States, North America west to the mainly French possessions of Louisiana and further again to the Spanish possessions in Texas and New Mexico, was engraved in 1757 - the date is engraved in the title - and was published by Jacques Nicolas Bellin for Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt, The Hague between 1747 & 1785.
Background: The map includes parts of the original 13 colonies from the Carolinas to Georgia and stretches north from the great Lakes to Florida and west to Texas & the Spanish territories. A great map published on the cusp of huge changes in North America. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Green, yellow, red
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15 1/2in x 10 1/2in (395mm x 265mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 9 1/2in (320mm x 230mm)
Margins: - min. 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1757 De Vaugondy Large Antique Maps x 2 of North & South Portugal
- Title : Partie Septentrionale Portugal; Partie Meriondalie Portugal
- Ref #: 41589/41590
- Size: 25in x 19in (635mm x 483mm) Each
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
These large beautifully hand coloured original antique maps x 2 of Portugal was published by Robert De Vaugondy in Atlas Universal, Paris 1757. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, yellow, green
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 25in x 19in (635mm x 483mm) Each
Plate size: - 24in x 19 1/2in (610mm x 495mm) Each
Margins: - Min 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1757 Robert De Vaugondy Large Antique Map of Franconia, Franken Southern Germany
- Title : Cercle De Franconie.....Par Le Sr. Robert
- Size: 26 1/2in x 19 3/4in (670mm x 505mm)
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Date : 1757
- Ref #: 41575
Description:
This large magnificent hand coloured original copper-plate engraved antique map of Franconia or Franken south central Germany by Robert De Vaugondy was published in the 1757 edition of De Vaugondys famous The Atlas Universel
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original & later
Colors used: - Blue, pink, red, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 26 1/2in x 19 3/4in (670mm x 505mm)
Plate size: - 22 3/4in x 19in (580mm x 490mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Franconia is a region in Germany, characterised by its culture and language, and may be roughly associated with the areas in which the East Franconian dialect group, locally referred to as fränkisch, is spoken. It commonly refers to the eastern part of the historical Franconian stem duchy, mainly represented by the modern Bavarian administrative districts of Lower, Middle, and Upper Franconia, the adjacent northeastern parts of Heilbronn-Franken in Baden-Württemberg, parts of Thuringia south of the Rennsteig ridge, and small parts of Hesse. Sometimes Vogtland is also regarded as part of Franconia (because the Vogtländisch dialect is often regarded as sub-group of East Franconian) but this is disputed. However, there is no fixed area that is officially defined as Franconia.
On 2 July 1500 during the reign of Emperor Maximilian I, as part of the Imperial Reform Movement, the Empire was divided into Imperial Circles. This led in 1512 to the formation of the Franconian Circle. Seen from a modern perspective, the Franconian Circle may be viewed as an important basis for the sense of a common Franconian identity that exists today. The Franconian Circle also shaped the geographical limits of the present-day Franconia. In the late Middle Ages and Early Modern Period, the Imperial Circle was severely affected by Kleinstaaterei, the patchwork of tiny states in this region of Germany. As during the late Middle Ages, the bishops of Würzburg used the nominal title of Duke of Franconia during the time of the Imperial Circle. In 1559, the Franconian Circle was given jurisdiction over coinage (Münzaufsicht) and, in 1572, was the only Circle to issue its own police ordinance.
Members of the Franconian Circle included the imperial cities, the prince-bishoprics, the Bailiwick of Franconia of the Teutonic Order and several counties. The Imperial Knights with their tiny territories, of which there was a particularly large number in Franconia, were outside the Circle assembly and, until 1806, formed the Franconian Knights Circle (Fränkischer Ritterkreis) consisting of six Knights\' Cantons. Because the extent of Franconia, already referred to above, is disputed, there were many areas that might be counted as part of Franconia today, that lay outside the Franconian Circle. For example, the area of Aschaffenburg belonged to Electoral Mainz and was a part of the Electoral Rhenish Circle, the area of Coburg belonged to the Upper Saxon Circle and the Heilbronn area to the Swabian Circle. In the 16th century, the College of Franconian Counts was founded to represent the interests of the counts in Franconia.
Franconia played an important role in the spread of the Reformation initiated by Martin Luther, Nuremberg being one of the places where the Luther Bible was printed. The majority of other Franconian imperial cities and imperial knights embraced the new confession. In the course of the counter-reformation several regions of Franconia returned to Catholicism, however, and there was also an increase in witch trials. In addition to Lutheranism, the radical reformatory baptist movement spread early on across the Franconian area. Important Baptist centres were Königsberg and Nuremberg.
In 1525, the burden of heavy taxation and socage combined with new, liberal ideas that chimed with the Reformation movement, unleashed the German Peasants\' War. The Würzburg area was particularly hard hit with numerous castles and monasteries being burned down. In the end, however, the uprisings were suppressed and for centuries the lowest strata of society were excluded from all political activity.
From 1552, Margrave Albert Alcibiades attempted to break the supremacy of the mighty imperial city of Nuremberg and to secularise the ecclesial estates in the Second Margrave War, to create a duchy over which he would rule. Large areas of Franconia were eventually devastated in the fighting until King Ferdinand I together with several dukes and princes decided to overthrow Albert.
In 1608, the reformed princes merged into a so-called Union within the Empire. In Franconia, the margraves of Ansbach and Bayreuth as well as the imperial cities were part of this alliance. The Catholic side responded in 1609 with a counter-alliance, the League. The conflicts between the two camps ultimately resulted in the Thirty Years\' War, which was the greatest strain on the cohesion of the Franconian Circle Initially, Franconia was not a theatre of war, although marauding armies repeatedly crossed its territory. However, in 1631, Swedish troops under Gustavus Adolphus advanced into Franconia and established a large encampment in summer 1632 around Nuremberg. However, the Swedes lost the Battle of the Alte Veste against Wallenstein\'s troops and eventually withdrew. Franconia was one of the poorest regions in the Empire and lost its imperial political significance. During the course of the war, about half the local population lost their lives. To compensate for these losses about 150,000 displaced Protestants settled in Protestant areas, including Austrian exiles.
Franconia never developed into a unified territorial state, because the patchwork quilt of small states (Kleinstaaterei) survived the Middle Ages and lasted until the 18th century. As a result, the Franconian Circle had the important task of preserving peace, preventing abuses and to repairing war damage and had a regulatory role in the region until the end of the Holy Roman Empire. Until the War of the Spanish Succession, the Circle had become an almost independent organization and joined the Grand Alliance against Louis XIV as an almost sovereign state. The Circle also developed early forms of a welfare state. It also played a major role in the control of disease during the 16th and 17th centuries. After Charles Alexander abdicated in 1792, the former margraviates of Ansbach and Bayreuth were annexed by Prussia. Karl August Freiherr von Hardenberg was appointed as governor of these areas by Prussia
Most of modern-day Franconia became part of Bavaria in 1803 thanks to Bavaria\'s alliance with Napoleon. Culturally it is in many ways different from Bavaria proper (Altbayern, Old Bavaria), however. The ancient name was resurrected in 1837 by Ludwig I of Bavaria. During the Nazi period, Bavaria was broken up into several different Gaue, including Franconia and Main-Franconia.
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Map, Plan of Tharangambadi, in Tamil Nadu, India
- Title : Ville de Tranquebar et Fort Danois de Dansbourg
- Ref #: 61071
- Size: 11 1/2in x 8in (290mm x 205mm)
- Date : 1755
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a plan of the City of Tharangambadi, in Tamil Nadu, India & the old Danish Trading Fort - with separate page Index of Buildings and important landmarks by Jakob van Schley in 1755 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Tharangambadi, formerly Tranquebar, is a town in the Nagapattinam district of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It lies 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) north of Karaikal, near the mouth of a distributary of the Kaveri River. Tharangambadi is the headquarters of Tharangambadi taluk while its name means "place of the singing waves". It was a Danish colony from 1620 to 1845, and in Danish it is still known as Trankebar.
The place dates back to 14th century. Masilamani nathar (Shiva) temple was built in 1306, in a land given by Maravarman Kulasekara Pandyan I. As of now, this temple is the oldest monument. Until 1620, when theDanes came, the place was under Thanjavur Nayak kingdom. Danish admiral Ove Gjedde felt the place would be a potential trading centre, made a deal with Raghunatha Nayak and built a fort, which is known as Fort Dansborg. Nevertheless, a jesuit Catholic church was already in place before that, catering for the Indo-Portuguese community. The Catholic church was probably demolished to build the fort. This fort was the residence and headquarters of the governor and other officials for about 150 years.
Among the first Protestant missionaries to set foot in India were two Lutherans from Germany, Bartholomäus Ziegenbalg and Heinrich Pluetschau, who began work in 1705 in the Danish settlement of Tranquebar. Ziegenbalg translated the Old and New Testaments into Tamil, imported a printing press, and printed the New Testament in Tamil in 1714.
The local people were forced to learn the broken Portuguese that was the lingua franca between Indians and Europeans at the time, and later on translated the Bible into the local Tamil language. They also established a printing press, which within a hundred years of its establishment in 1712 had printed 300 books in Tamil. At first they only made little progress in their religious efforts, but gradually the mission spread to Madras, Cuddalore and Tanjore. Today Bishop of Tranquebar is the official title of a bishop in theTamil Evangelical Lutheran Church (TELC) in South India which was founded in 1919 as a result of the German Lutheran Leipzig Mission and Church of Sweden Mission. The seat of the Bishop, the Cathedral and its Church House ("Tranquebar House") is in Tiruchirappalli.
The Zion church was consecrated in 1701, which is the oldest Protestant church in India. In 1718, The New Jerusalem Church was constructed. Moravian Brethren missionaries from Herrnhut, Saxony established the Brethren's Garden at Porayar near Tranquebar and operated it as a missionary centre for a number of years. An Italian Catholic FatherConstanzo Beschi, who worked in the colony from 1711 to 1740, found himself in conflict with the Lutheran pioneers at Tranquebar, against whom he wrote several polemical works.
Tranquebar was occupied by the British in February 1808 during the Napoleonic Wars but was restored to Denmark following the Treaty of Kiel in 1814 and The Norwegian Declaration of Independence. Along with the Danish settlement of Serampore in Bengal, it was sold to the British in 1845. Tranquebar was then still a busy port, but it later lost its importance after a railway was opened to Nagapattinam.
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9 1/2in (330mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1757 Prevost & Schley Antique Map VOC Fort Hoogly & Chuchura, West Bengal, India
- Title : Plan de la Loge Hollandoise d Ougly A. 1721
- Ref #: 61069
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a plan of the Dutch East Indies Fort of Hoogly in West Bengal, India and the Dutch Fort town Chuchura south of Hooghly - with separate Index of all the buildings and important places by Jakob van Schley in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyageswritten by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Hooghly district is one of the districts of the state of West Bengal in India. It can alternatively be spelt Hoogli or Hugli. The district is named after the Hooghly River.
The district of Hooghly derived its name from the town of Hooghly on the west bank of the Hooghly River about 40 km north of Kolkata. This town was a river port in the fifteenth century.
The district has thousands of years of rich heritage in the form of the great Bengali kingdom of Bhurshut. The first European to reach this area was the Portuguese sailor Vasco-Da-Gama. In 1536 Portuguese traders obtained a permit from Sultan Mahmud Shah to trade in this area. In those days the Hooghly River was the main route for transportation and Hooghly served as an excellent trading port.
Within a few decades the town of Hooghly turned into a major commercial center and the largest port in Bengal. Later in 1579-80 Emperor Akbar gave permission to a Portuguese captain Pedro Tavares to establish a city anywhere in the Bengal province. They chose Hooghly, and it became the first European settlement in Bengal. In 1599 the Portuguese traders built a convent and a church in Bandel. This is the first Christian church in Bengal known as ‘Bandel Church’ today.
The Portuguese traders started misusing their powers. They started slave trading, robbery and converting natives into Christians by pressure. At one of point they even stopped paying taxes to the Mughal Empire. As a result, Emperor Shah Jahan ordered the then-ruler of Bengal province, Qasim Khan Juvayni, to block the city of Hooghly. This eventually led to a war in which the Portuguese were defeated comprehensively.
Among other European powers that came to Hooghly were the Dutch, the Danish, the British, the French, the Belgians and the Germans. Dutch traders centered their activities in the town Chuchura which is south of Hooghly. Chandannagar became the base of the French and the city remained under their control from 1816 to 1950. Similarly, the Danish establishment in settlement in Serampore (1755). All these towns are on the west bank of the Hooghly River and served as ports. Among these European countries, the British ultimately became most powerful.
Initially the British were based in and around the city of Hooghly like traders from other countries. In 1690 Job Charnock decided to shift the British trading center from Hooghly-Chinsura to Calcutta. The reason behind this decision was the strategically safe location of Calcutta and its proximity to the Bay of Bengal. As a result, the center of gravity of trade and commerce in the Bengal province shifted from the town of Hooghly to Calcutta. Hooghly lost its importance as Calcutta prospered.
After the Battle of Buxar this region was brought under direct British rule until India’s independence in 1947. After independence this district merged into the state of West Bengal.
Though the city of Hooghly is more than 500 years old, the district of Hooghly was formed in 1795 with the city of Hooghly as its headquarters. Later the headquarters shifted to the town of Chuchura. In 1843 the Howrah district was created from the southern portion of this district. And in 1872, the south-west portion of this district was merged into the Medinipur district. The last change in area occurred in 1966.
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 12 1/2in x 8 1/2in (320mm x 215mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12 mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
Jakob van der Schley aka Jakob van Schley (1715 - 1779) was a Dutch draughtsman and engraver. He studied under Bernard Picart (1673-1733) whose style he subsequently copied. His main interests were engraving portraits and producing illustrations for \\\"La Vie de Marianne\\\" by Pierre Carlet de Chamblain de Marivaux (1688-1763) published in The Hague between 1735 and 1747.
He also engraved the frontispieces for a 15-volume edition of the complete works of Pierre de Brantôme (1540-1614), \\\"Oeuvres du seigneur de Brantôme\\\", published in The Hague in 1740.
He is also responsible for most of the plates in the Hague edition of Prévosts Histoire générale des voyages. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1758 Bellin Antique Map of Guadeloupe Islands, Caribbean, West Indies
- Title : Carte De L'Isle De La Guadeloupe...1758
- Ref #: 60955
- Size: 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully engraved hand coloured original antique map of the Caribbean Island of Guadeloupe was engraved in 1758 - the date is engraved in the title cartouche - and was published for Antoine-François Prevost's monumental 20 volume edition of L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt, The Hague between 1747 & 1780. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 15in x 10in (380mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 13in x 9in (330mm x 230mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1757 Bellin Antique Map of Madeira & Porto Santo Islands, Madeira Arc. Portugal
- Title : Carte Des Isles De Madere Et Porto Santo
- Ref #: 25797
- Size: 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
- Date : 1757
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map of Madeira & Porto Santo Islands in the Madeira Archipelago, Portugal by Nicolas Bellin in 1757 was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1790.
Madeira is a Portuguese archipelago situated in the north Atlantic Ocean, southwest of Portugal. Its total population was estimated in 2011 at 267,785. The capital of Madeira is Funchal on the main island's south coast.
It is just under 400 kilometres (250 mi) north of Tenerife, Canary Islands. Since 1976, the archipelago has been one of the two Autonomous regions of Portugal (the other being the Azores, located to the northwest). It includes the islands of Madeira, Porto Santo, and the Desertas, administered together with the separate archipelago of the Savage Islands. It is an outermost region of the European Union.
Madeira was claimed by Portuguese sailors in the service of Prince Henry the Navigator in 1419 and settled after 1420. The archipelago is considered to be the first territorial discovery of the exploratory period of the Portuguese Age of Discovery, which extended from 1415 to 1542. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 10in x 7in (255mm x 180mm)
Plate size: - 9 1/2n x 7in (240mm x 180mm)
Margins: - Min ½in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
One of Antoine Francois Prevosts monumental undertakings was his history of exploration & discovery in 15 volumes titledHistoire Générale des Voyages written between 1746-1759 and was extended to 20 volumes after his death by various authors.
The 20 volumes cover the early explorations & discoveries on 3 continents: Africa (v. 1-5), Asia (v. 5-11), and America (v. 12-15) with material on the finding of the French, English, Dutch, and Portugese.
A number of notable cartographers and engravers contributed to the copper plate maps and views to the 20 volumes including Nicolas Bellin, Jan Schley, Chedel, Franc Aveline, Fessard, and many others.
The African volumes cover primarily coastal countries of West, Southern, and Eastern Africa, plus the Congo, Madagascar, Arabia and the Persian Gulf areas.
The Asian volumes cover China, Korea, Tibet, Japan, Philippines, and countries bordering the Indian Ocean.
Volume 11 includes Australia and Antarctica.
Volumes 12-15 cover voyages and discoveries in America, including the East Indies, South, Central and North America.
Volumes 16-20 include supplement volumes & tables along with continuation of voyages and discoveries in Russia, Northern Europe, America, Asia & Australia.
1758 Bellin Very Large Antique Map Sea Chart of the Caribbean Island of Jamaica
- Title : Carte Particuliere De L'Isle De La Jamaique ...MDCCLVIII
- Date : 1758
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 50655
- Size: 36in x 25in (910mm x 635mm)
Description:
This very large finely engraved beautifully hand coloured original antique map, sea chart, of the Caribbean Island of Jamaica was engraved and published by Jacques Nicolas Bellin in 1758 - dated in the title cartouche.
A very attractive, large and detailed chart of this strategically and economically important island, by the leading French hydrographer of the period. With a lengthy text panel of observations in the lower left corner and decorative title cartouche in the upper right corner. The island is divided into its provinces with towns and villages named. Reference is also made to the cultivation of coffee and sugar. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - Blue
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 36in x 25in (910mm x 635mm)
Plate size: - 36in x 23 1/2in (910mm x 600mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (55mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Printers crease adjacent to bottom & top centerfold
Verso: - None
1755 Prevost & Schley Antique Map Hebei Province, China, The Great Wall & Forts
- Title: Plan de Long-men-hien Pres de la Grande Muraille, dependant de Duen hoa fu; Plan d une Partie de la Grande Muraille. Du coste de Yung-ping-fu. Soutenue par Diverses Plaees de Guerre
- Date: 1755
- Condition : (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 15833
- Size: 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Description:
This fine, original copper-plate engraved antique map a plans of parts of the Great Wall of China in what is today the north part of the Hebei Province of China - then called Pecheli - by Jakob van Schley in 1755 - after Jean-Baptiste Du Halde - was published in Antoine François Prevosts 15 volumes of Histoire Generale des Voyages written by Prevost & other authors between 1746-1789.
Jean-Baptiste Du Halde, born in Paris on 1 February 1674 and died 18 August 1743, was a French Jesuit historian specializing in China. He did not travel to China, but collected seventeen Jesuit missionaries\\\' reports and provided an encyclopedic survey of the history, culture and society of China and Chinese Tartary, that is, Manchuria.
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 7 1/2in (255mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Hebei is a province of Northern China. Its one-character abbreviation is Jì, named after Ji Province, a Han Dynasty province (zhou) that included what is now southern Hebei. The name Hebei literally means north of the river referring to its location entirely to the north of the Huang He Yellow River.
During the Tang Dynasty (618–907), the area was formally designated Hebei (north of the Yellow River) for the first time. During the earlier part of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, Hebei was fragmented among several regimes, though it was eventually unified by Li Cunxu, who established the Later Tang (923–936). The next dynasty, the Later Jin under Shi Jingtang, posthumously known as Emperor Gaozu of Later Jin, ceded much of modern-day northern Hebei to the Khitan Liao Dynasty in the north; this territory, called the Sixteen Prefectures of Yanyun, became a major weakness in the Chinese defense against the Khitans for the next century, since it lay within the Great Wall.
During the Northern Song Dynasty (960–1127), the sixteen ceded prefectures continued to be an area of hot contention between Song China and the Liao Dynasty. The Southern Song Dynasty that came after abandoned all of North China, including Hebei, to the Jurchen Jin Dynasty after the Jingkang Incident in 1127 of the Jin–Song wars.
The Mongol Yuan Dynasty divided China into provinces but did not establish Hebei as a province. Rather, the area was directly administrated by the Secretariat at capital Dadu. The Ming Dynasty ruled Hebei as Beizhili meaning Northern Directly Ruled, because the area contained and was directly ruled by the imperial capital, Beijing; the Northern designation was used because there was a southern counterpart covering present-day Jiangsu and Anhui. When the Manchu Qing Dynasty came to power in 1644, they abolished the southern counterpart, and Hebei became known as Zhili, or simply Directly Ruled. During the Qing Dynasty, the northern borders of Zhili extended deep into what is now Inner Mongolia, and overlapped in jurisdiction with the leagues of Inner Mongolia.
1760 Bowen, D Anville Map Entrance of River Sanaga, St Louis Senegal West Africa
- Title : A General Map of The River Sanaga or Senegal; Map of ye Entrance of the Sanga or Senegal; Island of Sanaga Senegal or St Louis.
- Date : 1760
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Ref: 31879
- Size: 16in x 10in (405mm x 255mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique map of three view of the River, River Mouth & Island of St Louis of the Sangha River in Senegal West Africa by Thomas Bowen - after D anville - was published in 1760. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - white
Age of map color: - Early
Colors used: - Yellow, green, pink, blue
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16in x 10in (405mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 10in (405mm x 255mm)
Margins: - min. 1/4in (6mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Folds as issued
Plate area: - Folds as issued, light creasing along folds
Verso: - Folds as issued, light creasing along folds
1760 Adam Large Original Antique Print of Admiralty Screen, Whitehall London
- Title : Plan and elevation of the new screen or gateway, before the front of the Admiralty...Robert Adams
- Ref #: 40450
- Size: 27 1/2in x 21in (700mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1760
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large original antique print a view & plan of what is known as the Admiralty Screen to the Admiralty Buildings in Whitehall, London, designed by the eminent 18th century Scottish architect Robert Adam was engraved by Fredrick Patton in 1760 - the date is engraved on the plan - and sold by A. Miller in the Strand 1761 Price 2 shillings 6 pence.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 27 1/2in x 21in (700mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 16in (635mm x 635mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Small repairs to margin edges
Plate area: - Light vertical fold
Verso: - None
Background:
The Admiralty complex lies between Whitehall, Horse Guards Parade and The Mall and includes five inter-connected buildings. Since the Admiralty no longer exists as a department, these buildings are now used by separate government departments:
The oldest building was long known simply as The Admiralty; it is now known officially as the Ripley Building, a three storey U-shaped brick building designed by Thomas Ripley and completed in 1726. Alexander Pope implied the architecture is rather dull, lacking either the vigour of the baroque style, fading from fashion at the time, or the austere grandeur of the Palladian style just coming into vogue. It is mainly notable for being perhaps the first purpose-built office building in Great Britain. It contained the Admiralty board room, which is still used by the Admiralty, other state rooms, offices and apartments for the Lords of the Admiralty. Robert Adam designed the screen, which was added to the entrance front in 1788. The Ripley Building is currently occupied by the Department for International Development.
Adam, Robert (1728-1792) An important Scottish architect, born in Kirkaldy, son of the Edinburgh architect William Adam. His three brothers also worked in the architectural profession, and James and William Adam joined Robert Adam in the London-based family practice (the eldest brother, John Adam, like his father, was a Palladian architect and was based in Scotland). Robert Adam studied at Edinburgh University, and then set off on the Grand Tour in 1754, travelling through France and Italy, and returning after 4 years well versed in classical and Italian Renaissance architecture. His own work was mainly Classical, in a lighter style than the Palladians, and some Gothic castles. He became one of the two most important architects of the latter part of the 18th Century - the other being William Chambers.
In London, the Adams Brothers designed the Adelphi scheme (1768-1772), built in Westminster and based on a Thames-side terrace with a parallel row closer to the Strand, with a ladder of side streets between. It was largely demolished in the 1930s. A few remain, in John Adam Street, Robert Street and so forth, among which is the Royal Society of Arts, with an elegant Ionic frontage. The south and east sides of Fitzroy Square are also theirs.A few of Robert Adam's town houses remain, including 20 Portman Square, 20 St James's Square, and Chandos House in Queen Anne Street. The majority of his work was on large country houses, usually altering existing ones rather than starting from scratch, and partly for this reason, he is particularly known today for his opulent interiors rather than exteriors. Around London we may mention Kenwood House, home of the Iveagh Collection of paintings, Osterley Park, and Syon House (near Kew). An early work of his is the facade for the Admiralty in Whitehall.
Among artists employed by Adam to decorate his interiors are the painter Angelica Kauffman, the sculptor John Flaxman, and the Italian painters Antonio Zucchi and Giovanni Cipriani. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
1760 Vue D Optique Antique Print View of London, Old London Bridge to St Pauls
- Title : 137. Vue Generale de la Ville de Londre
- Size: 16 1/2in x 11 3/4in (425mm x 295mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1760
- Ref #: 35502
Description:
This original hand coloured copper-plate engraved antique print, a general view of London from the Thames across old London Bridge to St Pauls, was published bewteen 1750 & 1798 in s series of Perspective views, or Vues d optique
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, blue, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 16 1/2in x 11 3/4in (425mm x 295mm)
Plate size: - 16 1/2in x 11 3/4in (425mm x 295mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Blue colour spot top left
Verso: - None
Background:
A series of perspective views, or vues d optique, a special type of popular print published in Europe during the eighteenth century. These prints were a form of entertainment meant to be seen through devices called optical machines, optiques, zograscopes or peepshows. These views are some of the most distinctive and interesting images of the eighteenth century, and their striking use of lines of perspective and bright original color makes them as visually delightful as they are historically fascinating.
Vue d Optique
The term a vue d optique or aperspective view is used for describing a very special genre of antique print. Originating in England it became widely produced in Europe during the second half of the 18th century. Augsburg, Paris, Bassano and several other places became centers for the production of these interesting, fascinating engravings.
Aperspective views are usually views of cities around the world (but also of other subject matters, historical, Biblical etc.). These were shown in apeep boxes which in turn were usually set up by travelling owners of such viewing devices on markets throughout Europe. People could, for a certain amount of money, look into a peep box and view these perspective views through a magnifying lense which, at the same time, gave the viewer the impression of three dimensional perception. Well-to-do people bought such viewing machines for their families and began collecting the vue doptique engravings showing them at home like slide show would be shown.
Perspective view prints were usually coloured quite boldly before they were sold. Black and white samples are the exception and rather rare. They also have more or less the same format (size), because they had to fit the peep boxes. The title of a view was not always, but quite frequently printed in several languages and often repeated above the view in inverted writing (which was corrected by the lens for the viewer).
The value of perspective view prints rapidly increased, when modern day collectors discovered the genre and began to be interested in collecting the prints. Some large collections of prints and viewing devices have been sold in some of the big auction houses with great success.
Since perspective view prints were actually used almost daily by moving them in and out of viewing boxes, they often show some wear and tear, unless they were handled with much care by private possessors. Prints are in good condition unles otherwise mentioned. A few minor spots and signs of wear are typical of antique prints.
1762 Lotter Twin Hemisphere Antique World Map
- Title : Planisphaerium Globi Terestris
- Ref #: 70092
- Size: 5 1/2in x 4 1/2in (140mm x 115mm)
- Date : 1762
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This beautifully hand coloured original antique Twin Hemisphere World Map by Tobias Conrad Lotter was engraved by Tobias Lobeck and published in the 1762 edition of Atlas Geographicus Portatilis, Augsburg.
The 18th century saw a cartographical revival in Germany and the increased output included some miniature atlases. This atlas is one such example with each map although small engraved with accurate and varied detail. (Ref: Tooley, M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Pink, green, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 5 1/2in x 4 1/2in (140mm x 115mm)
Plate size: - 5 1/2in x 4 1/2in (140mm x 115mm)
Margins: - Min 1/4in (5mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1764 Bellin Antique Map - Plan of The City of New Orleans, Louisiana, North America
- Title : Plan de la Nouvelle Orleans
- Ref #: 17041
- Size: 14 1/2in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
- Date : 1764
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This original beautifully hand coloured rare antique map, an early plan of the city of New Orleans, Louisiana by Jacques Nicolas Bellin, in 1764 was published in Antoine-François Prevosts 20 volume L`Histoire Generale des Voyages published by Pierre de Hondt in the Hague between 1747 & 1785.
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 14 1/2in x 10in (360mm x 255mm)
Plate size: - 11in x 8in (280mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - None
Background: This scarce 1764 map by Bellin is one of the earliest obtainable maps of New Orleans. Oriented to the east, Bellin's map covers the original settlement of New Orleans along the Mississippi River and inland as far theFosse plein d'eau (roughly translated: 'Pit full of Water') near modern day Dauphine Street, and from modern day Iberville Street (shown but not named) to modern day Barracks Street (shown but not named). The map shows some 100 buildings with some 18 specifically identified via an alphabetically coded table set just above the map.
Among the locations noted in the key is one that provides an eerie echo of the slave trade. Item Q is identified as Cabanes des Negroes qui prennent soin Moulin or 'Cabins of Negros that care for mill.' Note how these cabins, as well as the adjacent mill, are both well outside the ordered structure of the city as well as conveniently located near the Corps de Garde des Bourgeois
Antoine François Prévost d'Exiles 1697 - 1763, usually known simply as the Abbé Prévost, was a French author and novelist. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
1765 De Buffon Large Antique Folio Print of South American Butterfly's
- Title : Phalenes 1. La Vitree de Cayenne 2. et 3. la Hachette du Soissonnios
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 23514
- Size: 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique large folio print of three different South American Butterflies was engraved by Francois Nicolas Martinet and published in the Histoire Naturelle de Oiseaux by Georges-Louis Leclerc or Count de Buffon & Edme Louis Daubenton between 1765-80.
These prints are in extraordinary condition with superb original colour on clean heavy chain laid paper.
Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseaux, is a collection of 1,008 hand colored bird prints edited by Georges-Louis Marie Leclerc, the Count of Buffon. This was one of two major Buffon works, collectively the most comprehensive French natural history sets of their time. Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseauxwas published in 42 volumes from 1765 to 1780 by Edme Louis Daubenton in collaboration with Buffon, illustrated with engravings by Francois Nicolas Martinet.
Georges-Louis Leclerc or Count de Buffon (1707 - 1788) was a French aristocrat of formidable intellect and achievements, including books on mathematics and natural history. Although his father initially steered him toward law school, Buffon persisted in pursuing his interest in math. At the age of 20, he discovered the binomial theorem and later introduced differential and integral calculus into probability theory. He soon became fascinated with biological science, and his father relented and let him enroll in the faculty of medicine to study botany and zoology. As a young man in Paris, he befriended Voltaire and other intellectuals, and gained admission to the prestigious Academy of Science at age 27. Decades before Darwin introduced his theory of evolution, Buffon dared to challenge religious thought with empirical observations, suggesting that the earth was older than 6,000 years and that the physical resemblance between humans and apes might be explained by their having a common ancestry. While the theories he proposed to explain these phenomena were by and large incorrect, he correctly grasped that a new paradigm was needed.
De Buffon also published a different 44-volume natural history work with various studies, including birds, titled Histoire Naturelle Generale Et Particuliere (Natural History, General and Particular) (Paris, 1749-1804), which included works by various artists including Jacques Eustache de Sève. This work was his major achievement and an ambitious project characteristic of the 18th-century Enlightenment: a 44-volume encyclopedia attempting to include everything known about the natural world and widely disseminate scientific knowledge. It was the first complete natural history survey presented in a popular form, and also broke ground in attempting to separate science from theological dogma.
Francois Nicolas Martinet was a French engraver and draughtsman. In 1756, he was working for the court of France as Graveur du Cabinet du Roi, under the auspices of the Menus Plaisirs du Roi, making engravings after drawings by others of such subjects as the May Ball at Versailles during the Carnival of 1763. In the same period, Martinet produced illustrations for plays or comic operas by such contemporaries as Marmontel, Voltaire and Philidor. Some of these he engraved himself, while others were drawn by him but engraved by his sister Thérèse Martinet (born c. 1731). He is best known for his engravings of birds for Comte de Buffon's, Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseaux published in Paris from 1770-86. In 1768, a comprehensive group of natural history studies drafted by Martinet, and engraved by Robert Bénard were included in the natural history volume of Diderot and Alembert’sEncyclopédie. Martinet also drew and engraved portraits, landscapes and genre scenes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, blue, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1765 Count De Buffon Large Folio Antique Print The Giraffe & Rhinoceros Beetles
- Title : Scarabes Fig. 1 La Giraffette Fig 2. Le Taureau - Volant
- Ref #: 23515
- Size: 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique large folio print* of the Giraffe Beetle and the Rhinoceros Beetle was engraved by Francois Nicolas Martinet and was published in Histoire Naturelle Generale Et Particuliere by Georges-Louis Leclerc or Count de Buffon.
*Please do not be confused between these larger fine folio prints and the later, smaller 8vo prints.
Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseaux, is a collection of 1,008 hand colored bird prints edited by Georges-Louis Marie Leclerc, the Count of Buffon. This was one of two major de Buffon works, collectively the most comprehensive French natural history sets of their time. Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseauxwas published in 42 volumes from 1765 to 1780 by Edme Louis Daubenton in collaboration with de Buffon, illustrated with engravings by Francois Nicolas Martinet.
Georges-Louis Leclerc or Count de Buffon (1707 - 1788) was a French aristocrat of formidable intellect and achievements, including books on mathematics and natural history. Although his father initially steered him toward law school, Buffon persisted in pursuing his interest in math. At the age of 20, he discovered the binomial theorem and later introduced differential and integral calculus into probability theory. He soon became fascinated with biological science, and his father relented and let him enroll in the faculty of medicine to study botany and zoology. As a young man in Paris, he befriended Voltaire and other intellectuals, and gained admission to the prestigious Academy of Science at age 27. Decades before Darwin introduced his theory of evolution, Buffon dared to challenge religious thought with empirical observations, suggesting that the earth was older than 6,000 years and that the physical resemblance between humans and apes might be explained by their having a common ancestry. While the theories he proposed to explain these phenomena were by and large incorrect, he correctly grasped that a new paradigm was needed.
De Buffon also published a different 44-volume natural history work with various studies, including birds, titled Histoire Naturelle Generale Et Particuliere (Natural History, General and Particular) (Paris, 1749-1804), which included works by various artists including Jacques Eustache de Sève. This work was his major achievement and an ambitious project characteristic of the 18th-century Enlightenment: a 44-volume encyclopedia attempting to include everything known about the natural world and widely disseminate scientific knowledge. It was the first complete natural history survey presented in a popular form, and also broke ground in attempting to separate science from theological dogma.
Francois Nicolas Martinet was a French engraver and draughtsman. In 1756, he was working for the court of France as Graveur du Cabinet du Roi, under the auspices of the Menus Plaisirs du Roi, making engravings after drawings by others of such subjects as the May Ball at Versailles during the Carnival of 1763. In the same period, Martinet produced illustrations for plays or comic operas by such contemporaries as Marmontel, Voltaire and Philidor. Some of these he engraved himself, while others were drawn by him but engraved by his sister Thérèse Martinet (born c. 1731). He is best known for his engravings of birds for Comte de Buffon's, Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseaux published in Paris from 1770-86. In 1768, a comprehensive group of natural history studies drafted by Martinet, and engraved by Robert Bénard were included in the natural history volume of Diderot and Alembert’s Encyclopédie. Martinet also drew and engraved portraits, landscapes and genre scenes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, blue, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1765 De Buffon Large Antique Folio Bird Print of North American Hairy Woodpecker
- Title : Pic varie male, de Virginie
- Ref #: 23510
- Size: 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique ornithogical bird print of the North American Hairy Woodpecker was engraved by Francois Nicolas Martinet and published in the 1765 edition of George Louis Leclerc or Count de Buffon Histore Naturelle de Oiseauxwith the total volumes printed between 1765 to 1780.
*Please do not be confused between these larger fine folio prints and the later, smaller 8vo prints.
Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseaux, is a collection of 1,008 hand colored bird prints edited by Georges-Louis Marie Leclerc, the Count of Buffon. This was one of two major de Buffon works, collectively the most comprehensive French natural history sets of their time. Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseaux was published in 42 volumes from 1765 to 1780 by Edme Louis Daubenton in collaboration with de Buffon, illustrated with engravings by Francois Nicolas Martinet.
Georges-Louis Leclerc or Count de Buffon (1707 - 1788) was a French aristocrat of formidable intellect and achievements, including books on mathematics and natural history. Although his father initially steered him toward law school, Buffon persisted in pursuing his interest in math. At the age of 20, he discovered the binomial theorem and later introduced differential and integral calculus into probability theory. He soon became fascinated with biological science, and his father relented and let him enroll in the faculty of medicine to study botany and zoology. As a young man in Paris, he befriended Voltaire and other intellectuals, and gained admission to the prestigious Academy of Science at age 27. Decades before Darwin introduced his theory of evolution, Buffon dared to challenge religious thought with empirical observations, suggesting that the earth was older than 6,000 years and that the physical resemblance between humans and apes might be explained by their having a common ancestry. While the theories he proposed to explain these phenomena were by and large incorrect, he correctly grasped that a new paradigm was needed.
De Buffon also published a different 44-volume natural history work with various studies, including birds, titled Histoire Naturelle Generale Et Particuliere (Natural History, General and Particular) (Paris, 1749-1804), which included works by various artists including Jacques Eustache de Sève. This work was his major achievement and an ambitious project characteristic of the 18th-century Enlightenment: a 44-volume encyclopedia attempting to include everything known about the natural world and widely disseminate scientific knowledge. It was the first complete natural history survey presented in a popular form, and also broke ground in attempting to separate science from theological dogma.
Francois Nicolas Martinet was a French engraver and draughtsman. In 1756, he was working for the court of France as Graveur du Cabinet du Roi, under the auspices of the Menus Plaisirs du Roi, making engravings after drawings by others of such subjects as the May Ball at Versailles during the Carnival of 1763. In the same period, Martinet produced illustrations for plays or comic operas by such contemporaries as Marmontel, Voltaire and Philidor. Some of these he engraved himself, while others were drawn by him but engraved by his sister Thérèse Martinet (born c. 1731). He is best known for his engravings of birds for Comte de Buffon's, Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseaux published in Paris from 1770-86. In 1768, a comprehensive group of natural history studies drafted by Martinet, and engraved by Robert Bénard were included in the natural history volume of Diderot and Alembert’s Encyclopédie. Martinet also drew and engraved portraits, landscapes and genre scenes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, blue, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1765 De Buffon Large Folio Antique Bird Print of Rufous-Tailed Jacamar, Brasil
- Title : Le Jabiru, de Cayenne
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 23509
- Size: 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Description:
This fine, beautifully hand coloured original antique large ornithological folio print of the Roufus Tailed Jacamar of Brasil, South America was engraved by Francois Nicolas Martinet and published in the Histoire Naturelle de Oiseaux by Georges-Louis Leclerc or Count de Buffon & Edme Louis Daubenton between 1765-80.
These prints are in extraordinary condition with superb original colour on clean heavy chain laid paper.
Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseaux, is a collection of 1,008 hand colored bird prints edited by Georges-Louis Marie Leclerc, the Count of Buffon. This was one of two major Buffon works, collectively the most comprehensive French natural history sets of their time. Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseauxwas published in 42 volumes from 1765 to 1780 by Edme Louis Daubenton in collaboration with Buffon, illustrated with engravings by Francois Nicolas Martinet.
Georges-Louis Leclerc or Count de Buffon (1707 - 1788) was a French aristocrat of formidable intellect and achievements, including books on mathematics and natural history. Although his father initially steered him toward law school, Buffon persisted in pursuing his interest in math. At the age of 20, he discovered the binomial theorem and later introduced differential and integral calculus into probability theory. He soon became fascinated with biological science, and his father relented and let him enroll in the faculty of medicine to study botany and zoology. As a young man in Paris, he befriended Voltaire and other intellectuals, and gained admission to the prestigious Academy of Science at age 27. Decades before Darwin introduced his theory of evolution, Buffon dared to challenge religious thought with empirical observations, suggesting that the earth was older than 6,000 years and that the physical resemblance between humans and apes might be explained by their having a common ancestry. While the theories he proposed to explain these phenomena were by and large incorrect, he correctly grasped that a new paradigm was needed.
De Buffon also published a different 44-volume natural history work with various studies, including birds, titled Histoire Naturelle Generale Et Particuliere (Natural History, General and Particular) (Paris, 1749-1804), which included works by various artists including Jacques Eustache de Sève. This work was his major achievement and an ambitious project characteristic of the 18th-century Enlightenment: a 44-volume encyclopedia attempting to include everything known about the natural world and widely disseminate scientific knowledge. It was the first complete natural history survey presented in a popular form, and also broke ground in attempting to separate science from theological dogma.
Francois Nicolas Martinet was a French engraver and draughtsman. In 1756, he was working for the court of France as Graveur du Cabinet du Roi, under the auspices of the Menus Plaisirs du Roi, making engravings after drawings by others of such subjects as the May Ball at Versailles during the Carnival of 1763. In the same period, Martinet produced illustrations for plays or comic operas by such contemporaries as Marmontel, Voltaire and Philidor. Some of these he engraved himself, while others were drawn by him but engraved by his sister Thérèse Martinet (born c. 1731). He is best known for his engravings of birds for Comte de Buffon's, Histoire Naturelle Des Oiseaux published in Paris from 1770-86. In 1768, a comprehensive group of natural history studies drafted by Martinet, and engraved by Robert Bénard were included in the natural history volume of Diderot and Alembert’sEncyclopédie. Martinet also drew and engraved portraits, landscapes and genre scenes. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Green, blue, yellow
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 12in x 9in (305mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 10in x 8in (255mm x 205mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (15mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1765 Tardieu Large Antique Map A Plan of the City of Rome
- Title : Rome Superfice 4,00,00 Toises
- Date : 1765
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
- Ref: 92788
- Size: 22in x 16 1/2in (560mm x 420mm)
Description:
This large beautifully hand coloured original antique & contemporary (mid 18th century) map of the city of Rome was engraved by Charles Dubuisson and published by the famous French publisher Pierre Francois Tardieu (famous for publishing Diderots Encyclopedie in 1779) in 1765.
An extremely detailed map of Rome with an extensive legend of 170 buildings, landmarks and places of interest within the walls of the city. A truly spectacular map. (Ref: M&B;Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Light & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 22in x 16 1/2in (560mm x 420mm)
Paper size: - 18in x 13 1/2in (460mm x 340mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
1770 JN Bellin Very Large Original Antique World Map on Mercators Projection
- Title : Essay d' une Carte Reduite Contenant les parties connuees Du Globe Terrestre
- Date : 1770
- Size: 32in x 23in (815mm x 585mm)
- Ref #: 61143
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This very large beautifully hand coloured original antique World Map on Mercator's Projection was first engraved in 1748 by Jacques Nicolas Bellin, dated in the title, and was updated to 1770 showing the discoveries by Captain James Cook in Australia & New Zealand in 1769-1770.
Background: The map presents the entire world on Mercator Projection based on a Paris (L’Isle de Fer) meridian, exhibiting post-Cook geography throughout, but most specifically in the Pacific and along the northwest coast of America.
North America to the west of the Mississippi is vaguely rendered according to 16th century expeditions into the region by Coronado, La Salle, De Soto, and others.
Bellin identifies the semi-mythical civilizations of Quivira and Teguayo, both associated with legends of the Seven Cities of Gold, in what is modern day Utah, California, and Nevada. Along the western coast the strait discovered by Martin Aguilar is noted. Further north still the River of the West (Fl. de l’Ouest) extends from the west coast to the Lake of the Woods (Lac de Bois) and thence via additional waterways to the Great Lakes and the Atlantic. The River of the West appeared in many 18th century maps of the Americas and is reflective of French hopes for a water route from their colonies in Canada and Louisiana to the Pacific. Still further north the coastline becomes extremely vague, in places vanishing altogether. The Aleutians are vaguely rendered according to various sightings by Vitus Jonassen Bering and Aleksei Chirikov in the 1740s and identified as the “Archipel de Nord”.
In the Pacific, various Polynesian Island groups are noted though many are slightly or significantly misplaced. The Solomon Islands are vastly oversized referencing the early 17th claims of Quiros. The other lands discovered and erroneously mapped by Quiros in 1606 and Davis in 1686 during their search of the great southern continent are also noted. Hawaii, as yet undiscovered, is absent. New Zealand is rendered twice though is accurate in its form and position. Australia, here labeled “Nouvelle Holland”, has part of its southern coastline ghosted in and Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) is attached to the mainland. The southern coast of New Guinea is similarly ghosted in, suggesting its unexplored state.
It is of interest that there is a common misconception regarding this map that suggests the first edition was dated 1748. There are editions with a printed date of 1748, but these are actually later editions. The 1748 date is a printing error in which “8” and “4” are transposed, the actual date of publication being 1784. The first edition of this map is the 1778 example shown here. (Ref: Tooley; M&B)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color: - off white
Age of map color: - Original
Colors used: - Yellow, green, red, brown.
General color appearance: - Authentic and fresh
Paper size: - 32in x 23in (815mm x 585mm)
Plate size: - 28 1/2n x 20 1/2in (725mm x 520mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - Small worm hole restoration adjacent to SW Africa
Verso: - Folds as issued
1770 Thomas Kitchin Large Antique Map of Africa
- Title : Africa Drawn from the Latest and best Authorities by Thomas Kitchin
- Size: 16in x 14 1/2in (405mm x 370mm)
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
- Date : 1770
- Ref #: 25348
Description:
This large original antique copper-plate engraved map of Africa by the famous English cartographer Thomas Kitchin was published for the 1770 edition of William Guthries Geographical, Historical, and Commercial Grammar
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 16in x 14 1/2in (405mm x 370mm)
Plate size: - 16in x 14 1/2in (405mm x 370mm)
Margins: - Min 1/2in (10mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Left top margin extended from border
Plate area: - Text offsetting, fold as issued
Verso: - Text offsetting, fold as issued
Background:
William Guthrie (1708–1770) was a Scottish writer and journalist, now remembered as a historian.
Guthrie\\\'s first scholarly work was a History of England from the Invasion of Julius Cæsar to 1688, 4 vols., Lond. 1744–51; an attempt to base history on parliamentary records.
In 1763 he published a book titled Complete List of the English Peerage. In spite of revision by aristocrats, this work is inaccurate. About 1764–7 he published, along with collaborators, A General History of the World, from the Creation to the Present Time, in twelve volumes; this was favourably noticed in The Critical Review, it was said by the author himself. In 1767 appeared A General History of Scotland’ 10 vols. It is inaccurate, particularly in the early periods.
Probably his most noted book was his Geographical, Historical, and Commercial Grammar (1770), which reached numerous editions, and was translated into French in 1801.
1771 Bouganville Large Antique World Map - Global Route of Exploration
- Title : Dévelopement de la route des vaissaux du roy La Boudeuse et L’Étoile autour du monde
- Ref : 42015
- Size: 24in x 11 1/2in (610mm x 295mm)
- Date : 1771
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This large finely engraved original antique World map showing the global voyage of Louis Antoine de Bougainville’s route in the ships the Boudeuse and the Etoile was published inBougainville’s 1771 edition of Voyage autour du monde, par la fregate du roi La Boudeuse, et la flute L'Etoile en 1766, 1767, 1768 & 1769 Paris.
Bougainville’s voyage - the first French circumnavigation - was of immense importance in terms of the impetus it provided to a renewal of France’s colonial empire following territorial losses suffered to Britain in the Seven Years’ War: it opened up the Pacific for French expansion. Yet what cannot be overstated is the impact that Bougainville’s own vivid and romanticised descriptions of the Pacific - specifically Tahiti - had on the French public imagination, her writers, artists and thinkers. The utopian ideal of the noble savage living in an Earthly Paradise owes much to Bougainville’s response to his encounter with the Tahitian culture and landscape. Even though he was not the first European to reach Tahiti - the Englishman Samuel Wallis had done so one year earlier - Bougainville’s account is fundamental to the formation of the European romantic vision of the South Seas.
Bougainville had the imprimatur of the French government to undertake a voyage of exploration which would seek to gather scientific, geographical and cultural information. For example, his narrative includes the first vocabulary of the Tahitian language, which is also the first written glossary of any Polynesian language. The advancement of knowledge had not been the principle objective of French voyages of the preceding period, which were motivated by commercial interests.
After entering the Pacific through the Straits of Magellan early in 1768, Bougainville went in fruitless search of the fabled ‘Davis Land’, which was rumoured to exist to the west of Chile. He then took possession of the Tuamotu Archipelago and Tahiti for France, providing in his narrative an extensive, detailed and enthusiastic account of Tahiti. Crossing the Pacific he made landfall first in Samoa and then the New Hebrides. From the island of Espiritu Santo, with the thought of possibly discovering the east coast of New Holland, he struck out due west, a course which would have allowed him to reach the coast of Queensland. Fatefully, he was unable to navigate through the Great Barrier Reef, and sailing north instead, he passed through the Solomons (naming Bougainville for himself) and on to Batavia. Bougainville was to learn in Batavia of the exploits of the navigators Wallis and Carteret, both of whom had sailed across the Pacific a short time earlier. However, it was Bougainville’s narrative which was to cause a sensation in France upon its publication, in some part because of its contribution to scientific and geographical knowledge but primarily for the account of Tahiti, which was to have such an enduring effect on the European imagination. (Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 24in x 11 1/2in (610mm x 295mm)
Paper size: - 22 1/4in x 9 1/2in (570mm x 240mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - Light age toning in margins, small tears to left fold margins
Plate area: - Folds as issued
Verso: - Folds as issued
1771 Dalrymple Large Antique Map Philippines, Mindanao Sulu Arc Basilan Boobooan
- Title : The Sooloo Archipelago, laid down from observations in 1761, 1762, 1763, & 1764 by Dakymple. / Toolyan Bay. / Sooloo Road
- Ref #: 70068
- Size: 29in x 21in (740mm x 535mm)
- Date : 1771
- Condition: (A) Very Good Condition
Description:
This large fine hand coloured original antique map a sea chart of the Sulu Archipelago part of the Philippines, Basilan Island and tip of Mindanao - with 2 insets of Toolyan island and bay, and the islands of Palleeangan and Boobooan - was engraved in 1771 - the date is engraved at the foot of the map - by B Henry and was published by Alexander Dalrymple from D' apres De Mannevillette in 1767 in Discoveries in the South Pacific before 1764.
A most important milestone chart based upon the surveys made from navigational surveys in 1761-64 by Alexander Dalrymple (1737-1808]. He was the first hydrographer of the British Admiralty and the first writer in English to use the word Australia". He used the term to refer to the whole South Pacific region, not specifically to the Australian continent.
Latitude and longitude scales, soundings near coast and in bay areas.
D' Après de Mannevillette (1707-1780) was a famous French sailor and hydrograph. During a voyage to China in 1728 he succeeded in correcting the latitudes of many places using new instruments. Back in France he devised a plan to correct and publish all the existing maps of the route to China: the Red Sea, the coasts of India, Malaya, the northern parts of Indonesia, Indochina and China.
When the first edition of his Atlas Le Neptune Oriental (containing only 22 charts) was published in 1745, it was regarded as a major achievement and a library indispensable to navigators. In 1772, d'Après was appointed director of an office established by the Compagnie des Indes for the publication of charts.(Ref: M&B; Tooley)
General Description:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy & stable
Paper color: - White
Age of map color: - Later
Colors used: - Green, yellow, pink
General color appearance: - Authentic
Paper size: - 29in x 21in (740mm x 535mm)
Plate size: - 25in x 19in (635mm x 485mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: -None
1773 Cook Original 1st Ed. Antique Print of a Tattooed New Zealand Maori Warrior
- Title : No 13
- Ref : 35514
- Size: 11 1/2in x 8 1/2in (290mm x 230mm)
- Date : 1773
- Condition: (A+) Fine Condition
Description:
This fine original copper-plate engraved antique print of a tattooed New Zealand Maori Warrior - drawn by Sydney Parkinson during Captain Cooks 1st Voyage of Discovery in 1769 - was engraved by John James Barralet, after Sydney Parkinson - and was published in the 1773 1st edition of John Hawkesworth\'s An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of His Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successively Performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret, and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow, and the Endeavor, Drawn Up from the Journals Which Were Kept by the Several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq. 3 vols. 1st ed. London, 1773.
Below is an excerpt from Hawkesworth publication from Cooks journals regarding this and other Maori prints by Parkinson.
.....the bodies of both sexes are marked with black stains called Amoco, by the same method that is used at Otaheite, and called Tattowing; but the men are more marked, and the women less. . . . [T]he men, on the contrary, seem to add something every year to the ornaments of the last, so that some of them, who appeared to be of an advanced age, were almost covered from head to foot. Besides the Amoco, the have marks impressed by a method unknown to us, of a very extraordinary kind: they are furrows of about a line deep, and a line broad, such as appear on the bark of a tree which has been cut through . . . and being perfectly black, they make a most frightful appearance. . . . [W]e could not but admire the dexterity and art with which they were impressed. The marks upon the face in general are spirals, which are drawn with great nicety, and even elegance, those on one side exactly corresponding with those on the other. . . . [N]o two were, upon a close examination, found to be alike. [vol. 3, pp. 452–53]
General Definitions:
Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable
Paper color : - off white
Age of map color: -
Colors used: -
General color appearance: -
Paper size: - 11 1/2in x 8 1/2in (290mm x 230mm)
Plate size: - 9in x 7 1/2in (225mm x 190mm)
Margins: - Min 1in (25mm)
Imperfections:
Margins: - None
Plate area: - None
Verso: - None
Background:
Sydney Parkinson 1745 – 71 was draughtsman to the botanist Sir Joseph Banks on James Cook’s first voyage to the Pacific in 1768. He died of dysentery in 1771, on the homeward voyage.
Parkinson was the first European artist to create drawings of Indigenous Australian, Maori & South Sea peoples, as well as landscapes, from direct observation. Hundreds of his original drawings survive in the British Museum. He is particularly remembered for his plant illustrations which were later used to create the lavish plates for Joseph Banks’ Florilegium.
When the Endeavour returned to England in 1772, a dispute arose between Joseph Banks and Sydney’s brother, Stanfield Parkinson. As his employer, Banks claimed rights to Sydney’s drawings, papers and collections made on the voyage. Stanfield claimed that Sydney had willed them to his family. Banks lent the Parkinson family Sydney’s journal and drawings with instructions that they were not to be published, however Stanfield disregarded this and arranged for A Journal of a voyage to the South Seas to be printed from Sydney’s account of the voyage.
Banks managed to suppress Stanfield’s publication until the official account of the voyage, edited by John Hawkesworth, appeared. In return for Parkinson’s papers, Banks paid Stanfield Parkinson 500 pounds for balance of wages due to Sydney, but the dispute did not end there. Stanfield further accused Banks of retaining items collected by Sydney which were intended for his relatives. Stanfield Parkinson was declared insane soon after the publication of Sydney Parkinson’s Journal and died in an asylum.
John Hawkesworth An English writer and journalist, Hawkesworth was commissioned by the British Admiralty to edit for publication the narratives of its officers’ circumnavigations. He was given full access to the journals of the commanders and the freedom to adapt and re-tell them in the first person. Cook was already on his way back from his second Pacific voyage, temporarily docked at Cape Town (South Africa), when he first saw the published volumes: he was mortified and furious to find that Hawkesworth claimed in the introduction that Cook had seen and blessed (with slight corrections) the resulting manuscript. (In his defense, Hawkesworth also had been a victim of misunderstanding.) Cook had trouble recognizing himself. Moreover, the work was full of errors and commentary introduced by Hawkesworth and, in Cook’s view, too full of Banks, who had promoted himself and the publication. Still, the work was popular; the first edition sold out in several months.
John James Barralet 1747 - 1815 was an Irish artist who spent the later part of his career in the United States. Of French descent, Barralet was born in Dublin, Ireland. In early life he was a drawing-master in Dublin, but he later went to London and practised water-colour painting. He exhibited three landscapes at the Royal Academy in 1770, and occasionally exhibited in succeeding years. He was employed in illustrating books on Irish Antiquities. In 1795 he emigrated to America, settling in Philadelphia, where he died in 1815. His brother, J. Melchior Barralet, was a teacher in the Royal Academy School, and occasionally, between the years 1775 and 1789, sent tinted drawings to the Academy Exhibitions